Table of Contents
Introduction: The Role of Global Tech Innovations in Today’s Economy
Something shifted in the last decade. The world’s economic center of gravity began moving not just geographically but structurally. Walk into a factory in Vietnam, a hospital in Kenya, or a farm in Brazil, and you will find something unexpected. Technology is no longer confined to Silicon Valley boardrooms or research labs in Boston. It has arrived everywhere, quietly rearranging how nations compete and how economies grow.
Global Tech Innovations have become one of the major building blocks of the global economy. They do more than introduce new gadgets or services. They reshape trade flows, redefine labor markets, and shift competitive advantage from one nation to another. A country that masters renewable energy technology gains leverage in global energy markets. A region that adopts digital payment systems opens doors for millions of small entrepreneurs. Technology, in this sense, is not a product but a force that bends the trajectory of economic development.
Relationship Between Global Tech Innovations and Other Building Blocks of the Global Economy
| Building Blocks | Relationship with Global Tech Innovations |
|---|---|
| Global Trade | Digital platforms and automation enable faster cross-border transactions and reduce trade costs through streamlined logistics systems |
| Labor Migration | Automation reshapes job markets by displacing routine tasks while creating demand for technical skills, influencing migration toward tech hubs |
| Global Financial Systems | Fintech innovations like blockchain and digital currencies transform payment infrastructures and expand access to capital markets across borders |
| Natural Resources and Energy | Clean energy technologies reduce dependence on fossil fuels and create new economic value chains around renewable resources |
| Governance and Institutions | Digital tools improve government efficiency through e-governance platforms while raising challenges around data privacy and regulation |
| Global Supply Chain | IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics increase supply chain visibility and resilience, enabling just-in-time production systems |
| Geopolitics | Technology leadership becomes a strategic asset in international relations, with semiconductor supply chains influencing power dynamics |
| Demographics | Healthcare innovations and telemedicine extend productive lifespans while digital education addresses skills gaps in various populations |
| Climate and Sustainability | Green technologies provide pathways to decarbonization while creating economic opportunities in carbon markets and sustainable manufacturing |
1. Global Tech Innovations in Artificial Intelligence and Automation
Artificial intelligence has moved from theory to practice. What was once confined to academic papers now runs through manufacturing lines in Germany, customer service centers in the Philippines, and agricultural planning systems in India. The change is not merely about replacing human tasks with machines. It represents a fundamental shift in how decisions get made and how value gets created.
Productivity gains from AI and automation reach beyond simple efficiency metrics. A factory that uses machine learning to predict equipment failures reduces downtime and extends asset lifespans. A bank that employs AI for credit scoring can serve customers who lack traditional credit histories. A logistics company using route optimization algorithms cuts fuel costs while improving delivery times.
The economic impact varies by region but follows recognizable patterns. Developed economies use automation to offset labor shortages and maintain manufacturing competitiveness. China has deployed more industrial robots than any other nation, using automation to transition from low-cost assembly to higher-value production. Emerging economies must balance the productivity benefits of automation against potential job displacement in labor-intensive sectors.
AI and Automation Impact Across Key Economic Dimensions
| Dimension | Impact Description |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing Efficiency | AI-driven predictive maintenance reduces industrial downtime by up to thirty percent while extending machinery lifespan through optimized usage |
| Service Sector Transformation | Chatbots and virtual assistants handle routine customer inquiries at scale, allowing human workers to focus on complex problem-solving |
| Agricultural Productivity | Precision agriculture systems use computer vision and sensors to optimize irrigation and fertilizer application, reducing input costs |
| Healthcare Diagnostics | Machine learning algorithms analyze medical imaging with accuracy comparable to specialist physicians, expanding diagnostic access |
| Financial Services Access | Alternative credit scoring models using AI evaluate non-traditional data, extending loans to businesses excluded from conventional banking |
| Labor Market Evolution | Automation displaces routine tasks while creating new roles in AI training, system maintenance, and human-machine collaboration |
2. Global Tech Innovations in Advanced Manufacturing and Smart Factories
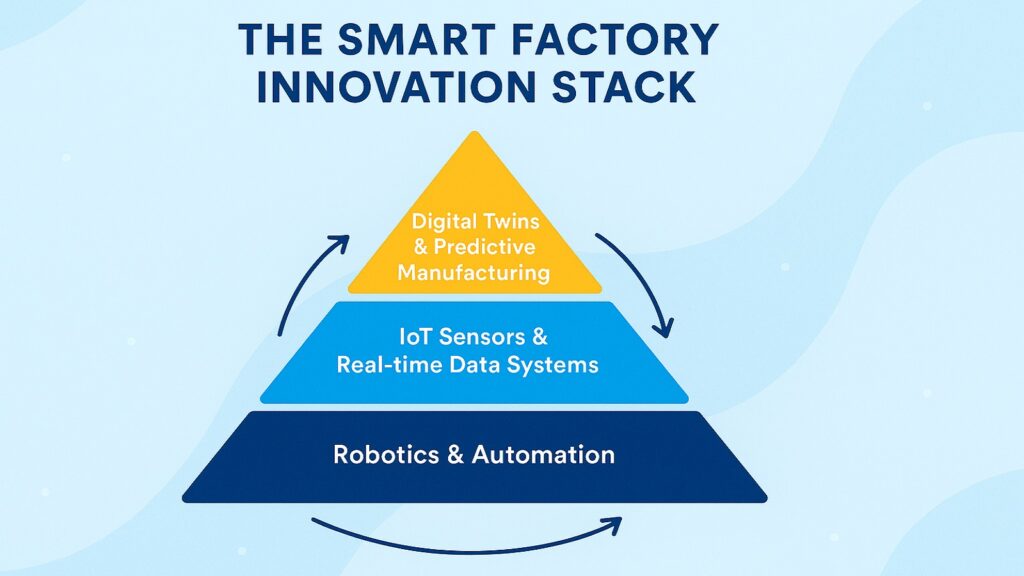
Walk into a modern factory and you will notice the absence of noise. What used to be clanging metal and shouting supervisors has given way to quiet hums and digital displays. Smart factories represent more than incremental improvement. They embody a complete reimagining of how physical goods get made.
Robotics, IoT sensors, and digital twins work together to create production systems that learn and adapt. A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical factory that runs simulations in real time. Engineers can test changes to production lines without stopping actual operations. IoT sensors embedded in equipment collect performance data continuously, feeding information to AI systems that optimize workflows.
This transformation shifts economic advantage toward nations and companies that adopt these technologies first. Germany’s Industry 4.0 initiative has positioned its manufacturing sector as a global leader. South Korea has integrated advanced robotics across its electronics and automotive industries. The United States maintains strength in software platforms that coordinate smart manufacturing systems.
Supply chain resilience has become a critical economic concern. Smart factories address this challenge through flexibility and visibility. A factory equipped with modular production systems can switch between product lines quickly in response to demand shifts or supply shortages.
Global Tech Innovations: Advanced Manufacturing Technologies and Economic Benefits
| Technology Application | Economic Benefit |
|---|---|
| Collaborative Robots | Cobots work alongside human workers, combining human flexibility with robotic precision to increase output quality and reduce injuries |
| Additive Manufacturing | Three-D printing enables on-demand production of complex parts, reducing inventory costs and allowing customization at scale |
| IoT Sensor Networks | Real-time monitoring enables predictive maintenance strategies that cut unplanned downtime by forty percent in automotive manufacturing |
| Digital Twin Simulation | Virtual factory replicas allow manufacturers to test process changes without disrupting operations, reducing time-to-market |
| Machine Vision Systems | Computer vision inspects product quality at speeds impossible for humans, catching defects early and reducing waste |
| Edge Computing Integration | Processing data at the factory floor reduces latency and enables instantaneous adjustments to production parameters |
3. Global Tech Innovations in Green and Clean Energy Technologies
Energy transitions have moved from environmental idealism to economic necessity. The shift toward renewable energy sources is reshaping industrial strategies, trade relationships, and competitive positioning among nations. What started as climate policy has evolved into a race for technological leadership and market share.
Solar and wind energy have crossed critical cost thresholds. In many regions, new renewable capacity is now cheaper than fossil fuel alternatives. This economic reality drives adoption faster than policy mandates alone could achieve. China manufactures more than seventy percent of global solar panels, turning renewable energy into an export industry. Europe leads in offshore wind technology, creating jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
Electric vehicles represent more than a transportation shift. They are reshaping automotive supply chains and energy infrastructure simultaneously. Battery production has become a strategic industry, with nations competing to secure lithium, cobalt, and rare earth supplies. The transition creates winners and losers.
Hydrogen technology adds another dimension to the energy transition. Green hydrogen, produced using renewable electricity, offers a pathway to decarbonize heavy industry and long-distance transport. Australia, Chile, and Saudi Arabia are investing billions in hydrogen production capacity, seeking to replace fossil fuel exports with clean energy alternatives.
Global Tech Innovations: Clean Energy Technologies and Economic Transformation
| Technology Sector | Economic Impact |
|---|---|
| Solar Photovoltaics | Global solar installations reached over two hundred gigawatts annually, creating manufacturing clusters in Asia while driving electricity costs below fossil alternatives |
| Offshore Wind Power | European offshore wind capacity provides power equivalent to fifteen million homes, spawning specialized vessel construction and maintenance industries |
| Battery Storage Systems | Lithium-ion battery costs fell by nearly ninety percent over the past decade, enabling grid-scale energy storage that makes renewable power reliable |
| Electric Vehicle Production | EV sales surpassed ten million units globally in 2022, triggering massive investments in battery factories and reshaping automotive supply chains |
| Green Hydrogen Infrastructure | Pilot projects in Germany, Japan, and Chile demonstrate hydrogen’s potential for steel production and shipping fuel |
| Smart Grid Technology | Digital grid management systems reduce transmission losses and integrate distributed renewable sources, improving energy efficiency by up to twenty percent |
4. Global Tech Innovations in Digital Finance and Fintech Infrastructure
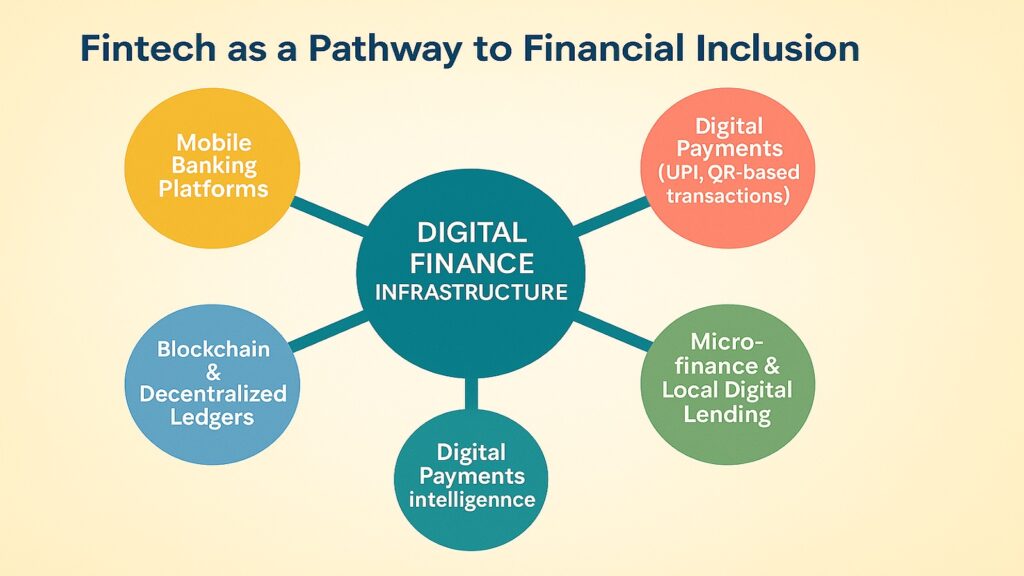
Money moves differently now. The pipes that carry financial flows have been rebuilt with digital technology, changing who can participate and how transactions occur. This transformation extends beyond convenience. It represents a fundamental expansion of economic opportunity.
Digital payments have replaced cash in large parts of the global economy. India’s Unified Payments Interface processes billions of transactions monthly, enabling instant money transfers between any two bank accounts using just a phone number. Mobile money services in Kenya and Tanzania allow farmers to receive payments directly from buyers, eliminating middlemen and increasing their share of sale proceeds.
Blockchain technology introduces transparency and security to transactions that previously required trusted intermediaries. Supply chain financing becomes more accessible when all parties can verify the movement and authenticity of goods through distributed ledgers. Cross-border remittances become cheaper and faster when blockchain networks replace traditional correspondent banking relationships.
Financial inclusion measures economic progress in human terms. When a street vendor in Lagos can accept digital payments, she enters the formal economy and gains access to credit. When a farmer in rural Indonesia can secure a microloan through a mobile app, he can invest in better seeds and equipment.
Global Tech Innovations: Fintech Innovations and Economic Access
| Innovation Area | Impact on Economic Participation |
|---|---|
| Mobile Payment Systems | UPI in India processes over eight billion transactions monthly, enabling digital commerce for millions of small merchants |
| Digital Banking Platforms | Neobanks provide low-cost banking services to previously unbanked populations, with Brazil’s digital banks serving over one hundred million customers |
| Blockchain Remittances | Cryptocurrency-based remittance services reduce transfer costs from traditional seven percent to under two percent for migrant workers |
| Alternative Credit Scoring | Fintech lenders analyze mobile phone usage patterns to extend loans to entrepreneurs without traditional credit records |
| Digital Currency Systems | Central bank digital currencies under development in over eighty countries promise to reduce payment system costs |
| Decentralized Finance Platforms | DeFi protocols enable peer-to-peer lending and borrowing without intermediaries, though regulatory uncertainty remains |
5. Global Tech Innovations in Healthcare and Biotechnology
Healthcare has entered a new phase. The convergence of digital technology and biological science is producing capabilities that seemed distant just years ago. These advances carry economic weight beyond their humanitarian value. Healthier populations work more productively, live longer, and consume healthcare resources more efficiently.
Digital health platforms have transformed how care gets delivered. Telemedicine connects patients in remote areas with specialists thousands of miles away. Wearable sensors monitor chronic conditions continuously, alerting providers to problems before they become emergencies. Electronic health records enable coordination across providers, reducing redundant tests and medication errors.
Gene editing technologies like CRISPR have moved from laboratory curiosities to practical therapies. Sickle cell disease treatments using gene editing entered clinical use in 2023. Cancer immunotherapies engineered to target specific tumor markers have improved survival rates. The economic implications extend beyond treatment costs. Precision medicine reduces trial-and-error approaches that waste resources.
Biomanufacturing represents a new industrial frontier. Synthetic biology techniques produce insulin, vaccines, and specialty chemicals through engineered microorganisms rather than traditional chemical processes. Singapore and Ireland have positioned themselves as biomanufacturing hubs, attracting pharmaceutical investment through supportive regulations and skilled workforces.
Global Tech Innovations: Healthcare Technology and Economic Value Creation
| Technology Domain | Economic Contribution |
|---|---|
| Telemedicine Platforms | Remote consultation services expanded access to specialist care while reducing healthcare costs by up to thirty percent |
| AI Diagnostic Systems | Machine learning algorithms analyze medical images to identify diseases earlier, improving treatment outcomes and reducing long-term care costs |
| Gene Therapy Development | CRISPR-based treatments for genetic disorders entered clinical practice, with the global gene therapy market projected to exceed twenty-five billion dollars by 2030 |
| Wearable Health Devices | Continuous monitoring devices help manage chronic conditions, reducing hospitalizations and enabling patients to maintain productive employment |
| Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing | Cell-based production methods for vaccines and biologics improve scalability and reduce contamination risks |
| Personalized Medicine Platforms | Genetic testing guides treatment selection, reducing adverse drug reactions that cost healthcare systems billions annually |
6. Global Tech Innovations in Global Connectivity and Digital Trade Networks
Distance matters less than it used to. The digital infrastructure connecting people, companies, and markets across borders has grown dense and fast. This connectivity reshapes trade patterns and competitive dynamics in ways that favor adaptability over geography.
Cloud computing platforms allow companies of any size to access computational resources that once required massive capital investment. A startup in Nairobi can use the same database and analytics tools as a multinational corporation, paying only for what it uses. This democratization of technology infrastructure lowers barriers to entry and accelerates innovation cycles.
Fiber optic networks and undersea cables carry data across oceans at the speed of light. New cable projects connect previously isolated regions to global digital networks. Real-time communication enables remote work arrangements that tap talent pools regardless of location. Supply chain coordination happens instantaneously across continents.
5G networks provide the bandwidth and low latency required for emerging applications. Autonomous vehicles need instant connectivity to navigate safely. Remote surgery demands video transmission without delay. Industrial IoT systems require reliable connections for thousands of sensors.
Digital trade has exploded over the past decade. Services that once required physical presence can now be delivered remotely. Software developers in the Philippines work for clients in California. Graphic designers in Indonesia serve customers in Europe. Educational content created in one country reaches students worldwide.
Global Tech Innovations: Digital Connectivity Infrastructure and Trade Expansion
| Infrastructure Element | Trade Impact |
|---|---|
| Cloud Computing Platforms | Global cloud services revenue exceeded five hundred billion dollars, enabling businesses worldwide to scale operations without massive infrastructure investments |
| Undersea Cable Networks | Over 1.3 million kilometers of submarine cables carry ninety-nine percent of intercontinental data traffic, reducing communication costs to near zero |
| 5G Network Deployment | Fifth generation mobile networks provide speeds up to one hundred times faster than 4G, enabling new applications in autonomous vehicles and industrial automation |
| Cross-Border E-Commerce | International online retail sales reached over one trillion dollars annually, with platforms facilitating trade for millions of small and medium enterprises |
| Digital Payment Corridors | Instant cross-border payment systems reduce transaction costs and settlement times from days to seconds |
| Remote Collaboration Tools | Video conferencing and project management platforms support distributed teams across time zones, enabling companies to access global talent pools |
Conclusion: The Future Path of Global Tech Innovations in a Changing World
Global Tech Innovations does not announce itself with trumpets. It arrives quietly, through small changes that accumulate into transformations. A factory adds sensors. A farmer downloads an app. A doctor consults a database. These individual moments aggregate into economic forces that reshape competitive landscapes and shift power among nations.
Global Tech Innovations function as invisible hands that pull economic gravity in new directions. The patterns are clear even if outcomes remain uncertain. Countries that invest in digital infrastructure, support innovation ecosystems, and adapt regulatory frameworks to new technologies position themselves at the center of emerging industries. Those that cling to outdated models find themselves increasingly peripheral.
The shifts underway are not uniform or fair. Technology creates winners and losers within countries and between them. Automation displaces workers even as it creates new opportunities. Digital platforms concentrate market power while expanding access. Clean energy transitions threaten fossil fuel-dependent regions while opening new economic frontiers.
The future is not predetermined but neither is it random. The choices made now about technology investment, education systems, and innovation policy will echo for generations. The opportunity exists to harness Global Tech Innovations for broad-based prosperity and sustainable development.
Emerging Global Tech Innovations Shaping Future Economic Competition
| Emerging Trends of Global Tech Innovations | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|
| Quantum Computing Development | Nations leading in quantum technology will gain advantages in cryptography, drug discovery, and complex system optimization |
| Advanced AI Systems | Artificial general intelligence capabilities could amplify productivity across all sectors while raising questions about workforce transitions |
| Synthetic Biology Expansion | Engineering biological systems to produce materials and chemicals will create new industries while disrupting petroleum-based manufacturing |
| Space-Based Infrastructure | Satellite networks providing global internet access will reduce information asymmetries and enable real-time monitoring of economic activity |
| Brain-Computer Interfaces | Direct neural connections to digital systems may transform human capability and productivity though widespread adoption remains distant |
| Climate Technology Scaling | Carbon capture, sustainable aviation fuels, and circular economy systems will become economically viable, reshaping heavy industry globally |
The story of Global Tech Innovations is still being written. The chapters ahead will be shaped by decisions made in boardrooms, laboratories, and government offices around the world. Those who understand technology not just as tools but as forces that reshape economic possibility will navigate the future most successfully. The path forward demands both ambition and humility, confidence and adaptability, vision and pragmatism.




