Table of Contents
Introduction: How Business Functions Shape Modern Companies

Every successful company operates through specialized departments that work together like instruments in an orchestra. These business functions create the framework that turns vision into reality. They provide structure when markets shift, direction when choices multiply, and resilience when challenges emerge. Understanding how business functions interconnect gives leaders a map for building organizations that last.
When business functions align properly, companies gain clarity about who does what and why it matters. Decisions move faster because authority sits in the right places. Resources flow to where they create the most value. This alignment reduces wasted effort and creates momentum that competitors struggle to match.
The ten essential business functions examined here form the core architecture of nearly every successful organization. Marketing builds awareness. Sales converts interest into revenue. Human Resources develops talent. Operations maintains efficiency. Finance manages capital. Corporate Strategy sets direction. Information Technology enables digital transformation. Customer Service protects loyalty. Legal and Compliance guards against risk. Procurement and Supply Chain ensures resource flow.
Together, these business functions create a system greater than the sum of its parts. Mastering them gives companies the foundation to grow sustainably and build competitive advantages that endure.
Business Functions Overview: Core Responsibilities and Strategic Impact
| Business Functions | Primary Responsibility and Strategic Impact |
| Marketing | Creates customer awareness, builds brand equity, and generates qualified demand through market research, positioning, and communication strategies |
| Sales | Converts prospects into customers, builds relationships, and drives revenue growth through direct engagement and consultative selling approaches |
| Human Resources | Attracts, develops, and retains talent while shaping organizational culture and ensuring workforce capability aligns with strategic goals |
| Operations | Manages production processes, quality control, and workflow efficiency to deliver products and services consistently at optimal cost |
| Finance | Controls capital allocation, monitors financial health, manages risk, and provides data-driven insights that guide strategic decision-making |
| Corporate Strategy | Defines long-term vision, competitive positioning, and growth pathways while aligning all departments toward unified organizational objectives |
| IT (Information Technology) | Builds and maintains digital infrastructure, protects data security, and enables automation that increases speed and accuracy across all functions |
| Customer Service | Resolves issues, gathers feedback, and maintains customer satisfaction to protect retention rates and strengthen brand reputation |
| Legal and Compliance | Ensures regulatory adherence, manages contracts, and protects the organization from legal risks that could damage operations or reputation |
| Procurement and Supply Chain | Sources materials, manages supplier relationships, and optimizes logistics to ensure resource availability while controlling costs |
1. Business Functions: Marketing as a Core of A Company
Marketing stands at the front line of business functions, creating the first connection between companies and potential customers. This business function shapes how the world sees a brand and why people choose one product over another. The scope extends beyond advertising to include customer research, competitive analysis, positioning strategy, and narrative development that differentiates offerings.
Digital transformation has expanded marketing’s complexity. Social media, search engines, content platforms, and email automation create channels requiring specialized expertise. Marketing teams now manage websites, optimize for search, create video content, and build brand communities. Each channel demands different skills and strategies.
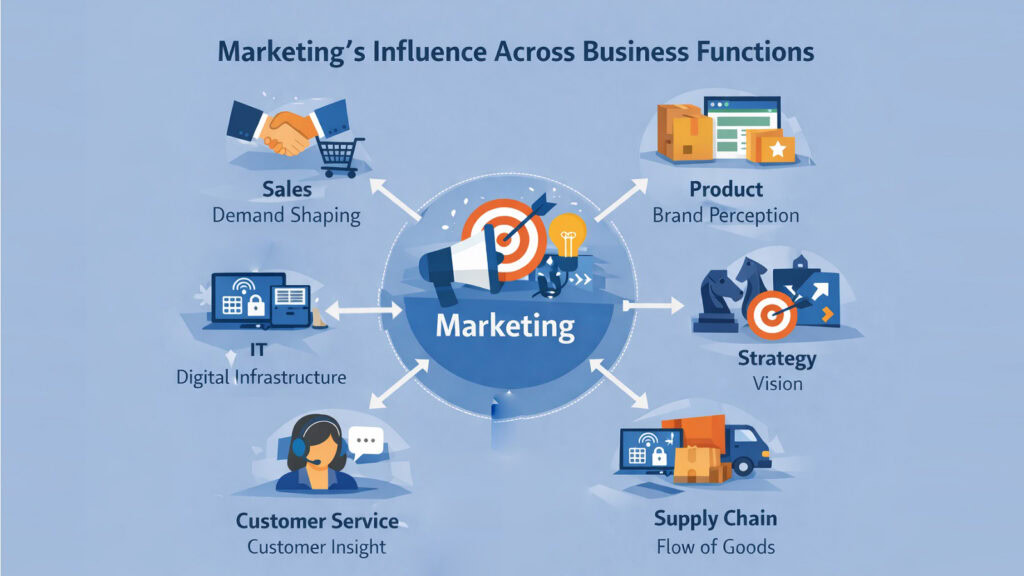
The connection between marketing and other business functions creates a multiplier effect. When marketing aligns with sales, lead quality improves. When it partners with product development, customer insights shape features markets want. This interconnection makes marketing a central nervous system touching nearly every organizational part.
Effective marketing builds assets that appreciate over time. Strong brands command loyalty surviving economic downturns. Content libraries generate traffic years after creation. Research from consulting organizations shows companies with sophisticated marketing capabilities grow revenue faster, understand customers more deeply, and adapt to market changes more quickly.
Business Functions in Marketing: Key Components and Strategic Activities
| Marketing Component | Strategic Purpose |
| Market Research | Identifies customer needs, preferences, and behaviors to inform product development and positioning decisions |
| Brand Management | Builds distinctive identity and emotional connection that differentiates offerings and commands customer loyalty |
| Content Strategy | Creates valuable information that attracts audiences, establishes expertise, and moves prospects through buying journeys |
| Digital Marketing | Leverages online channels including search, social media, and email to reach targeted audiences at scale |
| Campaign Management | Coordinates integrated promotional efforts across multiple touchpoints to drive awareness and generate qualified leads |
| Marketing Analytics | Measures performance metrics, tracks ROI, and provides data insights that optimize resource allocation and tactics |
| Product Marketing | Positions offerings against competitors, defines value propositions, and equips sales teams with effective messaging |
| Customer Segmentation | Divides markets into distinct groups to enable personalized messaging and more efficient targeting strategies |
2. Business Functions: Sales as a Revenue-Building Engine
Sales transforms marketing’s generated interest into actual revenue. This business function creates direct human connections that close deals and build lasting relationships. While marketing casts a wide net, sales works with precision, understanding individual customer situations and crafting solutions addressing specific needs.
Modern sales has evolved from transactional exchanges to consultative partnerships. Customers arrive educated after researching options independently. Sales teams must add value beyond product information by diagnosing problems, recommending solutions, and serving as trusted advisors. This consultative approach builds deeper relationships and creates expansion opportunities over time.
Sales forecasting connects this business function directly to financial planning and operations. Accurate revenue predictions help companies allocate resources wisely and manage cash flow. Companies with sophisticated forecasting spot trends early and maintain steady growth. Those without it stumble from quarter to quarter, surprised by shortfalls.
Technology has reshaped sales productivity dramatically. Customer relationship management systems track interactions, pipeline tools visualize deal progress, and automation handles routine tasks. Research from business schools shows sales teams effectively adopting technology close deals faster and achieve higher win rates than those relying on manual processes.
Business Functions in Sales: Critical Elements and Revenue Drivers
| Sales Component | Impact on Revenue Generation |
| Lead Qualification | Filters prospects based on fit and readiness to focus effort on opportunities most likely to convert |
| Sales Process Design | Standardizes steps from initial contact to close, creating predictability and enabling continuous improvement |
| Pipeline Management | Tracks deal progress, identifies bottlenecks, and ensures consistent flow of opportunities toward closure |
| Proposal Development | Crafts customized solutions that address specific customer needs and clearly articulate value propositions |
| Negotiation Strategy | Balances customer demands with business objectives to reach agreements that satisfy both parties |
| Sales Enablement | Provides tools, training, and resources that increase representative effectiveness and shorten ramp time |
| Account Management | Maintains relationships with existing customers to drive renewals, upsells, and referrals |
| Performance Metrics | Measures conversion rates, cycle times, and deal sizes to identify improvement opportunities and forecast accurately |
3. Business Functions: Human Resources as a People-Driven Department

Human Resources builds the workforce powering every other business function. This department finds talent, develops capabilities, shapes culture, and creates conditions where people do their best work. Companies with strong HR attract better candidates, retain top performers longer, and build cultures competitors struggle to replicate.
Recruitment represents the first critical intervention. Great hires multiply impact by mentoring others and raising performance standards. Poor hires drain resources through mistakes and eventual turnover. Modern HR teams use structured interviews, skills assessments, and cultural fit evaluations to improve selection accuracy.
Onboarding transforms new employees into productive contributors. Research from top universities shows employees experiencing comprehensive onboarding reach full productivity faster, report higher satisfaction, and stay with companies longer. Performance management systems align individual efforts with organizational goals through clear expectations and regular feedback.
Compensation strategies influence both attraction and retention. Competitive pay brings talent through the door while thoughtful benefits keep them engaged. Beyond base compensation, HR focuses on total rewards including recognition, career development, and workplace flexibility. Culture emerges from countless decisions about interactions and values. HR serves as primary architect and guardian of culture through hiring criteria, leadership development, and policy decisions.
Business Functions in Human Resources: Workforce Development and Organizational Strength
| HR Component | Organizational Impact |
| Talent Acquisition | Identifies, attracts, and selects candidates whose skills and values align with organizational needs and culture |
| Onboarding Programs | Accelerates new hire productivity and builds early engagement through structured introduction to role and company |
| Training and Development | Builds capabilities through formal learning, mentorship, and experiential opportunities that close skill gaps |
| Performance Management | Aligns individual goals with business objectives and provides feedback that drives continuous improvement |
| Compensation Strategy | Designs pay structures and benefit packages that attract talent and reward contributions fairly |
| Employee Relations | Resolves conflicts, addresses concerns, and maintains positive workplace environment that supports productivity |
| Succession Planning | Identifies and develops future leaders to ensure continuity and reduce risk from key employee departures |
| Culture Development | Shapes values, behaviors, and norms that define how work gets done and how people treat each other |
4. Business Functions: Operations as an Efficiency-Focused Unit
Operations keeps companies running smoothly day after day. This business function manages processes transforming inputs into outputs. Strong operations create reliability, reduce waste, and enable growth without proportional cost increases. Process design stands at the heart of operational excellence. Well-designed processes minimize handoffs and build quality checks at critical points. Poorly designed processes create confusion and delays.
Quality control protects brand reputation and customer satisfaction. Operations teams establish standards, measure performance, and intervene when deviations occur. Consistent quality separates professional organizations from amateur ones. Capacity planning balances current demand with future growth through decisions about facilities, equipment, and staffing levels.
Continuous improvement philosophies systematically identify waste, test changes, and embed learning. Organizations embracing continuous improvement see costs decline while quality rises. Supply chain integration connects operations with procurement and logistics. Products must arrive when needed. Operations teams coordinate with suppliers and optimize transportation to keep goods flowing smoothly.
Technology enables operational capabilities that seemed impossible decades ago. Automation handles repetitive tasks with perfect consistency. Sensors predict equipment failures before they occur. Analytics reveal production patterns humans would never spot. Companies leveraging these technologies gain significant advantages in speed, cost, and quality.
Business Functions in Operations: Process Excellence and Delivery Capability
| Operations Component | Efficiency and Quality Impact |
| Process Optimization | Streamlines workflows to reduce cycle times, eliminate waste, and improve resource utilization |
| Quality Assurance | Establishes standards and testing protocols that ensure consistent output and minimize defects |
| Capacity Management | Balances production capability with demand forecasts to avoid bottlenecks or excess fixed costs |
| Inventory Control | Optimizes stock levels to ensure availability while minimizing working capital tied up in materials |
| Production Planning | Schedules activities to meet delivery commitments while maximizing equipment and labor efficiency |
| Facility Management | Maintains safe, functional workspaces that support productivity and comply with regulatory requirements |
| Vendor Coordination | Manages external partners to ensure reliable supply of materials and services at competitive costs |
| Continuous Improvement | Implements systematic methods for identifying problems and testing solutions that incrementally enhance performance |
5. Business Functions: Finance as a Stability Provider
Finance provides the infrastructure supporting every business function. This department manages money flow, ensuring bills get paid, revenues get collected, and resources get allocated wisely. Companies with strong finance make better investment decisions and build stakeholder confidence attracting capital.
Budgeting translates strategy into financial terms. Finance teams work with department leaders to estimate costs, project revenues, and allocate resources. This process forces conversations about trade-offs and creates accountability. Financial reporting creates transparency enabling informed decisions. Regular statements show whether companies perform as expected and reveal which products generate profits.
Cash flow management often determines survival more than profitability. Profitable companies can fail if they run out of cash for immediate obligations. Finance teams monitor receipt and payment timing, arrange credit lines, and optimize vendor payment terms. Risk management identifies and mitigates financial health threats including currency fluctuations and economic downturns.
Investment analysis evaluates opportunities to deploy capital productively. Finance teams build models comparing expected returns against costs and risks. Tax planning minimizes obligations while maintaining compliance. Studies from accounting firms show sophisticated tax planning significantly reduces effective rates compared to companies using basic approaches.
Business Functions in Finance: Capital Management and Financial Stability
| Finance Component | Financial Health Impact |
| Budget Planning | Allocates resources across departments and initiatives based on strategic priorities and expected returns |
| Financial Reporting | Provides accurate, timely information about performance that enables informed decision-making |
| Cash Management | Ensures sufficient liquidity to meet obligations while optimizing returns on excess funds |
| Accounts Receivable | Manages customer billing and collections to accelerate cash inflows and reduce bad debt exposure |
| Cost Control | Monitors spending against budgets and identifies opportunities to reduce expenses without harming operations |
| Investment Analysis | Evaluates capital allocation opportunities using rigorous financial modeling and risk assessment |
| Risk Management | Identifies financial exposures and implements hedging strategies to protect against adverse events |
| Tax Optimization | Structures operations and transactions to minimize tax burden while maintaining full regulatory compliance |
6. Business Functions: Corporate Strategy as a Direction-Setting Unit
Corporate Strategy defines where companies head and how they plan to get there. This business function sets the course all other departments follow. Without clear strategy, organizations drift and spread resources too thin. With strong strategy, companies focus effort and build competitive advantages markets reward.
Strategic planning begins with understanding competitive landscapes. Strategy teams analyze which markets are growing, where competitors have advantages, and what trends will reshape industries. Competitive positioning determines how companies will win through price, quality, service, or niche focus. These choices influence product design, marketing messages, and investment priorities.
Resource allocation represents strategy in action. Every dollar spent either advances strategic priorities or dilutes them. Strategy provides the framework for allocation decisions and helps leaders decline attractive opportunities that do not fit. Growth strategy outlines expansion pathways through organic growth, acquisitions, or partnerships. Each approach carries different risks and timelines.
Business model innovation explores new ways to create and capture value. Subscription models create recurring revenue while platform approaches harness network effects. Scenario planning prepares organizations for multiple possible futures by developing contingency plans, transforming uncertainty from paralyzing to manageable.
Business Functions in Corporate Strategy: Direction and Competitive Advantage
| Strategy Component | Strategic Value Creation |
| Market Analysis | Examines industry dynamics, competitive forces, and emerging trends to identify opportunities and threats |
| Vision Development | Articulates long-term aspirations that inspire stakeholders and provide direction for tactical decisions |
| Competitive Positioning | Defines how the company will differentiate itself and win in chosen markets against rivals |
| Strategic Planning | Translates vision into concrete objectives, initiatives, and milestones with clear accountability |
| Portfolio Management | Evaluates business units and products to optimize resource allocation across current and future opportunities |
| Growth Strategy | Charts expansion pathways through organic development, acquisitions, partnerships, or new market entry |
| Innovation Planning | Identifies opportunities to create value through new products, services, business models, or processes |
| Performance Monitoring | Tracks progress against strategic objectives using key metrics that signal whether plans are working |
7. Business Functions: IT as The Digital Infrastructure
Information Technology builds the digital foundation enabling modern business. This business function manages systems, protects data, and creates capabilities impossible without technology. Companies viewing IT strategically see it multiply effectiveness across all departments.
Infrastructure management keeps digital machinery running reliably. Servers process transactions, networks connect offices, databases store information. IT teams monitor performance, patch vulnerabilities, and plan for disasters. Cybersecurity protects against growing threats. Hackers target customer data and financial systems while ransomware can paralyze operations overnight. IT implements layered defenses including firewalls, encryption, and access controls.
Application development builds custom software supporting unique business needs. Development teams work with stakeholders to understand requirements, design systems, and test thoroughly. Data management transforms raw information into strategic assets. IT teams build data warehouses, establish quality governance, and create analytics platforms extracting insights.
Digital transformation initiatives reimagine processes around technology capabilities. Automation eliminates manual tasks, self-service portals empower customers, and cloud computing provides unmatched scalability. Studies from industry analysts show companies waste billions on unused licenses and failed implementations, making vendor management a critical competency.
Business Functions in IT: Digital Capability and Technological Infrastructure
| IT Component | Operational and Strategic Impact |
| Systems Infrastructure | Provides reliable computing, networking, and storage capacity that supports all digital operations |
| Cybersecurity | Protects data, systems, and networks from breaches, attacks, and unauthorized access |
| Application Development | Builds custom software solutions that address specific business needs and enable competitive differentiation |
| Data Management | Organizes, governs, and analyzes information to support decision-making and reveal actionable insights |
| Cloud Services | Leverages remote computing resources for scalability, flexibility, and reduced infrastructure costs |
| Help Desk Support | Resolves technical issues quickly to minimize disruption and maintain workforce productivity |
| Technology Planning | Aligns IT investments with business strategy and anticipates future capability needs |
| Digital Automation | Implements tools that reduce manual effort, increase accuracy, and accelerate process execution |
8. Business Functions: Customer Service as a Loyalty-Building Department
Customer Service determines whether first-time buyers become loyal advocates or disappointed detractors. This business function handles moments when things go wrong or customers need help. Strong service organizations turn problems into opportunities demonstrating care and building trust.
Issue resolution represents the most visible aspect. Products fail, deliveries arrive late, features confuse users. Service teams must diagnose problems and communicate clearly. Speed matters because waiting frustrates already unhappy people. Empathy matters because customers want to feel heard and valued.
Multichannel support engages customers in their preferred modes of interaction, whether it be via phone, email, chat, or social media. Customer Service is required to handle all channels in a consistent manner. Knowledge management establishes systems that assist representatives in swiftly locating answers through documentation and troubleshooting guides.
Feedback collection transforms customer service into strategic intelligence. Complaints reveal product flaws and unmet needs. Service teams systematically capturing feedback provide invaluable insights to product and marketing teams. Self-service capabilities empower customers solving simple problems independently through help centers and chatbots. Research shows effective self-service increases satisfaction while reducing support costs. Retention initiatives proactively address situations where customers might leave by monitoring usage patterns and reaching out when engagement drops.
Business Functions in Customer Service: Support Excellence and Relationship Management
| Service Component | Customer Satisfaction Impact |
| Issue Resolution | Solves customer problems quickly and effectively to restore satisfaction and prevent churn |
| Multichannel Support | Provides consistent service quality across phone, email, chat, and social media touchpoints |
| Response Management | Ensures timely acknowledgment and resolution of customer inquiries within defined service levels |
| Knowledge Base | Maintains searchable repository of solutions that accelerates problem diagnosis and resolution |
| Customer Feedback | Gathers insights from interactions to identify improvement opportunities and measure satisfaction |
| Self-Service Tools | Enables customers to find answers independently through help centers, FAQs, and automated systems |
| Escalation Protocols | Routes complex issues to specialized resources who can provide expert assistance |
| Proactive Outreach | Contacts at-risk customers before problems escalate to prevent dissatisfaction and churn |
9. Business Functions: Legal and Compliance as a Risk-Control Department
Legal and Compliance protects companies from risks that could destroy value built over decades. This business function navigates regulatory requirements, manages contracts, and ensures operations stay within ethical and legal boundaries. Companies building strong capabilities avoid catastrophic mistakes.
Contract management governs agreements binding companies to customers, vendors, and partners. Legal teams draft contracts defining responsibilities clearly and include appropriate safeguards. They review agreements before signature to spot unfavorable terms. Regulatory compliance ensures operations meet government requirements. Industries face different regulatory regimes but all must follow labor laws and tax codes. Violations result in fines or operational restrictions.
Intellectual property protection secures innovations and brand assets. Patents prevent competitors from copying inventions while trademarks protect brand identities. Risk assessment identifies legal exposures before they materialize. Legal teams analyze scenarios and recommend mitigation strategies.
Ethics and governance establish standards for company operations. Codes of conduct define acceptable behavior while policies prevent conflicts of interest. Companies with strong governance attract investors valuing transparency. Litigation management handles legal disputes when they arise, developing defense strategies and controlling costs.
Business Functions in Legal and Compliance: Risk Mitigation and Regulatory Management
| Legal Component | Risk Protection Impact |
| Contract Drafting | Creates clear agreements that define obligations, protect interests, and minimize dispute potential |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensures operations meet legal requirements to avoid fines, penalties, and operational restrictions |
| Intellectual Property | Secures patents, trademarks, and copyrights that protect innovations and brand assets from infringement |
| Risk Assessment | Identifies potential legal exposures and recommends mitigation strategies before problems materialize |
| Corporate Governance | Establishes policies and oversight structures that ensure ethical operations and accountability |
| Dispute Resolution | Manages litigation efficiently to minimize costs, disruption, and reputational damage |
| Data Privacy | Implements controls that protect customer information and comply with privacy regulations |
| Employment Law | Ensures hiring, management, and termination practices follow labor regulations and reduce litigation risk |
10. Business Functions: Procurement and Supply Chain as a Value-Optimizing Division
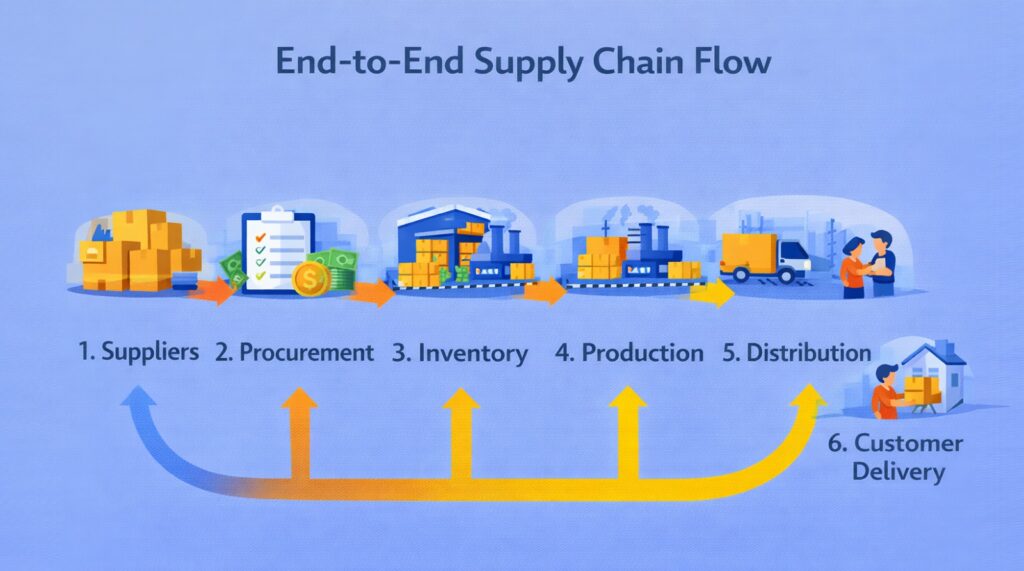
Procurement and Supply Chain ensures the right materials and services arrive at the right time and cost. This business function manages goods flow from suppliers through production to final delivery. Strong procurement organizations reduce costs, improve quality, and create resilient supply networks withstanding disruptions.
Supplier selection determines input quality and reliability. Procurement teams evaluate vendors on price, quality, delivery performance, and financial stability. The lowest bid often proves expensive when quality suffers or deliveries fail. Contract negotiation secures favorable terms while maintaining supplier relationships through volume commitments and long-term agreements.
Inventory optimization balances availability against carrying costs. Too much inventory ties up capital while too little creates stockouts halting production. Procurement teams use forecasting and just-in-time principles finding the right balance. Logistics management coordinates physical goods movement through transportation, routing, and warehousing decisions.
Risk management diversifies supply sources and prepares for disruptions. Natural disasters and political instability can sever supply chains overnight. Procurement identifies critical dependencies and develops backup suppliers. Cost reduction initiatives continuously find savings through spending analysis and volume consolidation. Consulting firm research shows sophisticated procurement functions reduce costs five to ten percent annually while maintaining quality.
Business Functions in Procurement and Supply Chain: Resource Flow and Cost Optimization
| Procurement Component | Supply Chain Value Impact |
| Supplier Selection | Identifies and qualifies vendors who provide optimal combination of quality, cost, and reliability |
| Contract Negotiation | Secures favorable pricing and terms while structuring agreements that align supplier incentives |
| Inventory Management | Optimizes stock levels to ensure material availability while minimizing working capital requirements |
| Logistics Planning | Coordinates transportation and warehousing to deliver goods efficiently at competitive costs |
| Demand Forecasting | Predicts material requirements to enable proactive ordering and prevent shortages |
| Supplier Performance | Monitors delivery, quality, and service metrics to ensure vendors meet contractual commitments |
| Cost Analysis | Identifies savings opportunities through spend consolidation, specification changes, and market intelligence |
| Risk Mitigation | Develops backup sources and contingency plans to maintain supply continuity during disruptions |
Conclusion: Why Business Functions Define Strong Modern Companies
Business functions create the architecture separating successful companies from struggling ones. Each function contributes specialized expertise while working toward shared goals. This division allows organizations to handle complexity that would overwhelm simpler structures.
Integration between business functions determines overall effectiveness. When marketing and sales align, conversion rates rise. When operations and procurement coordinate, costs decline. When strategy and finance collaborate, resources flow to the highest-return opportunities. Companies building strong connections between functions operate like well-oiled machines.
Understanding business functions helps leaders diagnose problems and identify improvements. This functional lens brings clarity to complex situations and points toward targeted solutions. The nature of business functions continues evolving as markets and technologies change, yet the fundamental need for specialized capabilities organized coherently remains constant.
Investment in strengthening business functions pays compound returns. Better recruiting improves workforce quality for years. Improved processes reduce costs permanently. These improvements accumulate, creating advantages competitors cannot easily replicate. The most successful companies view business functions as interconnected parts of a living system, building bridges between functions while maintaining integration. This balanced approach creates organizations combining specialized expertise with coordinated action. Mastering business functions positions companies for sustainable success in competitive markets.
Business Functions Integration: Cross-Functional Synergies and Organizational Strength
| Integration Point | Synergy and Value Creation |
| Marketing and Sales Alignment | Improves lead quality and conversion rates through consistent messaging and coordinated customer engagement |
| Operations and Procurement | Optimizes production efficiency through reliable material flow and strategic supplier partnerships |
| Finance and Strategy | Ensures capital allocation supports strategic priorities and resource deployment drives intended outcomes |
| HR and All Functions | Builds workforce capabilities that enable every department to execute effectively and improve continuously |
| IT and Operations | Automates processes and provides data visibility that increases efficiency and decision quality |
| Customer Service and Product | Creates feedback loops that inform development priorities and improve user experience |
| Legal and All Functions | Embeds compliance and risk management into operations to prevent problems before they occur |
| Strategy and Marketing | Translates competitive positioning into compelling customer messaging that supports market differentiation |