Table of Contents
Introduction: Modern Technology and the Foundations of the Digital Age
Modern Technology refers to the broad collection of tools, systems, and innovations that define how people live, work, and connect with one another today. It is not a single invention but rather a living ecosystem of devices, software, networks, and ideas that work together. From the phone in your pocket to the cloud servers storing your photos, every piece of this ecosystem plays a quiet but essential role.
The reach of Modern Technology extends far beyond gadgets. It touches the way businesses operate, the way governments deliver services, and the way individuals express themselves. Communication has shifted from letters to instant messages, and entertainment has moved from theaters to streaming on demand. Society has been reshaped by these changes in ways both visible and subtle.
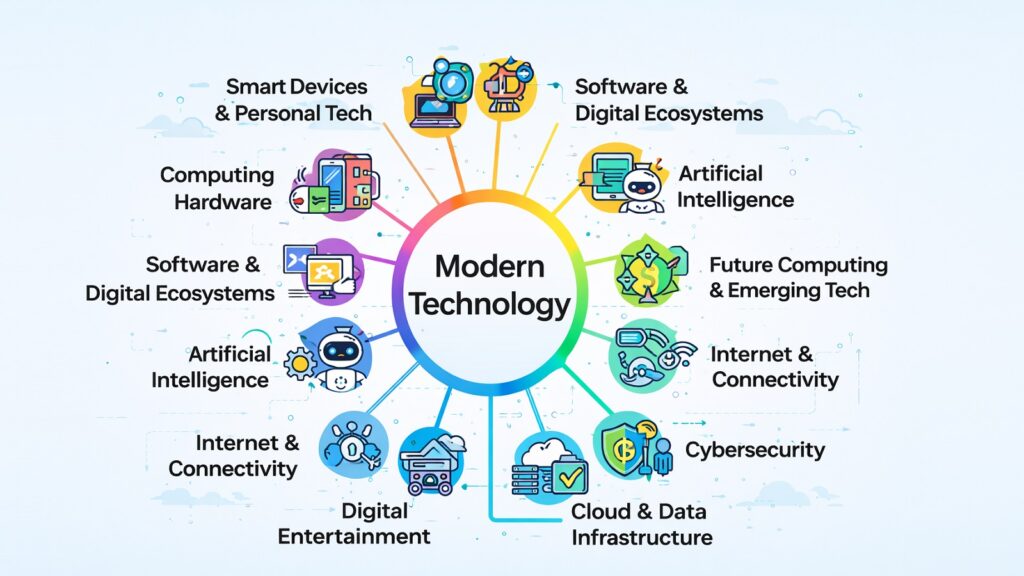
To understand Modern Technology in a meaningful way, it helps to break it into manageable parts. This article identifies twelve pillars that together form the structural map of the tech ecosystem. Each pillar reveals a different layer of how technology functions and why it matters. Some are about the physical world, like hardware and robotics. Others are about the invisible world, like software and cloud infrastructure. Together, they offer a grounded picture of where things stand today.
Table 1: The 12 Pillars of Modern Technology at a Glance
| Pillar | Role in the Tech Ecosystem |
| Smart Devices & Personal Tech | Includes smartphones, laptops, wearables, and tablets used daily. |
| Computing Hardware | CPUs, GPUs, and RAM that power device performance. |
| Software & Digital Ecosystems | Operating systems and platform ecosystems from Apple, Google, and Microsoft. |
| Artificial Intelligence | Machine learning and generative AI reshaping work and daily life. |
| Future Computing & Emerging Tech | Quantum computing, AR/VR, and next-generation interfaces. |
| Internet & Connectivity | Wi-Fi, 5G, fiber, and satellite networks keeping the digital world connected. |
| Cybersecurity & Digital Safety | Tools and practices protecting data, identity, and devices online. |
| Technology & Society | Cultural, ethical, and social effects of Modern Technology on daily life. |
| Digital Entertainment | Gaming, streaming, music, and content creation powered by digital tools. |
| Cloud Computing & Data Infrastructure | Remote servers and distributed systems behind most digital services. |
| Robotics & Automation | Machines and autonomous systems blending AI with physical hardware. |
| Green Tech & Sustainable Technology | Clean energy innovations and responsible tech lifecycle practices. |
1. Modern Technology: Smart Devices & Personal Technology
Smart devices and personal technology represent the most visible layer of Modern Technology. These are the products people interact with every single day. A smartphone serves as a communication hub, a camera, a navigation tool, and an entertainment center at once. Laptops and tablets power remote work and learning. Smartwatches track health metrics and deliver notifications at a glance.
The range of personal devices has expanded significantly over the past decade. E-readers offer a distraction-free reading experience. Smart speakers respond to voice commands and control home devices. Televisions have evolved into connected platforms that stream content and integrate with smart home systems.
What makes this pillar so important is its role as the entry point into the broader tech ecosystem. Most people first encounter Modern Technology through a device they hold or wear. The quality of hardware, the design of software, the speed of network connections — all of it is experienced through personal devices first.
Table 2: Smart Devices in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Device Category | Key Fact or Market Insight |
| Smartphones | Over 6.8 billion smartphone users globally as of 2024, per Ericsson. |
| Laptops | Global laptop market valued at roughly $340 billion in 2023, per Grand View Research. |
| Smartwatches | Apple Watch held about 30% of the global smartwatch market in 2023. |
| Tablets | iPad holds over 50% of the tablet market share historically. |
| Smart Speakers | Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant lead the smart speaker market globally. |
| Wearable Fitness Trackers | Wearable device market projected to reach $186 billion by 2030, per Allied Market Research. |
| E-Readers | Amazon Kindle dominates the e-reader category with over 85% market share. |
| Smart TVs | Over 70% of TV shipments globally in 2023 were smart TVs, per IDC. |
2. Modern Technology: Computing Hardware & Performance
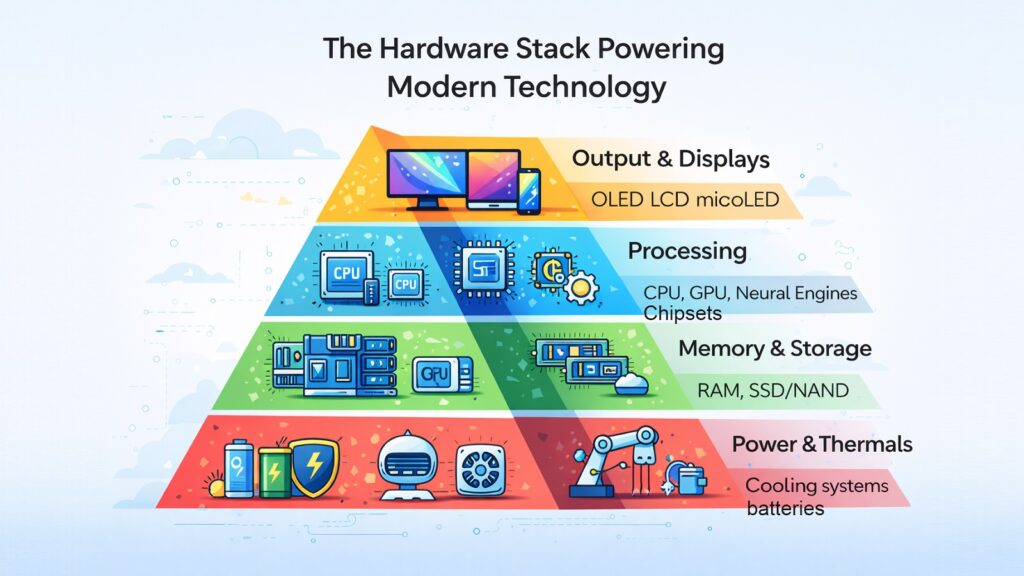
Behind every device that runs smoothly lies a set of physical components working in tandem. Computing hardware is the foundation on which all of Modern Technology is built. The processor, often called the CPU, executes instructions and determines how fast a device can think. The graphics processing unit, or GPU, handles visual tasks and has become increasingly important for AI workloads. RAM provides short-term memory so that multiple tasks can run without slowing down.
Storage technology has also changed dramatically. Solid-state drives have largely replaced traditional hard drives in laptops and desktops because they are faster and more durable. Display technology has moved toward higher resolutions and faster refresh rates. Chipset design has become more energy-efficient, which directly affects battery life.
Hardware performance matters because it sets the ceiling for everything else. No matter how well software is written, it can only do what the underlying hardware allows. The race to build better processors and more efficient chips is one of the defining competitions in the technology industry right now.
Table 3: Computing Hardware in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Hardware Component | Key Fact or Industry Trend |
| CPU (Processor) | Apple’s M-series and AMD/Intel processors set performance benchmarks for PCs. |
| GPU (Graphics Unit) | NVIDIA holds over 80% of the discrete GPU market as of 2024. |
| RAM | DDR5 memory is now standard in high-end PCs, offering double the bandwidth of DDR4. |
| SSD Storage | Global SSD shipments surpassed HDD shipments in units for the first time in 2022, per IDC. |
| Displays | OLED adoption in smartphones reached about 60% of global shipments in 2023. |
| Chipset Design | TSMC’s 3-nanometer process entered mass production in 2022, enabling smaller chips. |
| Thermal Management | Vapor chamber cooling is now standard in high-performance laptops and gaming devices. |
| System-on-Chip (SoC) | Mobile SoCs from Qualcomm, Apple, and MediaTek power most smartphones worldwide. |
3. Modern Technology: Software & Digital Ecosystems
Software is the invisible layer that gives hardware its purpose. Operating systems like Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android manage every interaction between a user and a device. Productivity tools like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace have become the daily rhythm of office work. Creative software from companies like Adobe enables designers and video editors to produce professional-quality work on consumer devices.
Digital ecosystems add another dimension to this picture. Apple, Google, and Microsoft have each built interconnected networks of devices, services, and apps that work most seamlessly within their own platforms. When you use an iPhone, an iPad, and a Mac together, the data flows between them with minimal friction. This is what an ecosystem means in practice.
The relationship between software and ecosystems is central to understanding how Modern Technology functions in real life. People do not just buy devices; they join systems. The software that runs on those devices and the services that connect them shape habits and workflows in ways that become deeply personal over time.
Table 4: Software & Ecosystems in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Software or Ecosystem | Key Fact or Market Data |
| Windows | Windows 10 and 11 combined hold over 72% of the global desktop OS market, per Statista. |
| macOS | macOS runs on roughly 15% of global desktops, with strong presence in creative industries. |
| Microsoft 365 | Over 400 million commercial users subscribe to Microsoft 365 as of 2024. |
| Google Workspace | Google Workspace serves over 3 billion users through Gmail, Drive, and Docs. |
| Adobe Creative Suite | Adobe holds over 85% market share in professional creative software. |
| iOS | iOS runs on over 2 billion active iPhones globally, per Apple’s 2023 earnings call. |
| Android | Android holds about 72% of the global mobile OS market share, per Statista. |
| App Stores | The global app economy generated over $180 billion in consumer spending in 2023, per data.ai. |
4. Modern Technology: Artificial Intelligence
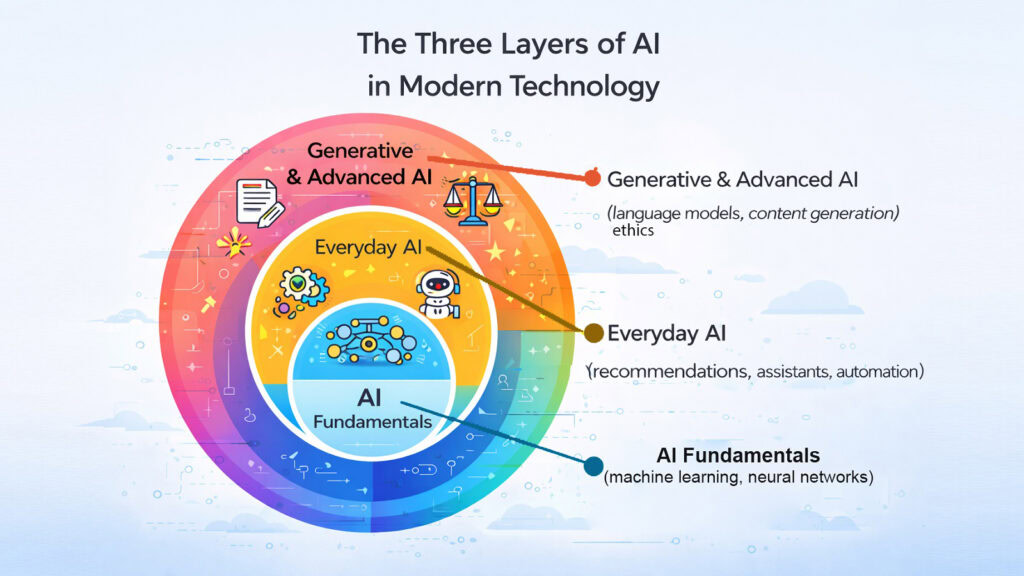
Artificial Intelligence has become one of the defining forces of Modern Technology. It is no longer a topic reserved for research labs or science fiction. AI now appears in the daily lives of billions of people, often without them realizing it. Recommendation algorithms decide what videos you watch next. Virtual assistants respond to spoken questions. Email filters catch spam before it reaches your inbox.
The emergence of generative AI has shifted public awareness significantly. Tools that can write text, generate images, and produce code have moved AI into something people interact with directly. Machine learning, the process by which systems improve through experience, underpins most of these advances.
Alongside the excitement, there are important questions about AI ethics, transparency, and accountability. How decisions are made by AI systems, who benefits from them, and how biases are corrected — these are conversations that society is actively having. Understanding AI as both a powerful tool and a subject requiring careful stewardship is essential to navigating Modern Technology responsibly.
Table 5: Artificial Intelligence in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| AI Topic | Key Fact or Data Point |
| Generative AI | ChatGPT reached 100 million users in two months after launch — the fastest app adoption at the time. |
| Machine Learning | ML models power most recommendation engines, including Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify. |
| Natural Language Processing | Google Translate processes over 100 billion characters of text per day using NLP. |
| Computer Vision | AI-based facial recognition is used in over 50 countries for law enforcement and consumer devices. |
| AI Assistants | Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri collectively reach over 2 billion devices worldwide. |
| AI in Healthcare | IBM Watson and Google DeepMind have shown AI applications in drug discovery and medical imaging. |
| AI Ethics | The EU AI Act, finalized in 2024, is the world’s first comprehensive legal framework for AI. |
| AI Investment | Global AI investment reached about $91.9 billion in 2022, per the Stanford AI Index Report. |
5. Modern Technology: The Future of Computing & Emerging Technologies
The future of computing is not a single destination but a wide landscape of technologies being developed in parallel. Quantum computing has the potential to solve certain problems that classical computers cannot handle in any reasonable timeframe. While quantum machines are still in early stages, companies like IBM and Google have made measurable progress in building functional quantum processors.
Beyond quantum, other emerging technologies are reshaping what computing can do. Neuromorphic chips mimic the way the brain processes information, making AI tasks far more energy-efficient. Photonic computing uses light instead of electricity to move data. Augmented and virtual reality are creating new ways for people to interact with digital information in physical space.
These technologies are still developing, but they represent the next era of Modern Technology. They will likely change not just how computers work but how people experience the digital world. The companies and researchers leading this work are investing heavily in bringing these innovations to practical use.
Table 6: Future Computing in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Emerging Technology | Current Status or Key Milestone |
| Quantum Computing | IBM’s 1,121-qubit Condor processor was unveiled in December 2023. |
| Neuromorphic Chips | Intel’s Loihi 2 chip processes information in a brain-inspired way for low-power AI. |
| Photonic Computing | Startups like Lightmatter are developing photonic processors for faster data transfer. |
| Exascale Computing | The Frontier supercomputer at ORNL became the first exascale machine in 2022. |
| Augmented Reality | Apple Vision Pro, launched in early 2024, represents a new spatial computing generation. |
| Virtual Reality | Meta’s Quest 3 headset sold millions of units, keeping Meta dominant in consumer VR. |
| Advanced Sensors | LiDAR sensors are now used in smartphones, autonomous vehicles, and robotics. |
| Next-Gen Interfaces | Neuralink and others are researching brain-computer interfaces for neural-to-digital connections. |
6. Modern Technology: Internet, Connectivity & Networks
Modern Technology depends on global connectivity the way a body depends on its circulatory system. Without networks, devices would be isolated tools rather than connected platforms. The internet is the invisible backbone that enables cloud services, AI processing, video streaming, and remote collaboration — activities that people take for granted every day.
Wi-Fi technology has progressed rapidly through generations. Wi-Fi 6 and 6E brought faster speeds and better handling of many simultaneous connections. Wi-Fi 7 is expected to push those boundaries further. On the cellular side, 5G networks have been rolling out across major cities worldwide, offering speed and latency improvements that benefit mobile apps and video calls. Fiber optic connections continue to offer the fastest and most reliable broadband available.
Satellite internet has entered the conversation in a meaningful way. Services like Starlink have brought connectivity to regions that traditional infrastructure could not reach. The Internet of Things connects billions of small sensors using dedicated network protocols. Together, these technologies form the connectivity layer that makes Modern Technology possible.
Table 7: Internet & Connectivity in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Network Technology | Key Fact or Global Metric |
| Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) | Wi-Fi 6 offers up to 9.6 Gbps throughput and is now standard in consumer routers. |
| Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) | Wi-Fi 7 is expected to offer speeds up to 46 Gbps, with availability by 2025. |
| 5G Networks | Over 70 countries had commercially launched 5G by end of 2023, per GSMA. |
| Fiber Optic Internet | Global fiber connections reached over 1.3 billion subscribers by mid-2023, per OECD. |
| Satellite Internet | SpaceX Starlink had over 2 million active subscribers by early 2024. |
| IoT Networks | An estimated 15 billion IoT devices were connected worldwide by 2023, per Statista. |
| 6G Research | Major telecoms and universities are researching 6G, targeting deployment around 2030. |
| Broadband Access | The UN reported about 5.5 billion people had internet access globally in 2023. |
7. Modern Technology: Cybersecurity & Digital Safety
Every benefit that Modern Technology brings also comes with a set of risks. Cybersecurity is the discipline that works to protect people, organizations, and governments from those risks. When personal data is stored online, it becomes a target. When devices are connected to networks, they become potential entry points for malicious actors.
Common threats include phishing, where attackers trick people into revealing passwords through deceptive emails. Malware can damage devices or steal data silently. Data breaches at major companies have exposed billions of records over the past decade. Identity theft has become a serious concern as more personal information moves online.
Digital hygiene — the set of practices that keeps accounts and devices secure — is one of the most practical skills a person can develop today. Using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and being cautious with unsolicited links are steps that significantly reduce risk. Cybersecurity underpins trust in Modern Technology, and without it, the ecosystem would be far less reliable.
Table 8: Cybersecurity in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Threat or Practice | Key Statistic or Finding |
| Phishing Attacks | Phishing accounted for roughly 16% of all data breaches in 2023, per Verizon DBIR. |
| Ransomware | Ransomware attacks cost businesses an estimated $20 billion globally in 2020. |
| Data Breaches | Over 8 billion records were exposed in data breaches in 2023. |
| Two-Factor Authentication | Accounts with 2FA enabled are 99.9% less likely to be compromised, per Microsoft. |
| Identity Theft | The FTC received over 1.1 million identity theft reports in the US in 2023. |
| Zero-Day Vulnerabilities | Google’s Project Zero documented over 60 zero-day exploits actively used in 2022. |
| Cybersecurity Spending | Global cybersecurity spending reached about $188 billion in 2023, per Gartner. |
| Password Breaches | Have I Been Pwned has indexed over 12 billion breached passwords as of 2024. |
8. Modern Technology: Technology & Society
Technology does not exist in a vacuum. It shapes culture, communication, work, and social norms in ways that are often gradual and hard to notice until deeply embedded. The way people form relationships and consume information has been fundamentally altered by digital platforms. Social media has created new forms of public discourse that did not exist a generation ago.
Screen time has become a topic of widespread concern, especially regarding children and adolescents. Research from institutions like the American Psychological Association has explored the relationship between heavy device use and mental health, though the findings remain nuanced. The question is not simply whether technology is good or bad but how it can be used with intention.
Digital access has also become a matter of equity. Not everyone has equal access to reliable internet or modern devices. This gap has real consequences for education, employment, and civic participation. The ethical dimensions of Modern Technology — including transparency and fairness — are becoming central to how societies govern the digital world.
Table 9: Technology & Society in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Social Dimension | Key Fact or Research Finding |
| Social Media Users | Over 4.7 billion people used social media globally in 2023, per DataReportal. |
| Screen Time | The average American adult spent roughly 7 hours per day on screens in 2023. |
| Digital Divide | About 2.7 billion people still lacked internet access in 2023, per ITU. |
| Remote Work | About 12% of full-time US workers were fully remote in 2023, per Stanford research. |
| Online Education | Global e-learning market revenue reached about $107 billion in 2023. |
| Digital Literacy | The OECD found 36% of adults in member countries had low digital literacy skills in 2022. |
| AI Regulation | Over 40 countries had introduced or were developing AI governance frameworks by early 2024. |
| Platform Moderation | Facebook removed over 30 billion pieces of harmful content in 2022 via automated review. |
9. Modern Technology: Digital Entertainment
Entertainment has been one of the areas most visibly transformed by Modern Technology. Streaming platforms have replaced physical media as the dominant way people consume movies, television shows, and music. Gaming has evolved from a niche hobby into a global industry that generates more revenue than film and music combined. Video content creation has become accessible to anyone with a smartphone and an internet connection.
The tools behind digital entertainment have also become remarkably powerful. Video effects software can create photorealistic scenes that would have required enormous budgets a decade ago. Music production apps allow hobbyists to record and mix tracks at home. Podcasting has given new voices a way to reach audiences without traditional media gatekeepers.
What makes digital entertainment a core pillar of Modern Technology is its scale and cultural role. The way stories are told and how people spend their leisure time are shaped by digital platforms. Entertainment is not separate from the tech ecosystem — it is one of the primary reasons the ecosystem exists.
Table 10: Digital Entertainment in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Entertainment Segment | Key Fact or Market Data |
| Streaming Video | Netflix, Disney+, and others combined reached over 1 billion subscriptions globally by 2023. |
| Music Streaming | Spotify had over 600 million total users, including 236 million premium subscribers, by late 2023. |
| Gaming Industry | The global gaming market generated about $182 billion in revenue in 2023, per Newzoo. |
| Video Content | YouTube reported over 500 hours of video uploaded every minute as of 2023. |
| Podcasting | Over 100 million Americans listened to podcasts regularly in 2023, per Edison Research. |
| Esports | The global esports audience reached about 577 million viewers in 2023, per Newzoo. |
| VFX in Film | Films using significant visual effects dominated the top box office earners in 2023. |
| Creator Economy | The global creator economy was estimated at over $100 billion in 2023, per Goldman Sachs. |
10. Modern Technology: Cloud Computing & Data Infrastructure
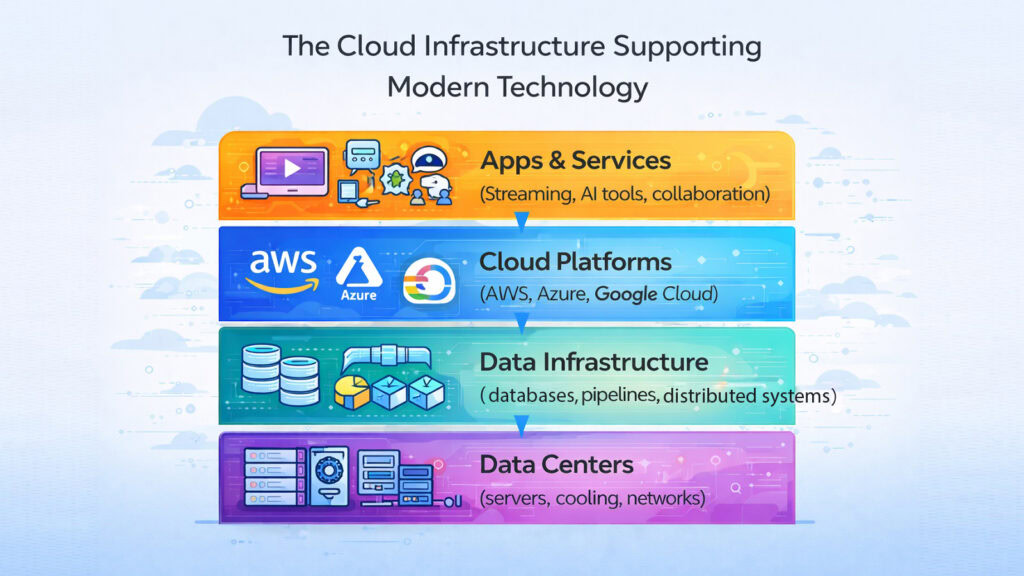
Most of what people do online is powered by servers they never see. Cloud computing is the practice of delivering computing resources — storage, processing power, and software — over the internet rather than through local hardware. When you save a photo to iCloud or Google Photos, it travels to a data center in another city or country. When a business runs its website, the hosting server is likely operated by a major cloud provider.
Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are the three largest cloud providers. Together they handle a significant portion of global internet traffic. These platforms support streaming video, AI model training, and corporate databases. Virtualization allows a single physical server to run many virtual machines, making cloud infrastructure flexible and cost-efficient.
Data pipelines — the systems that move and process information at scale — enable the real-time experiences that users expect. Cloud computing is not glamorous, but it is arguably the most important invisible layer of Modern Technology. Without it, most digital services would not exist.
Table 11: Cloud Computing in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Cloud or Infrastructure Topic | Key Fact or Market Insight |
| AWS | AWS held about 31% of the global cloud infrastructure market in 2023, per Synergy Research. |
| Microsoft Azure | Azure held roughly 24% of the global cloud market in 2023, per Synergy Research. |
| Google Cloud | Google Cloud held about 11% of the global cloud market in 2023, per Synergy Research. |
| Cloud Market Size | The global cloud computing market was valued at about $653 billion in 2023, per Gartner. |
| Data Centers | There were over 8,000 hyperscale and large data centers worldwide by 2023. |
| Virtualization | VMware, now part of Broadcom, has been the dominant virtualization platform for enterprise IT. |
| Cloud Storage | Major providers like AWS S3 store exabytes of data, serving millions of businesses. |
| Edge Computing | Edge computing is growing as organizations seek to process data closer to where it originates. |
11. Modern Technology: Robotics & Automation
Robotics has moved beyond factory floors and into warehouses, homes, and surgery suites. Industrial robots have been performing repetitive manufacturing tasks for decades, but the latest generation is far more capable and better at working alongside humans. Warehouse automation, driven by the growth of e-commerce, has made robots a daily presence in logistics operations.
Sensors and actuators are the sensory and muscular systems of robots. Sensors allow machines to perceive their environment — detecting distance, temperature, and visual information. Actuators convert electrical signals into physical movement. Together, these components enable robots to interact with the physical world in ways that were once limited to science fiction.
The intersection of AI and robotics is one of the most active areas of development in Modern Technology. When robots can learn from experience and make decisions in real time, they become significantly more useful. Humanoid robots are beginning to appear in research settings, and companies like Boston Dynamics and Tesla are pushing the boundaries of what autonomous machines can do.
Table 12: Robotics & Automation in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Robotics Area | Key Fact or Industry Data |
| Industrial Robots | Over 550,000 industrial robots were installed worldwide in 2022, per IFR. |
| Warehouse Robots | Amazon operates over 750,000 robots across its fulfillment centers as of 2023. |
| Surgical Robots | The da Vinci surgical system has been used in over 12 million procedures worldwide. |
| Agricultural Robots | Companies like John Deere and Burro are deploying autonomous robots for farming tasks. |
| Humanoid Robots | Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robot can perform backflips and navigate complex terrain autonomously. |
| Drone Technology | The global drone market was valued at about $12 billion in 2023, per Grand View Research. |
| Collaborative Robots | Cobots designed to work safely alongside humans are becoming standard in manufacturing. |
| Robot Automation Spending | Global spending on robotics and automation reached an estimated $150 billion in 2023. |
12. Modern Technology: Green Tech & Sustainable Technology

The technology industry has begun to reckon with its environmental footprint in a more serious way. Green technology refers to innovations in clean energy — solar panels, wind turbines, battery storage, and electric vehicle technology. Sustainable technology is a broader concept that also includes how products are designed, manufactured, used, and disposed of. The distinction matters because both clean energy and lifecycle responsibility are needed to address climate change.
Electric vehicles have seen dramatic growth in recent years. Countries like China, Norway, and the Netherlands have become leaders in EV adoption, and major automakers are investing billions in this transition. Battery technology, particularly lithium-ion and emerging solid-state batteries, is central to this shift. Battery costs directly affect how practical EVs are for everyday use.
E-waste is another growing concern. Discarded electronics contain valuable materials like gold and copper, but most ends up in landfills. Companies and governments are addressing this through recycling programs and extended producer responsibility laws. The future of Modern Technology depends not only on innovation but also on building systems that are sustainable from the start.
Table 13: Green Tech & Sustainability in Modern Technology — Key Facts
| Green or Sustainable Tech Area | Key Fact or Environmental Data |
| Solar Energy | Global solar capacity surpassed 1,400 GW of cumulative installations by end of 2023, per IEA. |
| Wind Energy | Global wind power generation reached about 2,100 TWh in 2023. |
| Electric Vehicles | Over 14 million EVs were sold globally in 2023, with China at roughly 60%, per IEA. |
| Battery Technology | Lithium-ion battery costs dropped by about 90% between 2010 and 2023, per BloombergNEF. |
| Solid-State Batteries | Toyota and QuantumScape are developing solid-state batteries expected to increase energy density by 50% or more. |
| E-Waste | The UN estimated about 62 million metric tons of e-waste were generated globally in 2022. |
| Energy-Efficient Data Centers | Google reported its data centers use 48% less energy than the industry average in 2023. |
| Carbon Neutrality Pledges | Microsoft, Google, and Amazon have all committed to carbon neutrality or net-zero targets. |
Conclusion: Modern Technology and the Interconnected Future Ahead
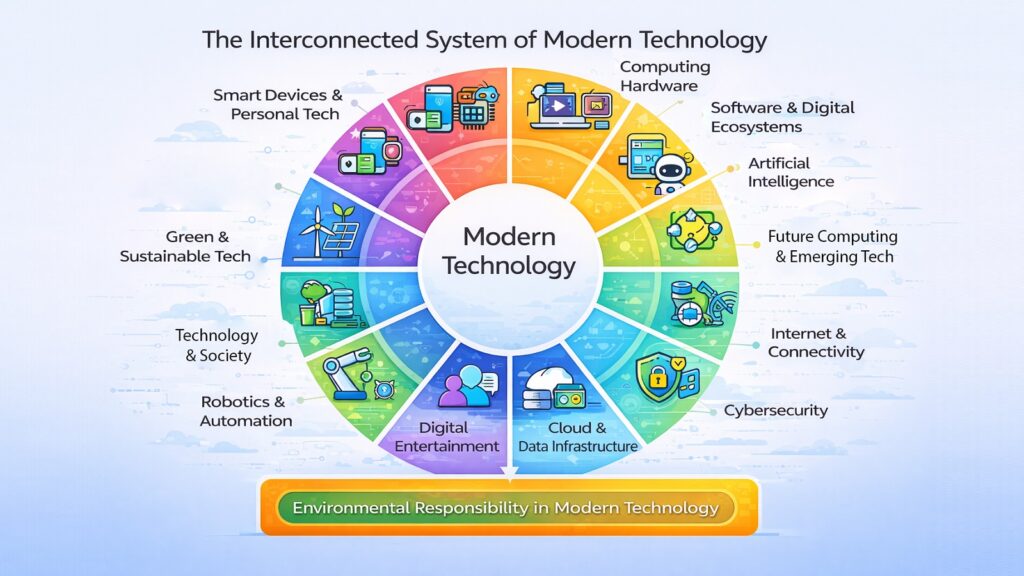
The twelve pillars covered in this article are not separate islands. They are connected threads in a single, evolving system. Smart devices depend on computing hardware. Hardware depends on software. Software depends on cloud infrastructure. All of it depends on connectivity, and all of it is increasingly shaped by artificial intelligence and measured by its impact on society and the environment.
Modern Technology is not a destination that has been reached. It is a continuous process of building, refining, and adapting. The tools that exist today will be improved upon, and new categories of technology will emerge that are difficult to predict right now. What remains constant is this pattern: technologies that once seemed distant eventually become ordinary, and ordinary technologies become essential.
The pillars explored here — from robotics and AI to green tech and digital entertainment — offer a map of where things stand at this moment. Each one is evolving on its own timeline, but they are all moving in the same direction: toward systems that are faster, smarter, more connected, and more sustainable.
The future belongs to those who engage with Modern Technology not just as consumers but as informed participants. The questions that matter most are not only about what these systems can do but about how they should be used and what kind of world they are helping to build.
Table 14: The Pillars of Modern Technology — A Summary View
| Pillars of Modern Technology | Role in Interconnected Future |
| Smart Devices & Personal Tech | Entry point for billions; smartphones and wearables define daily tech interaction. |
| Computing Hardware | Physical foundation; CPUs, GPUs, and memory set the performance ceiling for digital tasks. |
| Software & Ecosystems | Operating systems and platform ecosystems shape how people work and create. |
| Artificial Intelligence | From recommendation engines to generative AI, reshaping work and daily life. |
| Future Computing | Quantum, neuromorphic, and photonic computing will redefine what machines can do. |
| Internet & Connectivity | 5G, fiber, and satellite networks keep the digital world connected and responsive. |
| Cybersecurity | Protects data, identity, and devices, making the rest of the ecosystem reliable. |
| Technology & Society | Ethics, access, and cultural impact determine how technology serves people. |