Table of Contents
Introduction: Onboarding as the Step to Long-Term Loyalty
The first impression in business relationships often determines their trajectory, and employee onboarding represents perhaps the most critical first impression an organization can make. Onboarding is an important Human Resources function that extends far beyond mere administrative procedures or workplace tours. It serves as the strategic foundation upon which employee loyalty, engagement, and long-term organizational commitment are built.
Unlike traditional orientation programs that focus primarily on paperwork completion and policy explanation, modern onboarding encompasses a comprehensive integration process. While orientation typically lasts a few days and covers basic operational necessities, onboarding extends over weeks or months, weaving together cultural immersion, relationship building, and performance preparation. Orientation answers the question of what employees need to know, while onboarding addresses how they will thrive within the organizational ecosystem.
The distinction becomes clearer when examining their respective impacts on employee psychology. Orientation creates awareness, but onboarding creates belonging. Research from leading business schools consistently demonstrates that employees who experience structured onboarding programs show significantly higher retention rates, faster time-to-productivity, and stronger emotional connections to their organizations.
This article explores six fundamental ways through which strategic onboarding transforms initial employee interactions into lasting loyalty bonds. These approaches leverage psychological principles, business frameworks, and cultural dynamics to create experiences that resonate beyond the initial employment period.
The following analysis will examine how expectation alignment creates psychological contracts, how emotional touchpoints humanize workplace relationships, how cultural belonging satisfies fundamental human needs, how organizational storytelling builds identity connections, how customer loyalty principles apply to employee experiences, and how feedback systems foster mutual commitment.
Table 1: Onboarding’s Impact on Core HR Functions
| HR Function | How Onboarding Influences It | Strategic Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Recruitment | Sets realistic job previews and validates hiring decisions | Reduces early turnover and improves candidate quality |
| Training | Establishes learning foundations and skill development pathways | Accelerates competency acquisition and performance readiness |
| Leadership | Creates early leadership touchpoints and mentoring relationships | Develops future leaders and strengthens management pipeline |
| Employee Relations | Builds initial trust and communication patterns | Prevents conflicts and establishes positive workplace dynamics |
| Employee Engagement | Establishes emotional connections and purpose alignment | Increases discretionary effort and organizational commitment |
| Compensation and Benefits | Explains value propositions and total rewards philosophy | Enhances perceived value and reduces compensation-related turnover |
| Organizational Development | Introduces cultural values and behavioral expectations | Accelerates cultural integration and change adaptability |
| Change Management | Prepares employees for organizational evolution | Builds resilience and adaptability to future changes |
| Offboarding | Creates positive exit experiences through initial relationship quality | Maintains alumni networks and employer brand reputation |
1. Onboarding and Expectation Alignment: The Psychological Contract at Work
The Psychological Contract Theory, pioneered by organizational psychologist Edgar Schein, reveals how unwritten expectations between employers and employees fundamentally shape workplace relationships. During onboarding, organizations have their most powerful opportunity to establish clear, mutual expectations that form the foundation of this invisible contract.
When new employees join organizations, they arrive with assumptions about career progression, work-life balance, recognition systems, and cultural dynamics. Simultaneously, employers hold expectations about performance standards, cultural fit, innovation contributions, and long-term commitment. The onboarding process serves as the critical negotiation space where these expectations either align harmoniously or create future friction points.
Successful expectation alignment during onboarding prevents the disappointment and disillusionment that often emerge when reality conflicts with assumptions. Organizations that invest time in clarifying mutual expectations during the initial weeks see dramatic improvements in employee satisfaction and retention rates. This alignment process requires honest conversations about organizational challenges, growth opportunities, performance metrics, and cultural realities.
The psychological contract extends beyond job descriptions to encompass emotional and social expectations. New employees need clarity about how decisions are made, how conflicts are resolved, how recognition is distributed, and how career advancement occurs. When onboarding addresses these deeper psychological needs, it creates a foundation of trust that withstands future organizational challenges.
Companies like Patagonia and Southwest Airlines have mastered this approach by using onboarding to clearly communicate their values-driven cultures while honestly discussing the challenges of mission-driven work environments. This transparency creates psychological contracts based on shared understanding rather than unrealistic expectations.
Table 2: Psychological Contract Elements in Onboarding
| Contract Element | Employee Expectation | Employer Expectation | Alignment Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance Standards | Clear goals and fair evaluation | Consistent high-quality work and continuous improvement | Define specific metrics and provide regular feedback mechanisms |
| Career Development | Growth opportunities and skill building | Long-term commitment and leadership potential | Create visible career pathways and mentoring programs |
| Work Environment | Supportive culture and work-life balance | Professional behavior and team collaboration | Establish cultural norms and flexible work arrangements |
| Recognition | Fair compensation and acknowledgment | Results delivery and organizational contribution | Implement transparent reward systems and achievement celebrations |
| Communication | Open dialogue and transparency | Honest feedback and proactive problem-solving | Create multiple communication channels and regular check-ins |
2. Onboarding Creates Emotional Touchpoints That Humanize the Workplace
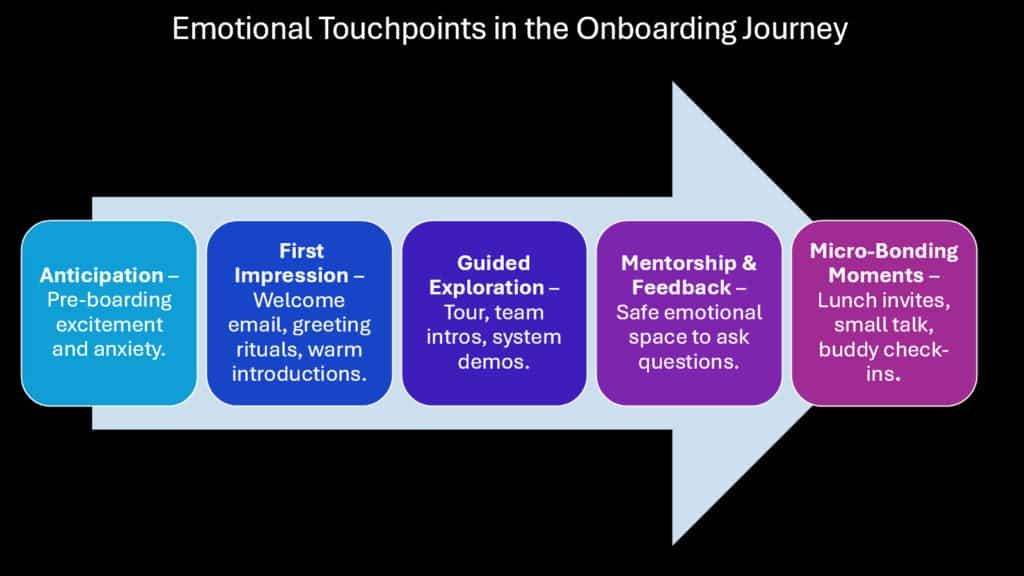
Modern workplaces often struggle with creating genuine human connections amidst technological efficiency and operational demands. Exceptional onboarding programs recognize that emotional engagement drives loyalty more powerfully than functional satisfaction alone. By designing experiences that evoke curiosity, warmth, and relief, organizations create memorable moments that transform transactional employment relationships into personal connections.
Emotional touchpoints during onboarding serve multiple psychological functions. They reduce anxiety associated with new environments, create positive associations with the organization, and establish emotional anchors that employees reference during challenging periods. These moments might include personalized welcome messages from senior leaders, surprise desk setups reflecting individual interests, or storytelling sessions where current employees share their journey narratives.
The connection between emotional engagement and innovation becomes particularly evident during onboarding. When new employees feel emotionally safe and personally valued, they demonstrate greater willingness to share ideas, challenge existing processes, and contribute creative solutions. This emotional foundation encourages intellectual risk-taking and collaborative problem-solving that drives organizational innovation.
Research from organizational psychology demonstrates that employees who experience positive emotions during their first month show significantly higher levels of creative thinking and innovative behavior throughout their tenure. The emotional safety established during onboarding creates psychological conditions conducive to innovation, as employees feel secure enough to propose unconventional approaches without fear of judgment or rejection.
Companies like Google and Airbnb have pioneered emotional onboarding approaches that create lasting impressions. Google’s “Noogler” program includes personalized gifts, mentorship matching based on interests, and immersive experiences that help new employees understand the company’s innovation culture. These emotional investments pay dividends through increased employee advocacy and innovative contributions.
Table 3: Emotional Touchpoints and Innovation Outcomes
| Emotional Touchpoint | Psychological Impact | Innovation Benefit | Implementation Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized Welcome | Creates sense of individual value | Increases confidence to share unique perspectives | Custom welcome packages reflecting personal interests |
| Storytelling Sessions | Builds emotional connection to mission | Inspires creative problem-solving aligned with values | Current employee journey narratives and challenge stories |
| Mentorship Pairing | Establishes safe learning relationships | Encourages intellectual risk-taking and idea sharing | Interest-based mentor matching with innovation focus |
| Team Integration Activities | Develops collaborative comfort | Facilitates cross-functional innovation partnerships | Project-based team challenges and creative workshops |
| Leadership Accessibility | Reduces hierarchical barriers | Promotes upward innovation communication | Informal coffee chats with executives and open-door policies |
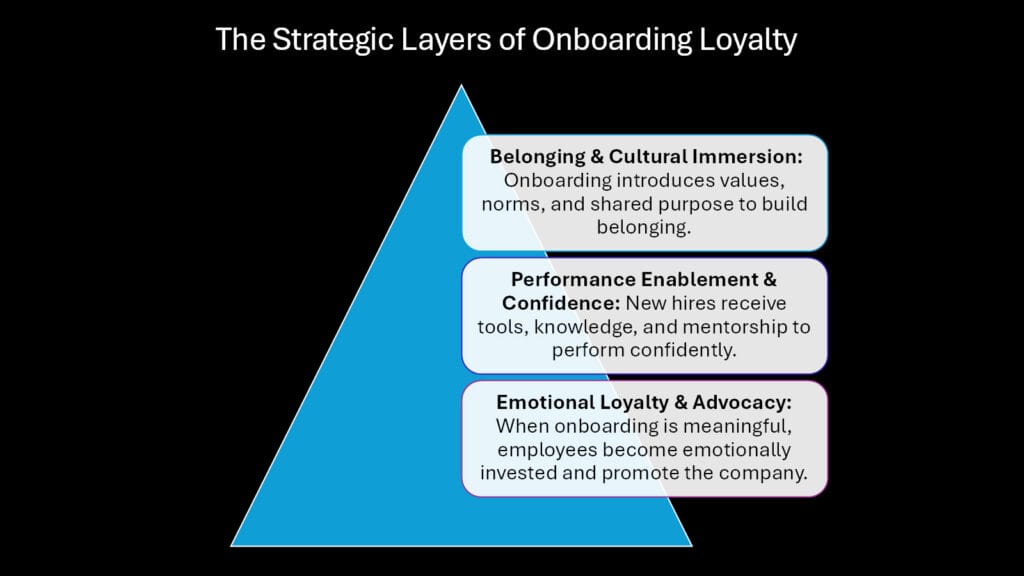
3. Onboarding and Belonging: Using Maslow’s Hierarchy to Anchor Culture
Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs provides a powerful framework for understanding how effective onboarding satisfies fundamental human motivations and builds lasting organizational loyalty. By systematically addressing physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs during the integration process, organizations create comprehensive belonging experiences that anchor employees to their cultural foundation.
At the physiological level, onboarding ensures new employees understand basic workplace necessities: where to find food, how to access facilities, and how to manage their physical comfort. While seemingly mundane, these considerations significantly impact initial stress levels and cognitive capacity for higher-level integration activities.
Safety needs encompass both physical and psychological security. Effective onboarding programs clearly communicate emergency procedures, security protocols, and reporting mechanisms while establishing psychological safety through inclusive communication, mistake tolerance, and support system introductions. When employees feel secure, they invest mental energy in relationship building and cultural absorption rather than self-protection.
Social belonging represents perhaps the most critical onboarding component for long-term loyalty development. Human beings have essential requirements for connection, acceptance, and belonging to a community.. Onboarding programs that facilitate authentic relationship formation through team introductions, collaborative projects, and social activities create the interpersonal bonds that make leaving emotionally difficult.
The level of esteem pertains to the needs for recognition, respect, and accomplishment. Strategic onboarding provides early wins, celebrates individual contributions, and creates opportunities for new employees to demonstrate their unique value. This validation builds confidence and emotional investment in organizational success.
Self-actualization opportunities emerge when onboarding connects individual purpose with organizational mission. By helping new employees understand how their roles contribute to meaningful outcomes, organizations satisfy the highest level of human motivation and create intrinsic loyalty bonds.
Table 4: Maslow’s Hierarchy in Onboarding Design
| Need Level | Onboarding Focus | Loyalty Impact | Cultural Integration Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physiological | Workplace navigation and basic comfort | Reduces initial stress and creates positive first impressions | Comprehensive facility tours and comfort amenity introductions |
| Safety | Security protocols and psychological support | Builds trust foundation and reduces anxiety | Clear emergency procedures and mental health resource introductions |
| Social | Relationship building and team integration | Creates emotional bonds that discourage turnover | Structured team introductions and collaborative project assignments |
| Esteem | Recognition opportunities and early achievements | Builds confidence and organizational pride | Quick wins identification and public acknowledgment systems |
| Self-Actualization | Purpose alignment and mission connection | Generates intrinsic motivation and deep loyalty | Mission storytelling and individual impact mapping |
4. Onboarding as Storytelling: How Narratives Shape Identity and Connection
Organizational storytelling during onboarding serves as a powerful mechanism for transmitting culture, values, and identity while creating emotional connections that transcend functional job requirements. The most effective onboarding programs recognize that humans are inherently narrative creatures who understand their place in the world through stories that provide context, meaning, and direction.
When organizations share their founding stories, evolution narratives, and future aspirations during onboarding, they invite new employees to become characters in an ongoing organizational story. This narrative inclusion creates psychological ownership and emotional investment that extends far beyond transactional employment relationships. Employees begin to see their individual contributions as chapters in a larger organizational narrative.
The strategic integration of storytelling into corporate strategy occurs when onboarding narratives align with broader organizational objectives. Companies use origin stories to reinforce core values, challenge stories to demonstrate resilience and adaptability, and vision stories to inspire innovative thinking. These narratives provide strategic context that helps new employees understand not just what the organization does, but why it exists and where it’s heading.
Effective organizational storytelling during onboarding creates continuity between past achievements and future possibilities. By sharing stories of previous employees who made significant contributions, organizations demonstrate career progression possibilities and cultural consistency. These narratives serve as proof points that validate the organization’s commitment to employee development and success.
The most powerful onboarding stories are those that acknowledge challenges alongside successes. Organizations that share stories about overcoming difficulties, learning from failures, and adapting to change create realistic expectations while demonstrating resilience and growth mindset cultures. These honest narratives build trust and prepare new employees for the complexities of organizational life.
Companies like Patagonia, Ben & Jerry’s, and Southwest Airlines have mastered the art of on-boarding storytelling by weaving their founding principles, cultural evolution, and mission-driven decisions into compelling narratives that new employees remember and retell throughout their tenure.
Table 5: Storytelling Elements in Strategic Onboarding
| Story Type | Strategic Purpose | Identity Impact | Corporate Strategy Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Founding Stories | Communicate core values and original mission | Creates connection to organizational DNA | Reinforces strategic differentiation and market positioning |
| Evolution Narratives | Demonstrate adaptability and growth mindset | Shows personal growth possibilities | Illustrates strategic pivots and market responsiveness |
| Challenge Stories | Build resilience and problem-solving culture | Prepares for future difficulties | Highlights competitive advantages and market challenges |
| Success Stories | Inspire excellence and achievement | Creates performance aspirations | Demonstrates strategic execution and market success |
| Vision Stories | Align individual purpose with organizational direction | Motivates innovative contributions | Connects daily work to long-term strategic objectives |
5. Onboarding and Retention: Applying the Customer Loyalty Loop to Employees
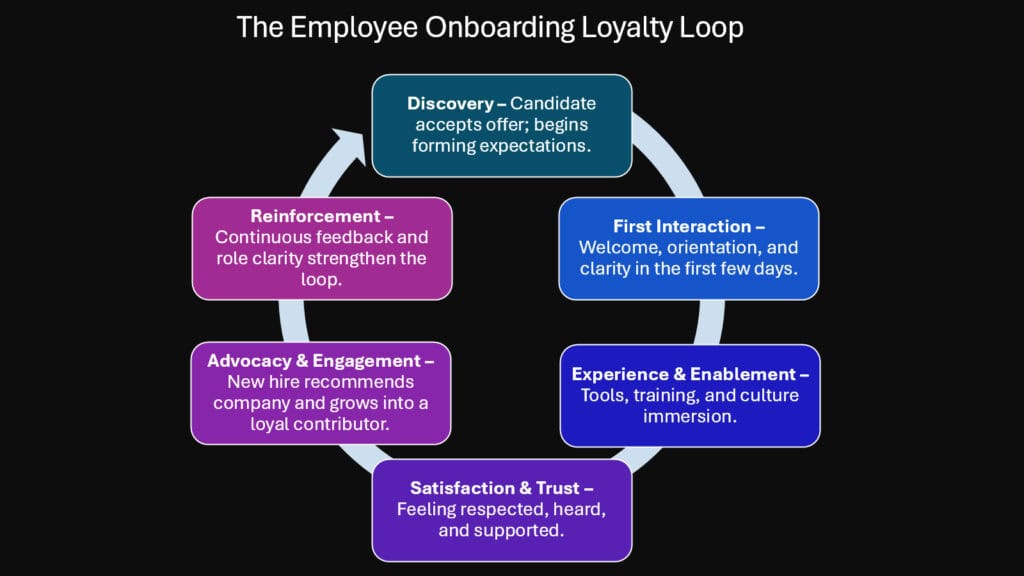
The Customer Loyalty Loop Model, originally developed for understanding consumer behavior, provides valuable insights for creating employee loyalty through strategic onboarding. This framework demonstrates how initial experiences, emotional connections, and value delivery create cycles of engagement that strengthen over time, ultimately leading to advocacy and long-term commitment.
The loyalty loop begins with awareness and first impressions, making onboarding the critical entry point for employee loyalty development. Just as customers form lasting opinions about brands based on initial interactions, employees develop fundamental attitudes toward their organizations during the first weeks of employment. Positive onboarding experiences create emotional deposits that generate goodwill for future organizational challenges.
The consideration phase in customer loyalty translates to employee engagement evaluation during onboarding. New employees continuously assess whether their decision to join was correct based on daily experiences, cultural observations, and relationship formation. Organizations that provide consistent positive reinforcement during this evaluation period strengthen employee confidence in their employment choice.
Purchase decisions in customer loyalty correspond to employee commitment levels. When on-boarding successfully demonstrates organizational value, career possibilities, and cultural fit, employees make psychological commitments that extend beyond initial employment agreements. This commitment phase represents the transition from cautious new employee to engaged team member.
The retention aspect of customer loyalty directly parallels employee retention strategies. Just as businesses create customer retention programs through continued value delivery and relationship building, organizations use ongoing onboarding elements to maintain employee engagement and prevent competitive recruitment efforts.
Customer advocacy, the final loop element, emerges when employees become organizational ambassadors who attract talent through positive word-of-mouth and referral behavior. Exceptional onboarding creates employee advocates who strengthen recruitment efforts and enhance employer brand reputation.
The connection to customer engagement becomes evident when onboarding includes customer interaction training, product knowledge development, and service philosophy education. Employees who understand customer needs and organizational value propositions through comprehensive onboarding provide superior customer experiences that drive business results.
Table 6: Customer Loyalty Loop Applied to Employee Onboarding
| Loop Stage | Customer Experience | Employee Experience | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Brand discovery and first impressions | Recruitment and initial workplace exposure | Attracts quality candidates and sets expectation foundation |
| Consideration | Product evaluation and comparison | Onboarding experience assessment and culture fit evaluation | Reduces early turnover and strengthens employment choice confidence |
| Purchase | Buying decision and initial satisfaction | Commitment development and psychological ownership | Creates deeper engagement and reduces competitive recruitment vulnerability |
| Retention | Continued usage and value realization | Ongoing development and career progression | Maintains long-term employee relationships and reduces replacement costs |
| Advocacy | Referrals and positive word-of-mouth | Employee referrals and employer brand promotion | Enhances recruitment effectiveness and organizational reputation |
6. Onboarding as a Feedback Loop: Listening Builds Loyalty Faster Than Telling
Traditional onboarding approaches focus heavily on information delivery, assuming that comprehensive orientation sessions and policy explanations create employee understanding and engagement. However, the most effective onboarding programs recognize that listening to new employee perspectives, concerns, and suggestions builds loyalty more effectively than one-way communication.
Feedback-driven onboarding creates psychological safety by demonstrating organizational respect for individual perspectives and experiences. When new employees see that their input influences processes, policies, or procedures, they develop emotional investment in organizational success. This participatory approach transforms passive recipients into active contributors who feel valued and heard.
The implementation of early feedback systems during on-boarding serves multiple strategic purposes. First, it provides organizations with fresh perspectives on existing processes that may have become inefficient or outdated. New employees often identify improvement opportunities that tenured staff overlook due to familiarity or acceptance of status quo conditions.
Second, feedback collection demonstrates organizational commitment to continuous improvement and employee development. When new hires observe that their suggestions receive serious consideration and implementation, they develop confidence in the organization’s responsiveness and adaptability. This responsiveness creates positive expectations for future communication and collaboration.
The psychological safety created through feedback-oriented onboarding encourages risk-taking, innovation, and honest communication throughout employee tenure. Organizations that establish listening cultures during onboarding benefit from higher levels of employee engagement, creative problem-solving, and proactive issue identification.
Two-way commitment emerges when feedback systems create mutual accountability between organizations and employees. New employees who contribute to organizational improvement feel responsible for outcomes, while organizations that implement employee suggestions demonstrate commitment to individual growth and organizational excellence.
Table 7: Feedback Systems in Onboarding Design
| Feedback Method | Implementation Approach | Loyalty Benefit | Organizational Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Check-ins | Scheduled one-on-one conversations with managers and HR | Creates personal connection and demonstrates individual importance | Identifies process gaps and cultural barriers |
| Anonymous Surveys | Digital feedback collection on onboarding experience quality | Encourages honest input without fear of judgment | Reveals systemic issues and improvement opportunities |
| Focus Groups | Small group discussions about onboarding effectiveness | Builds peer connections while gathering collective insights | Uncovers cultural dynamics and team integration challenges |
| Suggestion Systems | Formal channels for process improvement recommendations | Empowers employees to contribute organizational enhancement | Generates innovation ideas and efficiency improvements |
| Exit Interviews | Structured conversations with early departures | Understands retention failures and prevents future turnover | Identifies critical onboarding gaps and competitive disadvantages |
Conclusion: Onboarding is the First Chapter of Loyalty, Not a Checklist

The journey from new employee orientation to deep organizational loyalty begins with strategic onboarding that recognizes the profound psychological and emotional dimensions of workplace integration. Organizations that approach onboarding as a comprehensive loyalty-building process rather than an administrative necessity create competitive advantages through enhanced retention, engagement, and employee advocacy.
The six approaches explored throughout this analysis demonstrate that effective onboarding requires understanding of human psychology, business strategy, and cultural dynamics. Expectation alignment through psychological contract clarity prevents future disappointment and conflict. Emotional touchpoints create memorable experiences that humanize workplace relationships and encourage innovative thinking. Cultural belonging satisfies fundamental human needs while anchoring employees to organizational values and mission.
Organizational storytelling provides narrative context that helps new employees understand their role in broader strategic objectives while creating emotional connections to organizational history and future aspirations. Customer loyalty principles applied to employee experiences demonstrate how initial positive interactions create cycles of engagement that strengthen over time. Feedback-driven onboarding builds psychological safety and two-way commitment through respectful listening and responsive implementation.
The business implications extend far beyond human resources functions to encompass marketing effectiveness, sales performance, operational efficiency, financial results, strategic execution, and technological innovation. When employees feel genuinely welcomed, valued, and connected to organizational purpose from their first day, they contribute discretionary effort that drives superior business outcomes across all functional areas.
Looking forward, organizations must recognize that onboarding represents an investment in long-term relationship building rather than short-term information transfer. The employees who join organizations today will shape tomorrow’s culture, innovation, and competitive positioning. Their loyalty, developed through thoughtful onboarding experiences, becomes the foundation upon which sustainable organizational success is built.
The signal sent through exceptional onboarding resonates throughout employee tenure: you matter, you belong, and your contribution creates shared success. This message, delivered consistently through carefully designed experiences, transforms employment relationships into partnerships that withstand challenges and generate mutual growth.
Table 8: Onboarding’s Impact on Core Business Functions
| Business Function | Onboarding Influence | Strategic Outcome | Performance Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing | Employees become brand ambassadors with deep product knowledge | Enhanced brand credibility and authentic customer communication | Employee referral rates and social media advocacy |
| Sales | Customer-focused onboarding creates consultative selling capabilities | Improved customer relationships and higher conversion rates | Sales performance and customer satisfaction scores |
| Operations | Process understanding and cultural alignment improve efficiency | Reduced errors and enhanced productivity | Quality metrics and operational efficiency measures |
| Finance | Cost awareness and value creation understanding | Better resource utilization and profit consciousness | Cost per employee and revenue per employee ratios |
| Corporate Strategy | Mission alignment creates strategic execution commitment | Faster strategy implementation and cultural change adoption | Strategic objective achievement and change readiness scores |
| Information Technology | Security awareness and digital adoption readiness | Enhanced cybersecurity and technology utilization | Security incident rates and technology adoption metrics |




