Table of Contents
Human Resources: Shaping Leaders of Tomorrow

Human resources is one of the key business functions. Contrary to popular narrative, Human Resources is not just about recruitment, payroll, training, or compliance. It serves a broader role in shaping the leaders of tomorrow. An organization can grow or sustain itself in this dynamic corporate world if it does not have strong leadership at its core. Without HR, organizations can not impart leadership skills to employees, and employees without leadership skills drift away in a sea of confusion and unfulfilled ambitions.
Leadership can not be attained in the short term. It is built over a long period of time. It is shaped by experience and mentorship. Human Resources stands at the center of this transformation. It creates structured paths for employees to grow with the organization. Through training, career planning, and cultural development, Human Resources ensures that leadership is not limited to those with titles. It gives employees the tools to take ownership and make decisions.
The Role of HR in Leadership Growth
| HR Function | How It Shapes Leadership |
| Training Programs | Develops leadership skills through structured learning |
| Career Path Planning | Guides employees toward leadership roles |
| Performance Management | Identifies leadership potential and nurtures growth |
| Culture Building | Encourages a leadership mindset at all levels |
| Mentorship & Coaching | Provides direct guidance from experienced leaders |
Human Resources creates an environment where leadership qualities can take root in an organization. Without HR-driven leadership programs, organizations risk becoming stagnant. Employees may have potential, but without proper direction and training, their potential will remain untapped.
HR’s role is to unleash this potential. It helps employees to upgrade their skills and build relationships with other employees, customers, and suppliers. It allows employees to take control of their own growth while taking the organization forward in an uncertain business landscape. An organization that invests in HR-led leadership development is not just preparing for the future, rather, it is actively shaping it.
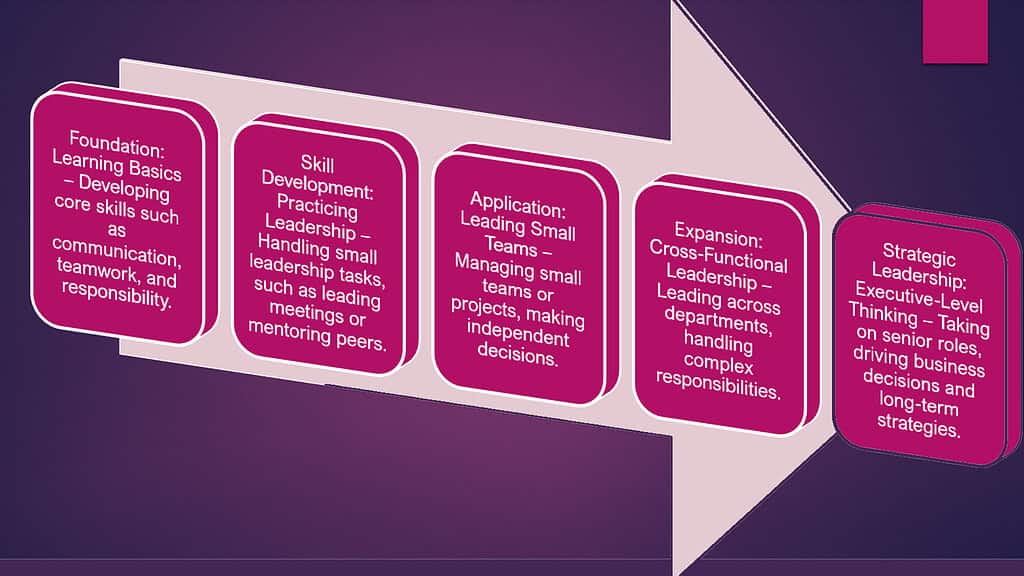
Leadership Development Path Created by Human Resources

How Human Resource Turns Employees into Leaders
1. Leadership Training Programs
Human Resources creates leadership training programs to shape employees into capable leaders. These programs go beyond mere technical skills. It focuses on various core aspects of leadership such as decision-making, team-building, adaptability, resilience, problem-solving, etc. Employees participate in workshops where they face real-world challenges. They learn how to navigate uncertainty and take responsibility.
Human Resources designs training programs that mix structured lessons with interactive experiences. This amalgamation of theory and practical experience develops leadership instincts in employees. Various interactive trainings, such as role-playing exercises, business simulations, and coaching sessions, teach employees to lead under pressure. Through these initiatives, HR creates confidence and foresight in employees. It prepares them for higher responsibilities.
Key Aspects of Leadership Training Programs
| Aspect | Description |
| Real-World Scenarios | Employees tackle simulated business crises to build decision-making skills. |
| Strategic Thinking | Training includes case studies that sharpen long-term planning abilities |
| Crisis Management | Employees learn to handle high-pressure situations with composure. |
| Mentorship | Senior leaders provide guidance to help employees transition into leadership roles. |
| Communication Skills | Programs focus on clear, persuasive, and empathetic leadership communication. |
Various leadership programs structured by Human Resources can enable employees to shift from task-driven workers to forward-thinking leaders. HR integrates mentorship into these programs, ensuring employees receive personal guidance. Interestingly, in this mentorship exercise, both mentors and mentees benefit. While mentees learn valuable skills and gain real-life experiences, the mentors sharpen their leadership and team-building skills.
Learning happens not just in classrooms but in real-world settings. Through various cross-functional projects, employees learn empathy and experience leadership firsthand. They learn to balance authority with humility. They acquire skills to manage teams and inspire action. These programs infuse a sense of ownership among employees. They can turn employees into decision-makers who ultimately drive innovation and bring changes.
Human Resources Leadership Training Structure
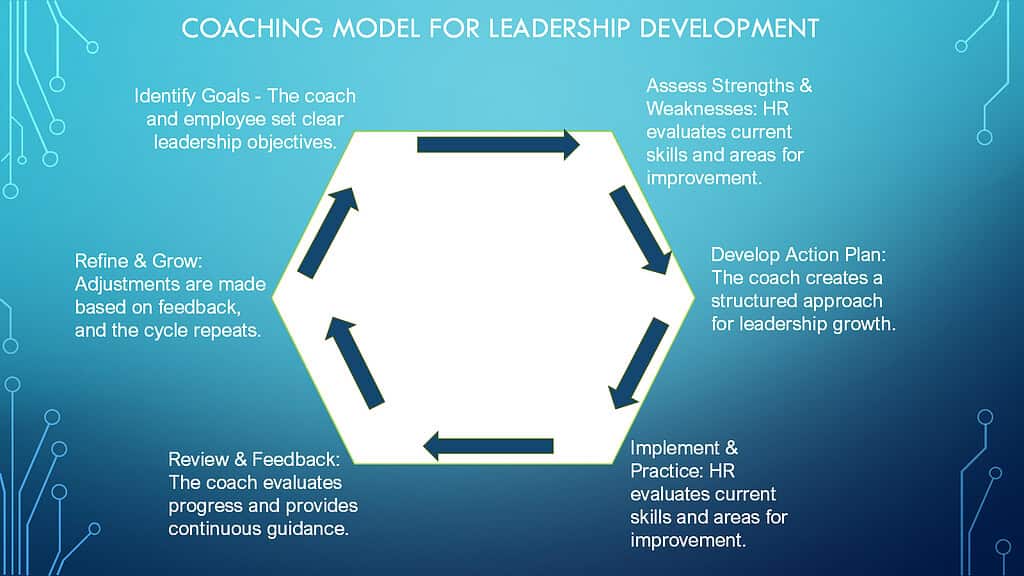
2. Mentorship and Coaching Initiatives
Human Resources instills leadership qualities in employees by creating strong mentorship and coaching programs. These programs are created by cross-functional team leaders who have both domain knowledge and practical experience. Human Resources pairs employees with seasoned leaders and professionals who have navigated crises, built teams, and made tough choices. Employees learn from these experienced mentors who transfer their skills and experience.
However, a mentor does more than just transfer skills and experience. They build a working relationship with mentees and show them how to build and lead a team. These relationships are not just about theories. They are about real conversations, shared struggles, and practical wisdom. Employees watch, listen, and slowly learn to think and act like leaders. Through this guidance, they understand the weight of responsibility. They learn the complicated art of decision-making.
Key Aspects of Mentorship and Coaching
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Experience Transfer | Employees gain real-world knowledge from seasoned leaders. |
| Decision-Making Growth | Mentors help employees refine judgment and strategic thinking. |
| Communication Development | Coaching sharpens clarity, persuasion, and listening skills. |
| Conflict Resolution | Employees learn to handle workplace disputes with tact. |
| Career Guidance | Mentors provide direction, helping employees plan long-term success. |
Mentorship is not a one-time event. It is a slow and steady process that changes how employees see themselves. Through mentorship, a once-hesitant employee gains confidence and a skilled employee learns patience. Through coaching, HR ensures that leadership is not just about authority but about vision and trust. The right mentor teaches by example, showing that leadership is as much about listening as it is about speaking.
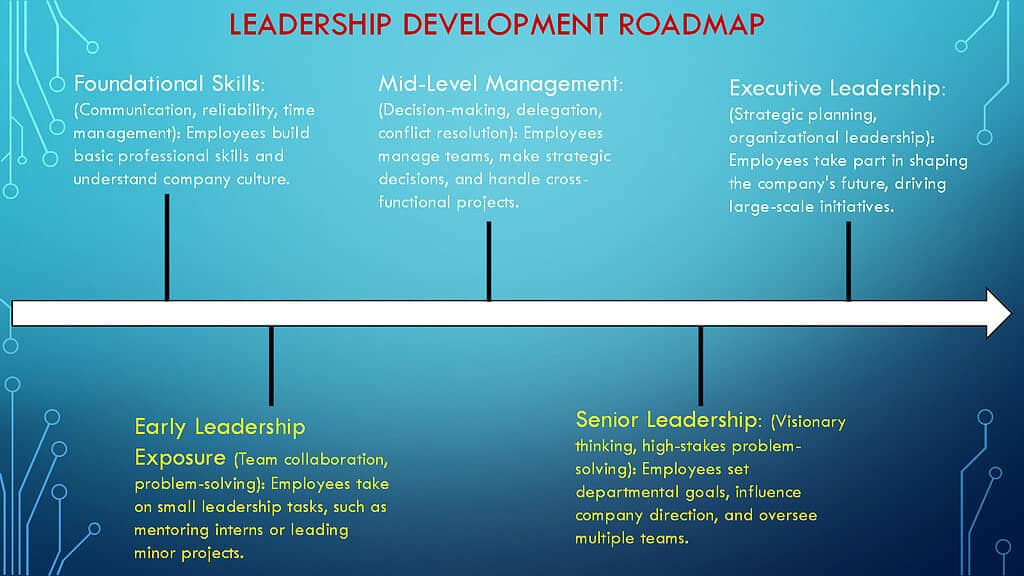
3. Strategic Job Rotations and Cross-Training
One of the impactful methods that Human Resources follows to instill leadership qualities in employees is by shifting them through different departments and roles. Each change teaches a new skill and broadens experiences of the employees. It also builds adaptability and problem-solving skills.
When a marketing executive who works in operations learns to see the overall picture. A finance specialist who spends time in customer service gains empathy for both the customers and for frontline colleagues. This exposure prepares employees for leadership by making them resourceful and agile. It also deepens their strategic thinking. Leaders cannot afford to be specialists in only one area. They need a well-rounded understanding of how different departments function and interact.
Benefits of Job Rotation for Leadership Growth
| Benefit | How It Helps Leadership Development |
|---|---|
| Adaptability | Employees learn to adjust to new environments. |
| Problem-Solving | Exposure to different challenges strengthens critical thinking. |
| Strategic Thinking | Employees develop a broader perspective of business functions. |
| Decision-Making | Rotations teach how different choices impact the company. |
| Communication | Employees learn to interact with diverse teams. |
Job rotations need careful planning. Moving an employee too quickly can cause stress. Keeping them in one place for too long leads to stagnation. A structured program with defined objectives is necessary. Employees should rotate through key departments that align with future leadership goals.
4. Encouraging Decision-Making and Ownership
Human Resources nurtures leaders by giving them responsibility. Employees often will find themselves in a situation when they have to make quick and correct decisions, especially when they are elevated to mid-level or senior-level positions. Decision-making skills can only be gained through practical experiences. Human Resources provides them with the opportunity to make their own decisions.
At first, decisions may not have to be big ones. Small choices can prepare employees for bigger ones. A junior manager deciding how to allocate a budget learns financial discipline. A team lead handling a client issue builds negotiation skills. HR pushes employees to take ownership of their work. Leadership is not about following instructions. It is about making decisions when there are no clear answers.
Impact of Decision-Making on Leadership Growth
| Encouraged Behavior | Leadership Skill Developed |
|---|---|
| Taking Initiative | Builds confidence and accountability. |
| Risk Assessment | Teaches how to weigh options before acting. |
| Problem-Solving | Strengthens ability to handle challenges. |
| Communication | Develops a persuasive and clear expression of ideas. |
| Responsibility | Prepares employees for higher-stakes decisions. |
Not all decisions are equal. Some require experience, while others can be handled early. HR should create a structure where employees gradually take on more responsibility. Assigning projects where they must own the outcome helps build their leadership instincts.

5. Performance Feedback and Leadership Development Plans
HR shapes future leaders by guiding employees with structured feedback. Leadership is not something people stumble into. It requires a roadmap. Without clear direction, employees remain in their comfort zones. A well-planned feedback system highlights strengths and identifies gaps. A promising employee might be a strong strategist but struggle with team communication. Another might be great at execution but weak in long-term planning. HR must ensure employees receive honest, actionable feedback.
| Feedback Type | Leadership Skill Strengthened |
|---|---|
| Constructive Criticism | Helps employees identify and improve weaknesses. |
| Strength-Based Feedback | Reinforces confidence and expertise. |
| Real-Time Feedback | Encourages quick adaptation and learning. |
| 360-Degree Reviews | Provides a full perspective from peers, managers, and subordinates. |
| Leadership Roadmaps | Sets clear goals for professional growth. |
6. Cultivating a Leadership-Driven Culture
Creating a workplace where leadership qualities are both valued and encouraged is essential for organizational success. When employees are motivated to take initiative and lead, even without formal titles, it fosters an environment of proactive problem-solving and innovation. Human Resources (HR) plays a pivotal role in embedding this culture by implementing programs that recognize and reward leadership behaviors across all levels of the organization.
Impact of Leadership Development on Employee Engagement and Performance
| Organization | Initiative | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| General Organizations | Investment in employee development programs | 94% of employees would stay longer if companies invested in their careers |
| General Organizations | Leadership development as a top priority for HR leaders in 2025 | 60% of HR leaders focus on improving management effectiveness |
| General Organizations | Effective leadership behaviors and organizational design | Significant impact on employee well-being and reduction in burnout |
| General Organizations | Leadership development programs | Substantial boost in personal growth and well-being when implemented correctly |
The data above underscores the tangible benefits that leadership development initiatives can have on employee engagement and organizational performance. Companies that prioritize leadership training not only enhance employee satisfaction but also drive innovation and efficiency. These outcomes highlight the critical role of Human Resources in cultivating a leadership-driven culture that motivates employees to take initiative and lead, regardless of formal titles.
Key Aspects of a Leadership-Driven Culture
| Aspect | Description | Impact on Employees | Impact on Organization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encouraging Initiative | Employees are empowered to make decisions and take ownership of tasks. | Increases confidence, problem-solving skills, and engagement. | Leads to innovation, faster decision-making, and adaptability. |
| Transparent Communication | Open dialogue between leadership and employees fosters trust. | Boosts morale and teamwork. | Enhances collaboration and reduces misunderstandings. |
| Recognition & Reward | Encourages leadership behaviors and motivation. | Retains talent and builds a strong leadership pipeline. | |
| Collaboration Over Hierarchy | Leadership is encouraged at all levels, not just at the top. | Empowers employees to take responsibility. | Improves agility and responsiveness to challenges. |
| Continuous Learning | Leadership training, mentorship, and skill-building programs. | Enhances career growth and self-improvement. | Creates a culture of knowledge-sharing and development. |
A leadership-driven culture thrives when employees feel valued, heard, and empowered to take responsibility. HR fosters this by shaping policies and practices that encourage leadership at every level. Organizations that cultivate such a culture see long-term benefits, including higher engagement, better retention, and improved business performance.
Future of Leadership Development in Human Resources

As organizations navigate an ever-evolving business landscape, the role of Human Resources (HR) in developing future leaders has become increasingly vital. The Human Resources department is uniquely positioned to identify, nurture, and promote leadership qualities within the workforce. It can ensure that organizations remain resilient and competitive. Organizations can enhance individual performance and drive overall organizational success by prioritizing leadership development.
IBM has established a framework for leadership development, implementing various programs. These programs aim at nurturing talent and fostering innovation. The table below outlines some of these initiatives, their descriptions, and reported outcomes.
Overview of IBM’s Leadership Development Programs and Outcomes
| Program/Initiative | Description | Reported Outcomestive |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Blue Internship Program | A 12-week internship that pairs technical and business interns to work on high-impact projects, emphasizing innovation and leadership development. | Participants gain skills in design thinking, agile methodologies, and professional advocacy, contributing to their early career development. |
| General Management Leadership Development Program (GMLDP) | Recruiting from top MBA programs for an accelerated path to general management positions, involving rotations across various business units to develop a comprehensive understanding of IBM’s operations. | Offers exclusive networking, mentoring, and coaching opportunities with senior executives, preparing participants for leadership roles within the company. |
| Basic Blue for New Leaders (BBNL) | A program initiated in 1999, focusing on developing essential leadership skills for new managers through a globally integrated curriculum. | Recognized as a competitive advantage, with continuous updates to maintain quality and effectiveness since its inception. |
| Transformational Leadership Framework (TLF) | A system designed to identify and develop transformational leaders who are collaborative and outcomes-oriented, aligning leadership development with strategic goals. | Emphasizes developing 11 key skills and behaviors of exceptional leaders, utilizing technology and continuous learning methodologies. |
IBM’s leadership development programs provide a structured approach to cultivating future leaders. It integrates mentorship, experiential learning, and strategic career progression. The table highlights key initiatives such as the General Management Leadership Development Program and the Transformational Leadership Framework. These programs reflect broader industry trends where Human Resources departments play a central role in leadership growth, aligning with the article’s core argument.
As organizations prioritize structured development plans, IBM’s model offers insight into how companies can systematically nurture leadership qualities. The data reinforces the fact that Human Resource-driven leadership initiatives create a competitive edge, shaping employees into strategic decision-makers.
Leadership development programs are beneficial not only to big corporations, but Small and Mid-size enterprises (SME) can also benefit from them. The UK’s “Help to Grow” scheme exemplifies a successful initiative aimed at bolstering leadership and management skills among SME leaders. The table below provides an overview of this program, its structure, and reported outcomes:
Overview of the UK’s “Help to Grow” Management Training Scheme
| Program Component | Description | Reported Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Program Duration and Structure | 12-week MBA-style course offering 50 hours of training and mentoring support. | Over 10,000 SME owner-managers enrolled since its launch in June 2021. |
| Participant Cost and Subsidy | Over 10,000 SME owner-managers have enrolled since its launch in June 2021. | 91% of participants would recommend the program; 62% reported benefits to revenue growth. |
| Target Audience | SME leaders from businesses with 5-249 employees across various sectors | Aims to train 30,000 business leaders by March 2026, contributing to enhanced productivity and leadership skills. |
The “Help to Grow” scheme demonstrates the tangible benefits of structured leadership development in the SME sector. By providing affordable, high-quality training, the program has garnered positive feedback from participants, with a significant majority recommending it to peers.
Leadership is not just a title—it’s vision, responsibility, and influence. Human Resources shapes future leaders through training, mentorship, and a strong workplace culture. As businesses evolve, investing in leadership development remains essential for long-term success.




