Table of Contents
Introduction: The Unseen Engines Behind Business Growth Strategies
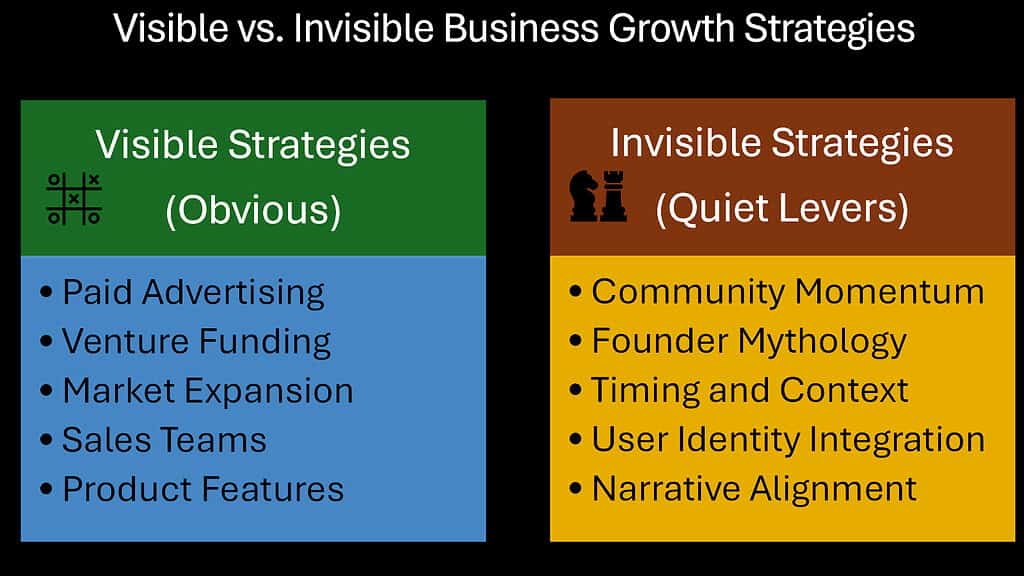
Most businesses pursue obvious growth tactics—advertising campaigns, securing funding rounds, or aggressive market expansion. Yet beneath these visible efforts lies a different reality: sustainable, transformative growth often emerges from quieter, less recognized forces. While executives present polished quarterly reports highlighting marketing spend and acquisition numbers, the true catalysts for remarkable business growth frequently operate in the background.
These invisible growth engines—perfect timing, community momentum, founder mythology, and belief-driven narratives—rarely make their way into business school case studies or investor presentations. Yet companies that master these subtle forces often outperform those focusing exclusively on conventional metrics and tactics.
This disconnect happens because invisible business growth strategies work through compounding effects rather than immediate results. They build slowly but create exponential returns once established. Airbnb’s community-driven approach didn’t show immediate market dominance, but eventually revolutionized hospitality. Patagonia’s identity-driven strategy wasn’t designed for quarterly profits but created decades of sustainable growth and unwavering customer loyalty.
The most remarkable aspect of these invisible strategies is their resistance to competitive replication. While traditional business growth strategies can be copied by competitors with sufficient resources, these lesser-known business growth strategies emerge from unique organizational cultures, founder values, and authentic relationships with customers. They represent a competitive moat that deepens over time.
| Invisible Business Growth Strategies | Traditional Business Growth Strategies | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|
| Timing-First | Market Expansion | Anticipates shifts vs. reacts to them |
| Ecosystem-Led | Strategic Partnerships | Builds mutual dependency networks |
| Narrative-Based | Brand Marketing | Creates belief systems vs. awareness |
| Community-Driven | Customer Acquisition | Customers become advocates by choice |
| Founder-Led | Executive Leadership | Leverages personal mythology and values |
| Identity-Driven | Product Development | Products express customer worldviews |
In this article, we’ll explore six invisible business growth strategies that work wonders but rarely get the spotlight they deserve. These approaches don’t replace traditional growth tactics but rather provide the foundation upon which tactical execution becomes exponentially more effective. By understanding and implementing these strategies, businesses can create sustainable momentum that transcends short-term growth hacking and develop the kind of market presence that competitors find nearly impossible to displace.
1. Timing-First Business Growth Strategies: Catching the Moment Before It Peaks
Timing isn’t merely luck—it’s strategic awareness translated into decisive action. Companies that seem to experience “overnight success” have often been methodically positioning themselves at the convergence point of multiple trends long before most market participants recognized the opportunity. These businesses don’t just benefit from good timing; they make timing their primary strategic advantage.
Consider how Zoom achieved its remarkable growth trajectory. While video conferencing technology existed for decades, Zoom’s founder Eric Yuan recognized a specific convergence of factors: increasing remote work trends, improved bandwidth capabilities, frustration with existing solutions, and rising collaborative workflows. While competitors were still focused on enterprise sales cycles, Zoom built a freemium model perfectly timed for the coming shift to distributed teams. When the pandemic dramatically accelerated this trend in 2020, Zoom had already established the foundation for explosive growth, increasing its customer base by 470% within months.
Similarly, TikTok’s seemingly sudden dominance wasn’t accidental. ByteDance observed multiple converging signals: declining attention spans, the rise of smartphone-native content creation, algorithm-driven personalization, and the underserved short-form video market. ByteDance launched TikTok precisely when these forces reached critical mass, creating the impression of overnight success after years of careful market analysis.
Timing-first business growth strategies require constant environmental scanning using frameworks like PESTEL to detect early signals before they become obvious to the broader market. By systematically analyzing political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors, companies can identify emerging opportunity windows with remarkable precision.
| PESTEL Factor | Key Timing Signals | Notable Example |
|---|---|---|
| Political | Regulatory changes, policy shifts | Square (now Block) launching when mobile payment regulations evolved |
| Economic | Spending pattern changes, economic cycles | Airbnb growing during recession when homeowners needed extra income |
| Social | Changing values, demographic shifts | Oatly timing its expansion with mainstream plant-based diet adoption |
| Technological | Infrastructure readiness, technology inflection points | Netflix transitioning to streaming as broadband became widely available |
| Environmental | Sustainability awareness, resource constraints | Tesla scaling as environmental consciousness reached critical mass |
| Legal | Legal framework evolution, compliance requirements | Plaid growing as open banking regulations expanded financial data access |
Companies employing timing-first strategies don’t waste resources building markets prematurely or enter too late when competition has intensified. Instead, they develop environmental sensing mechanisms and maintain the organizational flexibility to rapidly pivot when conditions align. This approach requires patience, restraint, and the courage to move decisively when opportunity windows open.
The difficulty in replicating timing-first strategies stems from their requirement for both advanced pattern recognition and organizational readiness. Most organizations either lack the perceptual tools to identify emerging trends or remain too rigid to mobilize quickly when opportunity emerges. Those mastering this invisible strategy create growth that appears effortless but derives from sophisticated environmental awareness.
2. Ecosystem-Led Business Growth Strategies: Let Others Pull You Up
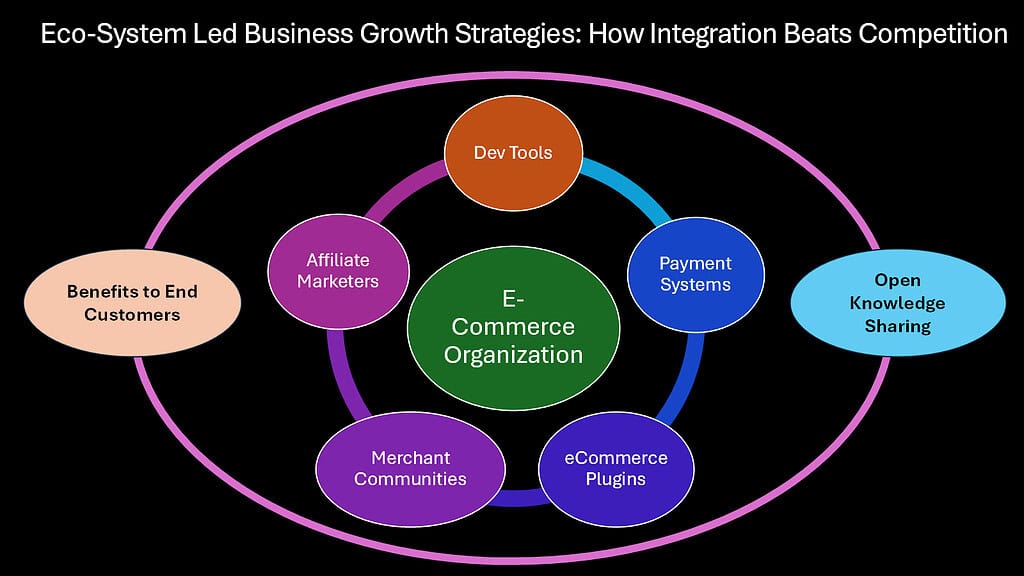
Some of the most powerful business growth strategies operate through integration rather than isolation. Ecosystem-led growth occurs when companies position themselves as essential nodes within larger business networks, creating a situation where their success becomes intertwined with the success of many other entities. Rather than fighting for market share in zero-sum competition, these companies grow by enhancing the capabilities of entire business ecosystems.
Consider how Stripe transformed payments processing. Rather than competing head-on with established payment providers, Stripe created developer-friendly APIs (Application Programming Interface) that empowered countless other businesses to build innovative financial products. As these ecosystem partners grew, Stripe grew automatically, processing billions in payments without direct customer acquisition costs. The company’s value proposition became increasingly embedded in thousands of applications, creating a network effect where each new integration strengthened Stripe’s market position.
Shopify provides another compelling example. Instead of competing with large retailers directly, Shopify empowered a generation of direct-to-consumer brands with tools previously available only to enterprise companies. By focusing on merchant success rather than end-consumer relationships, Shopify built an ecosystem where thousands of independent businesses, app developers, and service providers collectively strengthened its market position. As these ecosystem participants prospered, Shopify’s growth accelerated without proportional marketing investment.
| Ecosystem Component | Growth Function | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|
| Platform Foundation | Creates standard infrastructure for others to build upon | AWS enabling thousands of SaaS companies |
| Developer Tools | Empowers technical communities to extend core functionality | Slack’s API ecosystem with 2,400+ integrated apps |
| Marketplace Dynamics | Connects supply and demand through network orchestration | Etsy connecting craftspeople with niche buyers |
| Educational Resources | Reduces adoption barriers and builds capability | HubSpot’s free academy that trains future customers |
| Partner Networks | Creates service ecosystems around core products | Salesforce’s consulting partner network |
| Data Interchange | Facilitates value creation through information flow | Plaid connecting fintech apps with banking data |
The invisible power of ecosystem-led business growth strategies lies in their ability to harness external innovation and resources. Companies practicing this approach deliberately design their business models to benefit from complementary businesses rather than attempting to capture all value themselves. This creates sustainable competitive advantages as ecosystem partners become vested in the company’s ongoing success.
Notably, ecosystem-led growth often occurs in stages. Companies like Microsoft initially focused on establishing critical mass with their Windows operating system before deliberately fostering third-party software development. Once this ecosystem gained momentum, Microsoft’s growth became partly autonomous as partners continuously expanded the platform’s capabilities and market reach.
What makes ecosystem strategies particularly powerful is their compounding network effects. Each new participant increases the system’s value, attracting additional participants in virtuous cycles. While traditional business growth strategies often face diminishing returns from marketing spend, ecosystem-led approaches can demonstrate increasing returns over time as network effects strengthen.
3. Narrative-Based Business Growth Strategies: Let Belief Do the Selling
In today’s complex marketplace, what consumers believe about a company often matters more than specific product attributes. Narrative-based business growth strategies harness the profound human connection to stories, creating emotional resonance that transforms customers from occasional buyers into passionate advocates. These strategies recognize that people make purchasing decisions based on identity and values as much as utility and price.
Simon Sinek’s Golden Circle framework provides a powerful lens for understanding narrative-based growth. While conventional business thinking starts with what a company does and how it does it, transformative companies begin with why they exist. This inside-out approach creates narrative cohesion that resonates at a deeper psychological level.
Apple exemplifies this approach perfectly. While competitors focused marketing on product specifications and features (the “what”), Apple consistently communicated its core narrative of challenging conformity and enabling creativity (the “why”). This narrative approach created emotional connections transcending product cycles, allowing Apple to maintain premium pricing and customer loyalty across decades of technological change.
Tesla similarly built its remarkable growth through narrative rather than traditional automotive marketing. By positioning itself primarily as a sustainability mission rather than a car company, Tesla created customer relationships based on shared values rather than mere transportation needs. This narrative approach generated waiting lists and customer excitement that eliminated traditional advertising needs.
| Golden Circle Component | Strategic Function | Brand Example |
|---|---|---|
| WHY (Purpose) | Creates emotional connection and shared identity | Patagonia: “We’re in business to save our home planet” |
| HOW (Process) | Demonstrates distinctive approach and values | Airbnb: Facilitating authentic local connections |
| WHAT (Products) | Serves as physical manifestation of purpose | Tesla: Electric vehicles as climate action tools |
| Brand Story | Connects company history to larger cultural narratives | Ben & Jerry’s activism-based origin story |
| Customer Role | Defines how customers participate in the narrative | TOMS Shoes making customers part of giving narrative |
| Future Vision | Creates aspiration and ongoing engagement | SpaceX’s multi-planetary civilization vision |
Narrative-based strategies work particularly well when they tap into broader cultural movements or values shifts. Liquid Death water company grew explosively not by advertising water quality but by crafting an irreverent narrative that connected hydration to counter-cultural identity. By packaging water in beer cans with extreme sports marketing, they transformed a commodity into a statement product, achieving valuation above $700 million despite entering an incredibly crowded category.
What makes narrative-based business growth strategies invisible is their indirect commercial nature. While traditional marketing focuses on purchase conversion, narrative approaches build relationship infrastructure that yields dividends across years of customer interaction. This patient approach often confuses competitors focused on immediate metrics, creating space for narrative-driven companies to establish deep customer relationships before competitive responses emerge.
The most effective narrative strategies maintain consistency across all customer touchpoints, ensuring that product experience, visual identity, employee behavior, and communication all reinforce the core narrative. This alignment creates a coherent brand experience that feels authentic rather than constructed, enabling belief-based connections that transcend traditional marketing.
4. Community-Driven Business Growth Strategies: When Users Become the Engine
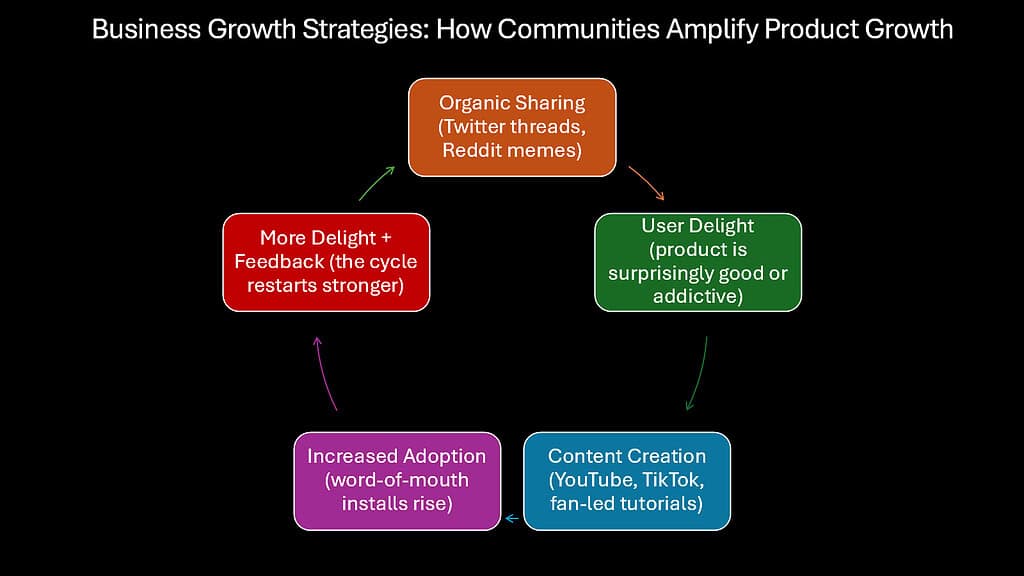
Traditional growth models position customers as targets to acquire through marketing expenditure. Community-driven growth inverts this approach, transforming customers into active growth participants who voluntarily expand the business through their own social connections and creative contributions. This invisible strategy has powered some of the most remarkable business expansions of the digital era without proportional marketing investment.
When examining modern business success stories, we frequently find communities at their core. Reddit grew to hundreds of millions of users not through advertising campaigns but by empowering volunteer moderators to build thousands of specialized communities. This decentralized approach created an engagement ecosystem where users continuously generated content and recruited new participants without company intervention.
Duolingo provides a particularly instructive example of community-driven growth. While traditional language learning companies spent heavily on advertising, Duolingo harnessed user momentum through several community mechanisms: gamification that encouraged daily engagement, social sharing of achievements, and volunteer translation contributions that improved the product. This approach generated organic growth across global markets, with users creating memes, challenges, and content that expanded awareness far beyond what conventional marketing could achieve.
| Community Growth Mechanism | Function | Market Example |
|---|---|---|
| User-Generated Content | Creates self-replenishing value without company resources | Wikipedia’s volunteer-created knowledge base |
| Social Proof Systems | Leverages social psychology to encourage participation | Strava’s community challenges and leaderboards |
| Community Governance | Gives users ownership stake in platform direction | Discord’s server moderation and customization |
| Status Hierarchies | Incentivizes deeper engagement through recognition | Stack Overflow’s reputation system for developers |
| Identity Formation | Transforms product usage into personal identity marker | Peloton’s community-reinforced fitness identity |
| Cultural Production | Encourages users to create artifacts extending brand reach | Minecraft’s player-created YouTube content ecosystem |
The Japanese economy has particularly embraced community-driven approaches, with companies like Nintendo building growth through fan communities that create content, organize events, and drive cultural conversation. In European economies, particularly Scandinavian markets, community-driven models have flourished in sectors ranging from renewable energy cooperatives to technology platforms.
The Indian economy has seen remarkable community-driven growth in companies like ShareChat, which built language-specific content communities that expanded organically through cultural relevance rather than advertising spend. In the USA, companies like Glossier transformed beauty marketing by building product development processes directly incorporating customer communities.
What makes community-driven business growth strategies particularly powerful is their compound growth nature. While traditional customer acquisition costs typically rise over time as markets saturate, community-driven approaches often demonstrate declining acquisition costs as network effects strengthen. Each engaged community member potentially brings multiple additional users, creating acquisition leverage traditional marketing struggles to match.
The invisible nature of community-driven growth often causes it to be underestimated by competitors focused on traditional metrics. While marketing-driven companies track impressions and conversions, community-driven businesses measure engagement depth, user contributions, and relationship durability—metrics that predict long-term growth but may not appear in conventional dashboards.
5. Founder-Led Business Growth Strategies: When Myth Becomes Marketing
In an era of increasing business commoditization, the founder’s personal story, vision, and values can become powerful differentiation engines. Founder-led business growth strategies harness the human tendency to connect with individuals rather than abstract corporate entities, creating relationship bonds that transcend typical brand-consumer dynamics. These strategies transform founders from mere executives into narrative anchors that attract customers, talent, investors, and media attention.
Elon Musk serves as a prime example of how founder mythology can propel business expansion. In addition to fulfilling standard CEO duties, Musk has developed a public image that combines aspects of a technological innovator, environmental advocate, and space exploration leader. This multifaceted identity attracts significant media attention, resulting in billions of dollars in free publicity for both Tesla and SpaceX. The relatively modest marketing budget of Tesla, especially when compared to traditional automotive companies, illustrates how a well-crafted founder narrative can effectively substitute for conventional advertising strategies.
Founder-led business growth strategies aren’t limited to technology sectors. Yvon Chouinard built Patagonia into a globally influential brand by embodying authentic environmental values decades before sustainability became mainstream. His consistent personal narrative—the reluctant businessman prioritizing planet over profit—created a distinctive brand identity that resonated deeply with values-aligned customers.
The Personal Branding Matrix, adapted from Kapferer’s Brand Identity Prism, provides a framework for understanding how founder identity translates into business growth:
| Personal Branding Component | Business Impact | Founder Example |
|---|---|---|
| Voice & Communication Style | Creates distinctive market presence | Steve Jobs’ minimalist presentation style |
| Core Values & Principles | Attracts aligned customers and employees | Howard Schultz’s community-focused Starbucks vision |
| Unique Expertise | Establishes authority and credibility | Sara Blakely leveraging personal Spanx origin story |
| Personal Journey | Creates emotional connection through narrative | Richard Branson’s adventurer persona extending to Virgin brands |
| Public Persona | Generates media interest and visibility | Mark Cuban’s outspoken personality driving attention |
| Vision Articulation | Inspires investment and alignment | Brian Chesky framing Airbnb as belonging movement |
Founder-led growth operates differently across global economies. In Japan, founders like Masayoshi Son of SoftBank have leveraged their personal vision to drive corporate strategy and direction while maintaining cultural appropriateness. In European markets, founders often balance personal visibility with institutional stability, as demonstrated by IKEA founder Ingvar Kamprad, who created a distinctive narrative while building sustainable organizational structures.
The Indian business landscape has seen tremendous founder-led growth, with figures like Ritesh Agarwal of OYO leveraging personal journey narratives to build trust in emerging market contexts. In American markets, founder stories continue driving growth across sectors from technology to consumer products.
What makes founder-led strategies invisible is their integration of personal and corporate identity. While traditional marketing separates brand from leadership, founder-led approaches deliberately blend these elements, creating authentic narratives that resist conventional marketing analysis. This integration allows founders to communicate through channels and formats unavailable to corporate entities, expanding reach while reducing formal marketing requirements.
The sustainability challenge for founder-led business growth strategies involves institutionalizing founder values without founder dependence. Companies like Apple and Disney demonstrate how founder principles can outlive founders themselves when properly encoded into organizational culture and business processes.
6. Identity-Driven Business Growth Strategies: Products That Mirror Beliefs
The most powerful form of customer loyalty transcends rational product evaluation, entering the realm of identity. Identity-driven business growth strategies recognize that certain products serve as physical manifestations of customer beliefs, values, and self-perception. These products aren’t merely purchased; they’re incorporated into how customers define themselves and signal their worldview to others.
Consider the phenomenon of Apple customers tattooing the company logo on their bodies—an extraordinary level of brand commitment transcending normal consumer behavior. This occurs because Apple products have become identity markers representing creativity, design appreciation, and a particular technological worldview. Customers aren’t buying devices; they’re affirming who they are through visible consumption choices.
Similarly, Patagonia customers often wear the brand like armor—not primarily for functional benefits but as external signifiers of environmental values and outdoor lifestyle commitment. The company’s products serve as physical embodiments of a specific worldview, allowing customers to communicate their identity through everyday consumption choices.
| Identity Dimension | Growth Mechanism | Brand Example |
|---|---|---|
| Value Signaling | Products communicate customer beliefs | Toms Shoes signaling social consciousness |
| Group Membership | Usage creates belonging in desired communities | Harley-Davidson creating rider identity |
| Self-Narrative Support | Products reinforce customer self-perception | CrossFit gear supporting athletic identity |
| Aspiration Embodiment | Products represent desired future self | Lululemon connecting products to wellness aspirations |
| Worldview Expression | Consumption reflects philosophical position | Whole Foods shopping as ethical consumption statement |
| Cultural Positioning | Brand usage signals cultural affinities | Supreme clothing as cultural capital marker |
What makes identity-driven strategies particularly powerful is their self-reinforcing nature. As customers incorporate products into their self-concept, they develop resistance to competitor offerings regardless of functional advantages or price differences. This creates remarkable pricing power and customer retention without corresponding marketing expenditure.
Identity-driven approaches work particularly well when aligned with emerging cultural shifts. Brands like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods have grown rapidly by connecting plant-based products to evolving environmental and ethical identities. Customers adopt these products not merely as food choices but as statements about sustainability values and personal commitment to planetary health.
The invisibility of identity-driven business growth strategies stems from their psychological rather than transactional nature. While conventional marketing focuses on product attributes and value propositions, identity-driven approaches operate at deeper psychological levels where customers make decisions based on self-perception rather than utility maximization. This creates growth momentum that confounds competitors focused on feature-by-feature comparison.
Identity-driven business growth strategies require exceptional authenticity and consistency. Customers forming identity connections expect brands to genuinely embody the values they represent rather than merely appropriating cultural symbols. Companies like Patagonia have built remarkable growth by maintaining an authentic commitment to environmental principles across decades, creating trust that enables deep identity integration.
The most successful identity-driven brands recognize that they don’t create customer identity but rather provide vehicles through which existing identities find expression. This subtle distinction explains why attempts to artificially manufacture identity connections typically fail while organically evolved identity relationships demonstrate exceptional durability.
Conclusion: How to Feel the Invisible Pulse of Business Growth Strategies
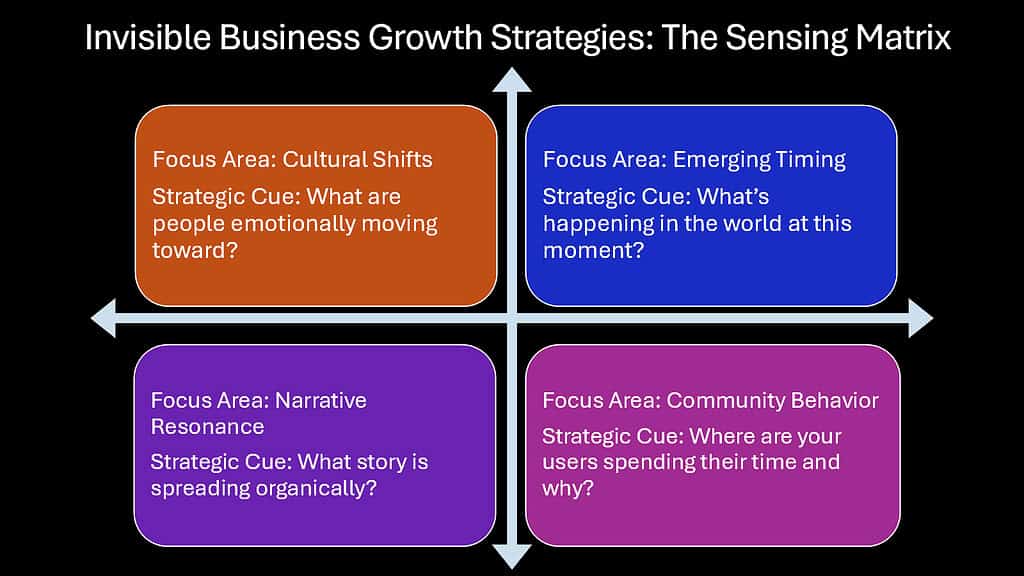
The most powerful business growth strategies often remain invisible precisely because they operate through psychological, social, and cultural mechanisms rather than traditional marketing tactics. These approaches create momentum that traditional metrics struggle to capture but that ultimately drives sustained competitive advantage. While conventional business growth strategies focus on immediate visibility and quarterly metrics, invisible strategies build foundations for decades of sustainable growth.
Implementation of invisible business growth strategies requires fundamentally different organizational capabilities. Companies must develop environmental sensing mechanisms to detect timing opportunities, ecosystem design thinking to foster partnership networks, narrative capabilities to communicate deeper purpose, community facilitation skills to empower user contribution, founder story articulation to personalize corporate identity, and cultural awareness to connect products with identity formation.
The integration of these invisible strategies creates compounding advantages that transcend individual tactics. When timing awareness combines with narrative consistency and identity relevance, companies create market positions that competitors struggle to displace regardless of resource advantages. This explains how upstarts frequently displace established players despite resource disadvantages—they master invisible growth dynamics that incumbents overlook.
| Invisible Business Growth Strategies | Key Implementation Focus | Success Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Timing-First | Environmental scanning systems | Market entry during emergence phase |
| Ecosystem-Led | Partnership architecture design | Partner-driven growth percentages |
| Narrative-Based | Purpose articulation clarity | Customer emotional engagement depth |
| Community-Driven | User empowerment mechanisms | User-generated content volume |
| Founder-Led | Authentic leadership communication | Media coverage without promotion |
| Identity-Driven | Value alignment with customers | Brand-based personal expression |
For leaders seeking to implement these approaches, the first step involves shifting organizational attention from tactical execution to pattern recognition. This requires creating space for reflection, environmental scanning, and cultural analysis—activities that don’t directly produce quarterly results but create the conditions for exponential future growth.
Equally important is developing the organizational patience to allow invisible growth strategies to mature. Unlike conventional tactics showing immediate dashboard results, invisible approaches build momentum gradually before demonstrating remarkable returns. This patience challenge explains why many companies resort to visible but unsustainable growth tactics rather than investing in invisible growth strategies with more durable advantages.
Perhaps most critically, leaders must recognize that invisible business growth strategies cannot be inauthentic. Attempts to manufacture narrative without genuine purpose, create community without real empowerment, or foster identity connections without actual values alignment inevitably fail. The power of invisible strategies emerges from their authenticity—they don’t manipulate markets so much as align deeply with human psychological and social needs.
As business landscapes grow increasingly competitive and traditional differentiation becomes harder to maintain, mastery of invisible business growth strategies will likely determine which companies achieve sustained success. By sensing these subtle forces and building capabilities to harness them, organizations can create momentum that transcends typical business cycles and competitive pressures.




