Table of Contents
Introduction: Business Essentials for Modern Success

Business Essentials represent the fundamental knowledge, principles, and practices that organizations need to operate effectively in a dynamic marketplace. These are living frameworks that shape how companies make decisions, allocate resources, manage people, and respond to change. Business Essentials connect strategic vision with operational reality, bridging the gap between what leaders want to achieve and what teams can actually accomplish.
In today’s environment, Business Essentials extend beyond traditional categories like accounting and marketing. They now encompass technology integration, sustainability thinking, emotional intelligence, and global awareness. Organizations that master these Business Essentials build resilience, adapt faster, and create value for shareholders, employees, customers, and communities. This article explores eight powerful paths that define modern Business Essentials, revealing how foundational principles guide growth, innovation, and long-term stability.
These eight dimensions work together in powerful ways. Growth depends on strategy. Strategy requires leadership. Leadership shapes culture. Culture influences technology adoption. Technology enables global reach. Global thinking demands sustainability. Sustainability connects to human well-being. Understanding Business Essentials means seeing these connections clearly and acting on them consistently.
Business Essentials Framework Overview
| Growth Mindset | Organizations that prioritize 360-degree growth focus on both financial metrics and operational capabilities, creating sustainable competitive advantages |
| Core Functions | Marketing, sales, operations, finance, human resources, and other functions operate most effectively when grounded in shared principles and clear accountability |
| Strategic Direction | Business strategy provides the clarity needed to prioritize resources, make trade-offs, and align diverse teams toward common objectives |
| Leadership Quality | Effective leaders build trust, communicate vision, and create environments where people feel motivated to contribute their best work |
| Technology Integration | Modern organizations treat technology as a core capability rather than a support function, enabling speed and precision in decision-making |
| Global Awareness | Understanding international markets, supply chains, and geopolitical risks helps companies navigate complexity and identify new opportunities |
| Sustainable Practices | Environmental responsibility and long-term thinking influence reputation, operational costs, and regulatory compliance across industries |
| Human-Centered Approach | Empathy, emotional intelligence, and psychological safety form the foundation for innovation, collaboration, and organizational resilience |
1. Business Essentials in a Business 360° Growth Framework
Growth is not a single metric but a constellation of improvements across revenue, capability, reputation, and stability. Business Essentials provide the framework for thinking about growth holistically. When leaders focus only on quarterly earnings, they miss opportunities to strengthen systems, develop talent, and build customer loyalty. A 360-degree growth mindset recognizes that financial results flow from operational excellence, strategic clarity, and organizational health.
Consider how Business Essentials shape different growth levers. Leadership sets the tone for ambition and accountability. Management translates vision into action through clear processes. Marketing identifies customer needs and communicates value. Operations ensure consistent delivery. Finance allocates capital efficiently. Innovation explores new possibilities. Culture determines how people collaborate and solve problems. Each lever depends on foundational Business Essentials like transparency, discipline, and customer focus.
Organizations that master Business Essentials in their growth framework tend to outperform competitors over extended periods. They invest in capability building alongside revenue generation. They measure leading indicators like employee engagement and customer satisfaction, not just lagging indicators like profit margins. They understand that growth compounds when systems improve, when teams learn, and when processes become more efficient.
The 360-degree framework also highlights interdependencies. Strong marketing generates leads, but those leads convert only if sales processes are effective. Sales succeeds when operations delivers quality consistently. Quality depends on motivated employees. This circular reinforcement makes sustainable growth possible.
Business Essentials in Growth Dimensions
| Revenue Growth | Expanding income streams through market penetration, product development, and customer retention strategies that align with organizational capabilities |
| Operational Capacity | Building systems, processes, and infrastructure that enable the organization to scale efficiently without compromising quality or speed |
| Market Position | Strengthening brand recognition, competitive differentiation, and customer loyalty through consistent delivery of value |
| Strategic Capability | Developing the organizational ability to plan effectively, execute with discipline, and adapt quickly to changing market conditions |
| Talent Development | Investing in employee skills, leadership pipeline, and knowledge retention to ensure the organization can meet future challenges |
| Innovation Pipeline | Creating structures and incentives that encourage experimentation, learning from failure, and commercializing new ideas |
| Customer Value | Deepening understanding of customer needs, improving products and services, and building relationships that generate recurring revenue |
| Financial Health | Maintaining strong cash flow, manageable debt levels, and sufficient reserves to weather uncertainty while funding growth initiatives |
2. Business Essentials in Core Business Functions
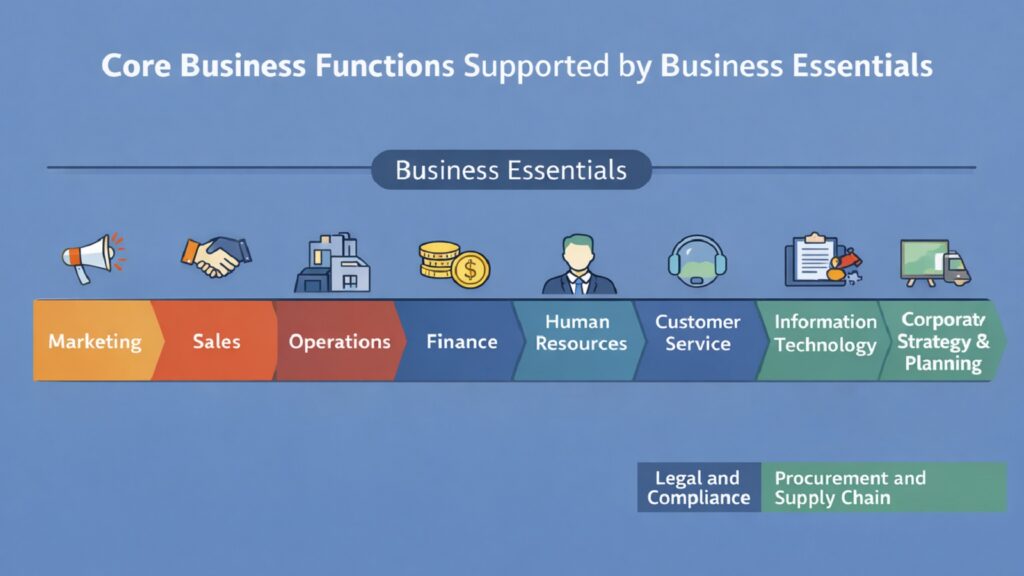
Every organization divides work into functions. Marketing attracts customers. Sales converts interest into revenue. Operations produces and delivers products. Finance manages resources. Human resources develops talent. These functions operate most effectively when they share common Business Essentials like clarity, accountability, and collaboration. Without these foundations, functional silos emerge, communication breaks down, and performance suffers.
Business Essentials create alignment across functions. When marketing and sales agree on target customers, campaigns generate qualified leads that convert efficiently. When operations and finance collaborate on capacity planning, companies avoid overinvestment. When human resources partners with leadership on succession planning, organizations maintain continuity. These connections matter more than functional excellence in isolation.
Each function contributes unique capabilities while depending on shared principles. Marketing requires creativity and data analysis. Sales demands relationship building. Operations needs process discipline. Finance relies on analytical rigor. Human resources combines psychology and administration. Customer service balances empathy with efficiency. Information technology merges technical expertise with business understanding. Legal and compliance protect while enabling transactions. Corporate strategy synthesizes information into plans. Procurement optimizes costs while ensuring supply reliability.
Business Essentials provide the common language enabling diverse functions to work together effectively. They establish expectations for communication, decision rights, and performance standards. They clarify how functions coordinate on initiatives like product launches or digital transformations, ensuring that functional goals ladder up to organizational objectives.
Business Essentials Across Core Functions
| Marketing | Identifies customer segments, develops positioning strategies, manages brand perception, and generates demand through integrated campaigns |
| Sales | Converts prospects into customers through relationship building, needs assessment, solution presentation, negotiation, and closing |
| Operations | Manages production, service delivery, quality control, inventory, and logistics to ensure consistent fulfillment of customer commitments |
| Finance | Oversees budgeting, financial reporting, capital allocation, cash management, and risk assessment to maintain organizational health |
| Human Resources | Recruits talent, manages compensation and benefits, facilitates training and development, and maintains employee relations |
| Customer Service | Provides support, resolves issues, gathers feedback, and builds loyalty through responsive and empathetic customer interactions |
| Information Technology | Develops and maintains systems, manages data security, enables digital capabilities, and supports technology-driven innovation |
| Legal and Compliance | Ensures regulatory adherence, manages contracts, protects intellectual property, and mitigates legal risks across business activities |
| Corporate Strategy | Synthesizes market intelligence, competitive analysis, and internal capabilities into coherent strategic plans and priorities |
| Procurement and Supply Chain | Sources materials and services, negotiates supplier contracts, manages inventory levels, and optimizes end-to-end supply networks |
3. Business Essentials in the Strategic Core
Strategy is the art of making choices. Organizations face countless opportunities and constraints. Business Essentials help leaders determine which paths to take and which to decline. Strategy provides direction by articulating what the organization will accomplish, how it will compete, and why its approach creates value. Without this clarity, companies drift, resources scatter, initiatives conflict, and performance stagnates.
Effective strategy emerges from deep understanding of Business Essentials. Leaders must assess competitive dynamics, customer preferences, technological trends, and internal capabilities. They must balance short-term pressures with long-term ambitions while allocating limited resources to maximize returns. This work requires analytical rigor, creative thinking, and honest assessment of strengths and weaknesses.
Business Essentials transform strategy from abstract planning into concrete execution. Strategic frameworks provide structured approaches to analysis and decision-making. Planning cycles create rhythms for review and adjustment. Performance metrics translate strategy into measurable outcomes. Communication plans ensure that teams understand priorities and their role in achieving them.
The strategic core also includes governance mechanisms that determine how leaders evaluate proposals and allocate funding. Business Essentials establish the disciplines that make strategy operational rather than aspirational, ensuring that strategic choices cascade through the organization and influence functional plans, team goals, and individual objectives.
Business Essentials in Strategic Elements
| Vision and Mission | Clear articulation of organizational purpose, aspirations, and values that guide decisions and inspire stakeholder commitment |
| Competitive Positioning | Deliberate choices about where to compete, how to differentiate, and which customer segments to prioritize for sustainable advantage |
| Resource Allocation | Systematic processes for evaluating opportunities, distributing capital and talent, and balancing investments across growth and maintenance |
| Strategic Planning | Structured cycles for environmental scanning, opportunity assessment, goal setting, and action planning that translate vision into execution |
| Performance Management | Metrics, dashboards, and review processes that track progress, identify variances, and enable rapid course correction |
| Risk Management | Identification and mitigation of threats to strategic objectives, including market shifts, operational failures, and external disruptions |
| Portfolio Management | Coordination of multiple initiatives, products, or business units to optimize collective performance and avoid resource conflicts |
| Strategic Communication | Clear and consistent messaging about direction, priorities, and progress that aligns stakeholders and maintains organizational focus |
4. Business Essentials in Leadership and Management
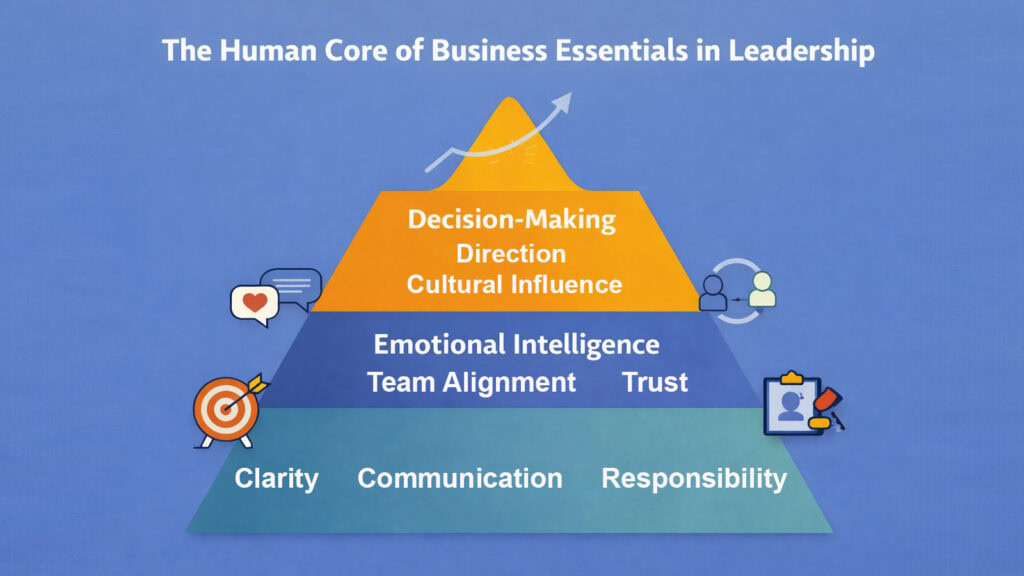
Leadership stands among the most critical Business Essentials. Leaders set direction, build culture, and inspire performance. They create environments where talented people choose to stay and contribute their best efforts. They navigate uncertainty with confidence and humility. They balance competing demands without losing sight of core values. Leadership quality determines whether organizations thrive during challenges or stumble.
Business Essentials shape how leaders approach their responsibilities. Effective leaders understand that authority comes from expertise, integrity, and earned trust rather than titles alone. They communicate clearly and listen actively. They delegate appropriately while maintaining accountability. They develop successors systematically rather than hoping talent emerges spontaneously. They recognize that their decisions ripple through the organization, affecting morale, productivity, and retention.
Management translates leadership vision into daily operations. Managers coordinate work, solve problems, coach individuals, and remove obstacles. They apply Business Essentials like planning, organizing, monitoring, and adjusting. They create predictability through consistent processes while maintaining flexibility for exceptions. They balance standardization with adaptation. They measure what matters and use data to drive improvement.
The human dimension of leadership represents perhaps the deepest Business Essential. Leaders must understand motivation, manage conflict, build consensus, and navigate organizational politics. They need emotional maturity to remain calm under pressure, acknowledge mistakes, and maintain relationships during disagreements. They create psychological safety so teams feel comfortable taking risks and sharing concerns. These capabilities separate good leaders from great ones.
Business Essentials in Leadership Capabilities
| Vision Setting | Articulating compelling pictures of the future that inspire commitment and provide directional clarity for strategic and operational decisions |
| Decision Making | Balancing analysis with intuition, gathering diverse perspectives, and making timely choices even with incomplete information |
| Communication | Conveying messages clearly across multiple channels, adapting style to audience, and ensuring understanding through active listening |
| Team Building | Assembling diverse talents, fostering collaboration, resolving conflicts constructively, and creating shared accountability for results |
| Performance Coaching | Providing feedback that develops capabilities, recognizing achievements, addressing underperformance, and creating growth opportunities |
| Change Leadership | Guiding organizations through transitions, managing resistance, maintaining momentum, and reinforcing new behaviors until they become habits |
| Talent Development | Identifying high-potential individuals, providing stretch assignments, facilitating learning, and building robust leadership pipelines |
| Cultural Stewardship | Modeling desired behaviors, reinforcing values through decisions and actions, and shaping norms that influence how work gets done |
5. Business Essentials in Business and Technology
Technology has evolved from a support function to a core Business Essential. Organizations now compete on their ability to leverage digital tools, automate processes, analyze data, and serve customers through technology-enabled channels. Companies that treat technology as optional fall behind competitors who integrate it deeply into operations and strategy. Digital capability determines speed, accuracy, scalability, and customer experience.
Business Essentials guide how organizations adopt technology. Leaders must understand capabilities without becoming experts. They need frameworks for evaluating solutions, prioritizing investments, and managing risks. They should balance standardization with customization and incremental improvement with transformational change. These choices shape competitive position and operational efficiency.
Artificial intelligence, cloud computing, automation, and data analytics represent the current frontier. AI enables personalization at scale and predictive insights. Cloud platforms provide flexibility and cost efficiency. Automation eliminates repetitive tasks. Analytics transform information into insights. Organizations that master these capabilities create advantages that compound over time.
Technology integration requires cultural change. Teams must learn new tools and adapt workflows. Leaders need patience during transitions and commitment to training. Business Essentials include the change management disciplines that make technology adoption successful.
Business Essentials in Technology Domains
| Digital Infrastructure | Cloud platforms, networks, security systems, and computing resources that provide reliable and scalable foundations for applications |
| Data Management | Systems for collecting, storing, governing, and analyzing information to generate insights that inform decisions across the organization |
| Process Automation | Tools that streamline workflows, reduce manual effort, improve accuracy, and free employees for higher-value activities |
| Customer Technology | Digital channels, mobile applications, self-service portals, and communication platforms that enhance customer experience and accessibility |
| Artificial Intelligence | Machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and predictive models that enable personalization, optimization, and intelligent automation |
| Cybersecurity | Policies, technologies, and practices that protect data, systems, and networks from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats |
| Integration Architecture | Middleware, APIs, and integration patterns that enable different systems to share data and coordinate processes seamlessly |
| Technology Governance | Frameworks for selecting vendors, managing licenses, overseeing projects, and ensuring technology investments deliver expected returns |
6. Business Essentials in the Global Economy
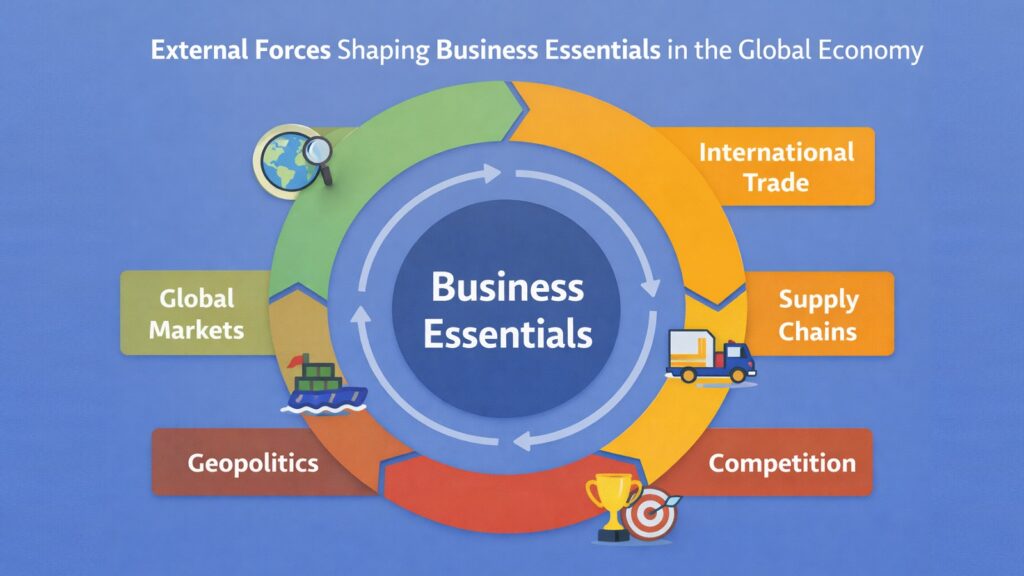
No organization operates in isolation. Global markets, international supply chains, cross-border competition, and geopolitical developments influence even domestic businesses. Business Essentials now include awareness of global economic patterns, currency fluctuations, trade policies, and political risks. Leaders who understand these external forces make better decisions about sourcing, pricing, expansion, and risk management.
The global economy creates both opportunities and challenges. Companies can access larger markets, lower-cost suppliers, and diverse talent pools. However, global engagement also introduces complexity around different regulations, cultural expectations, and business practices. Organizations face currency risk, supply chain disruptions, and political uncertainty.
Business Essentials help leaders manage global complexity. Understanding trade agreements informs sourcing decisions. Monitoring geopolitical developments helps anticipate supply chain risks. Analyzing currency trends influences pricing strategies. Building relationships across cultures enables effective partnerships. Companies that develop these capabilities compete more effectively than those focused narrowly on domestic markets.
Global awareness also shapes long-term strategy. Emerging markets offer growth opportunities but require patient capital. Developed markets provide stability but feature intense competition. Regional trade blocs influence market access. Business Essentials include the frameworks that help leaders navigate this complexity and identify sustainable competitive positions.
Business Essentials in Global Dimensions
| International Markets | Understanding customer preferences, competitive dynamics, and growth potential across different geographic regions and economic zones |
| Supply Chain Networks | Managing global sourcing, logistics complexity, inventory positioning, and supplier relationships to ensure reliable and cost-effective operations |
| Trade and Tariffs | Navigating customs regulations, import duties, trade agreements, and compliance requirements that affect cross-border transactions |
| Currency Management | Monitoring exchange rate fluctuations, implementing hedging strategies, and pricing products appropriately across multiple currency zones |
| Geopolitical Risk | Assessing political stability, regulatory changes, sanctions, and conflicts that could disrupt operations or market access |
| Cultural Intelligence | Adapting business practices, communication styles, and management approaches to align with local norms and expectations |
| Global Competition | Analyzing competitive threats from international players, understanding their strategies, and developing responses that protect market position |
| Emerging Economies | Evaluating opportunities in rapidly developing markets while managing risks related to infrastructure, institutions, and volatility |
7. Business Essentials in Sustainability and Responsibility
Sustainability has transitioned from optional corporate social responsibility to essential business strategy. Environmental pressures, regulatory requirements, investor expectations, and customer preferences now demand that organizations consider long-term ecological and social impacts. Business Essentials include understanding how sustainability influences reputation, operational costs, risk exposure, and competitive differentiation.
Companies face growing expectations to measure and reduce carbon emissions, minimize waste, conserve resources, and protect ecosystems. These commitments affect procurement, manufacturing, product design, and logistics. Organizations that embrace sustainability often discover cost savings through efficiency improvements, waste reduction, and energy conservation. They also build stronger relationships with environmentally conscious customers and employees.
Environmental, social, and governance frameworks provide structure for sustainability thinking. Environmental factors include carbon footprint and water usage. Social considerations encompass labor practices and community relations. Governance involves ethical leadership and transparent reporting. Business Essentials help leaders balance these dimensions with financial objectives.
Long-term thinking represents the core of sustainability as a Business Essential. Leaders must consider how today’s decisions affect future generations and ecosystem health. They need frameworks for evaluating trade-offs between short-term profits and long-term resilience. This expanded perspective creates durability that purely financial optimization cannot achieve.
Business Essentials in Sustainability Areas
| Carbon Management | Measuring greenhouse gas emissions, setting reduction targets, implementing energy efficiency measures, and exploring renewable energy sources |
| Circular Economy | Designing products for longevity, repair, and recycling while minimizing waste through closed-loop material flows |
| Resource Efficiency | Optimizing water usage, reducing material consumption, and improving yields to lower environmental impact and operational costs |
| Supply Chain Ethics | Ensuring suppliers meet labor standards, environmental requirements, and ethical practices throughout the value chain |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Building relationships with communities, NGOs, regulators, and other groups affected by business operations |
| Climate Risk | Assessing physical risks from extreme weather and transition risks from policy changes that could affect assets, operations, and markets |
| Transparent Reporting | Disclosing environmental and social performance through standardized frameworks that enable stakeholder evaluation and comparison |
| Sustainable Innovation | Developing products and services that deliver customer value while reducing environmental footprint and advancing social goals |
8. Business Essentials in Human Elements and Emotional Intelligence
Organizations succeed through people. Technology amplifies capability, but humans provide creativity, judgment, empathy, and adaptability. Business Essentials increasingly emphasize emotional intelligence, psychological safety, work-life balance, and employee well-being. Companies that create supportive environments attract better talent, experience lower turnover, and generate higher productivity.
Emotional intelligence includes self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. Leaders possessing high emotional intelligence accurately interpret situations, manage their responses in a constructive manner, and foster strong relationships. They cultivate environments in which individuals feel acknowledged, appreciated, and supported. They tackle conflicts promptly and equitably. These skills constitute essential business fundamentals for contemporary leadership.
Psychological safety enables teams to perform at their highest level. When people feel safe taking risks, admitting mistakes, and offering dissenting opinions, organizations innovate faster and solve problems more effectively. Creating this safety requires consistent leadership behavior. Leaders must respond to bad news without anger, welcome challenges to their ideas, and acknowledge uncertainties.
Work-life balance and employee well-being represent increasingly important Business Essentials. Burnout reduces productivity and drives turnover. Organizations that respect boundaries, provide flexibility, and support mental health create sustainable performance. This understanding generates loyalty and commitment that financial incentives alone cannot match.
Business Essentials in Human-Centered Elements
| Emotional Awareness | Understanding one’s own emotions, recognizing how they influence decisions, and managing reactions to maintain effective relationships |
| Empathy and Compassion | Perceiving others’ feelings and perspectives, responding with care and understanding, and building trust through genuine concern |
| Psychological Safety | Creating environments where people feel comfortable taking interpersonal risks, speaking honestly, and learning from mistakes without fear |
| Inclusive Culture | Valuing diverse perspectives, ensuring equitable opportunities, and building teams where everyone feels respected and able to contribute |
| Work-Life Integration | Supporting flexibility, respecting boundaries, and recognizing that sustainable performance requires time for rest and personal priorities |
| Mental Health Support | Providing resources for stress management, offering counseling services, and destigmatizing conversations about psychological well-being |
| Feedback Culture | Encouraging regular, constructive conversations about performance that support growth while maintaining dignity and respect |
| Purpose and Meaning | Connecting individual work to organizational mission, helping people understand their impact, and fostering intrinsic motivation |
Conclusion: Business Essentials for Long-Term Growth
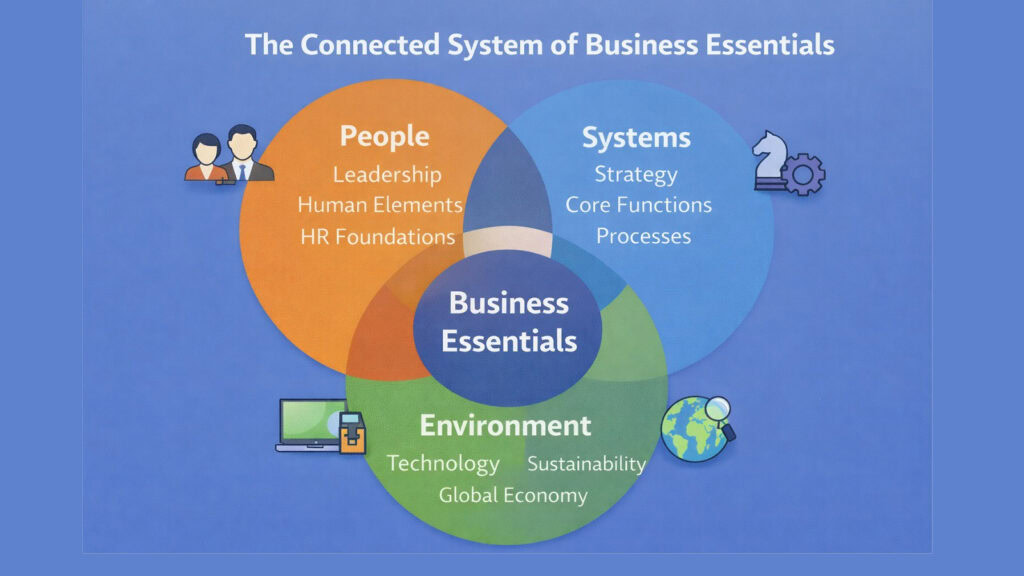
Business Essentials provide the foundation for organizational success in an increasingly complex world. The eight pillars explored in this article reveal how fundamental principles connect across strategy, operations, leadership, technology, global awareness, sustainability, and human well-being. Organizations that master these Business Essentials build resilience, adapt to change without losing direction, and balance competing priorities without sacrificing core values.
Growth emerges from this integration. When strategy aligns with capabilities, when leadership inspires trust, when technology amplifies human potential, when global thinking informs local action, when sustainability shapes decisions, and when emotional intelligence guides relationships, organizations create sustainable competitive advantages that compound over time.
The journey toward mastering Business Essentials never ends. Markets evolve, technologies advance, customer expectations shift, and regulatory requirements change. However, the fundamental principles remain stable. Clarity beats confusion. Collaboration outperforms silos. Purpose motivates more than profit alone. Trust enables speed. These timeless Business Essentials guide leaders through uncertainty toward lasting success.
Apply these Business Essentials thoughtfully. Start with honest assessment of current capabilities. Identify gaps between aspiration and reality. Prioritize improvements that create the most value. Measure progress systematically and adjust based on results. Remember that excellence in Business Essentials develops through consistent practice rather than sudden transformation.
Business Essentials Integration Framework
| Strategic Clarity | Well-articulated direction that aligns resources, guides decisions, and provides the context needed for effective execution across functions |
| Leadership Excellence | Trusted leaders who communicate vision, develop talent, build culture, and create environments where people contribute their best efforts |
| Operational Capability | Efficient processes, reliable systems, and continuous improvement disciplines that enable consistent delivery of customer value |
| Technology Enablement | Digital tools, data analytics, and automation that enhance speed, accuracy, and decision-making across the organization |
| Global Perspective | Awareness of international markets, geopolitical developments, and cross-border opportunities that inform strategy and risk management |
| Sustainable Practices | Long-term thinking about environmental impact, social responsibility, and stakeholder relationships that build lasting organizational resilience |
| Human-Centered Approach | Emotional intelligence, psychological safety, and well-being practices that unlock creativity, engagement, and sustained performance |
| Integrated Execution | Coordination across all Business Essentials that creates synergies, reinforces strengths, and transforms principles into competitive advantages |




