Table of Contents
Introduction: Why Training Is the Unsung Hero of Market Leadership
When Apple transformed from a near-bankrupt company in 1997 to the world’s most valuable corporation, many attributed this meteoric rise to innovative products and visionary leadership. Yet beneath the surface lay a deeper truth: Apple’s relentless commitment to train its workforce across every function, from design thinking to customer service excellence. This transformation illustrates how training serves as more than employee development—it becomes a quiet but forceful driver of innovation, resilience, and long-term market leadership.
Modern businesses face unprecedented challenges in an economy where technological disruption arrives at breakneck speed. Companies that survive and thrive share a common characteristic: they treat training not as an expense but as a strategic investment. Research from Harvard Business Review indicates that organizations with comprehensive upskilling programs achieve significantly higher employee engagement, customer satisfaction, and financial performance compared to their peers who view it as discretionary spending.
Training represents a critical Human Resources function that extends far beyond traditional employee development. It shapes organizational culture, builds competitive capabilities, and creates the foundation for sustainable market leadership. The most successful companies understand that training transforms individual competencies into collective organizational intelligence, enabling firms to respond faster to market changes and deliver superior value to customers.
The following analysis explores six fundamental ways training powers market leadership: building strategic capabilities across the value chain, enhancing organizational agility, reinforcing competitive advantage through core competency development, strengthening customer-centric thinking, driving innovation through learning organization principles, and optimizing workforce productivity. Each pathway demonstrates how investments in this critical HR function compound over time, creating sustainable competitive advantages that competitors struggle to replicate.
| Upskilling Investment Areas | Market Leadership Impact | Implementation Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Skills Development | Enhanced product quality and innovation | 6-12 months |
| Leadership Development | Improved decision-making and strategic thinking | 12-18 months |
| Customer Service Training | Increased customer loyalty and retention | 3-6 months |
| Digital Literacy Programs | Accelerated digital transformation | 9-15 months |
| Cross-functional Collaboration | Improved operational efficiency | 6-12 months |
| Innovation Workshops | Enhanced creative problem-solving | 3-9 months |
1. Training Builds Strategic Capabilities Across the Value Chain
Michael Porter’s Value Chain Framework reveals how organizations create competitive advantage through interconnected activities spanning from inbound logistics to after-sales service. Training becomes the catalyst that transforms each link in this chain, helping firms extract more value, lower costs, and deliver differentiation that customers recognize and reward. Consider how Toyota revolutionized automotive manufacturing through its comprehensive upskilling approach. The company’s Production System relies heavily on continuous employee training in lean manufacturing principles, quality control, and problem-solving methodologies. This investment enables Toyota to maintain superior quality standards while achieving cost efficiencies that competitors struggle to match. Every employee understands their role within the broader value chain and receives ongoing development to optimize their contribution.
Training enhances primary activities by building specialized capabilities that directly impact customer value. In inbound logistics, trained procurement teams negotiate better supplier relationships and identify cost-saving opportunities. Operations benefit from it in process optimization, quality management, and safety protocols. Outbound logistics teams trained in supply chain management and customer service ensure seamless delivery experiences. Marketing and sales professionals equipped with advanced upskilling in customer psychology and digital marketing drive higher conversion rates and customer acquisition.
Support activities gain equal importance through targeted training investments. Human resource teams trained in talent management and organizational psychology build stronger workforces. Technology development benefits from upskilling in emerging technologies and innovation methodologies. Procurement skill development ensures optimal supplier relationships and cost management. Infrastructure improvements emerge from training in organizational design and change management.
The cumulative effect creates what Porter describes as activity linkages, where training in one area reinforces capabilities in another. Manufacturing upskilling that emphasizes quality directly supports marketing efforts by reducing defects and customer complaints. Customer service training that focuses on problem resolution supports operations by identifying recurring issues and improvement opportunities.
| Value Chain Activity | Focus Areas | Competitive Advantage Created |
|---|---|---|
| Inbound Logistics | Supplier relationship management, quality inspection | Reduced costs, improved quality |
| Operations | Process optimization, safety protocols | Higher efficiency, lower defects |
| Outbound Logistics | Supply chain management, customer service | Faster delivery, better experience |
| Marketing & Sales | Customer psychology, digital marketing | Higher conversion, market share |
| After-sales Service | Problem resolution, relationship building | Customer loyalty, repeat business |
2. Training Enhances Organizational Agility and Speed to Market
Organizations that consistently outperform competitors share a common trait: their teams respond to change with remarkable speed and precision. This agility emerges from systematic training that prepares employees to navigate uncertainty, adapt to new technologies, and execute strategic pivots without losing momentum. Amazon exemplifies this principle through its culture of continuous learning and experimentation. The company invests heavily in upskilling and reskilling programs that encourage employees to think like entrepreneurs, test new ideas rapidly, and learn from failures. This philosophy enables Amazon to enter new markets quickly, adapt to changing customer preferences, and maintain leadership across diverse business segments from cloud computing to retail.
Training creates agility by building cognitive flexibility and problem-solving capabilities across the organization. When employees possess broad skill sets and deep understanding of business principles, they can shift roles, adapt to new technologies, and contribute to different projects as market conditions change. This flexibility becomes particularly valuable during economic downturns or industry disruptions when rigid organizations struggle to adapt.
Speed to market depends on teams that can collaborate effectively across functional boundaries. Training programs that emphasize cross-functional understanding and communication enable faster decision-making and execution. Engineering teams that understand marketing requirements deliver products that better meet customer needs. Marketing teams that grasp technical constraints develop more realistic and achievable campaigns. Sales teams that comprehend operational capabilities make promises they can deliver.
The learning curve advantage emerges when organizations train employees to acquire new skills rapidly. Companies, that train their employees diligently, create internal capabilities for continuous adaptation. It reduces dependence on external consultants or new recruitment cycles when market conditions shift. This internal capacity for learning and adaptation becomes a sustainable competitive advantage that compounds over time.
| Agility Component | Investment | Market Response Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Flexibility | Problem-solving workshops, scenario planning | Rapid adaptation to market changes |
| Cross-functional Skills | Job rotation, collaborative projects | Faster product development cycles |
| Technology Adoption | Digital literacy, tool training | Quick implementation of new systems |
| Change Management | Leadership development, communication skills | Smooth organizational transitions |
| Innovation Mindset | Creative thinking, experimentation methods | Faster identification of opportunities |
3. Training Reinforces Competitive Advantage Through Core Competency Development
Prahalad and Hamel’s Core Competency Theory identifies how organizations build and sustain competitive advantage through unique, inimitable capabilities that span multiple business units. Training becomes the mechanism that embeds these competencies deep within the organization, creating expertise that competitors cannot easily replicate or acquire.
Disney’s method of training for customer experience exemplifies this principle flawlessly. The company has developed proprietary methods that teach employees to create magical experiences for guests. This goes beyond basic customer service to encompass storytelling, emotional intelligence, and problem-solving in ways that align with Disney’s brand values. The result is a core competency in experience design that competitors struggle to match despite similar resources.
Core competencies emerge from upskilling that combines technical expertise with organizational culture and values. When employees understand not just what to do but why certain approaches align with company strategy, they make decisions that reinforce competitive positioning. This deep understanding creates consistency across all customer touchpoints and business functions.
Training builds core competencies by developing collective learning capabilities within the organization. Individual expertise becomes valuable when it can be shared, replicated, and applied across different contexts. Upskilling and reskilling programs that emphasize knowledge sharing and mentorship create organizational memory that persists beyond individual employees. This institutional knowledge becomes increasingly valuable as it accumulates over time.
The inimitability of core competencies strengthens when training creates complex social relationships and tacit knowledge within the organization. Competitors can observe successful practices but cannot easily replicate the underlying systems, cultural norms, and collaborative relationships that make those practices effective. This intricate social structure establishes obstacles to imitation, thereby safeguarding competitive advantages.
| Core Competency Area | Components | Competitive Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Expertise | Specialized skill development, certification programs | High barriers to entry |
| Cultural Values | Leadership development, cultural immersion | Difficult to replicate |
| Innovation Capability | Creative problem-solving, experimentation | Unique solution approaches |
| Customer Relationship | Emotional intelligence, service excellence | Strong customer loyalty |
| Operational Excellence | Process optimization, quality management | Sustained cost advantages |
4. Training Strengthens Customer-Centric Thinking Across Functions
Customer-centricity represents more than a marketing slogan—it requires every employee to understand and prioritize the customer journey regardless of their functional role. Training programs that embed customer perspective throughout the organization create seamless experiences that build loyalty and brand trust, ultimately driving sustainable competitive advantage.
Southwest Airlines demonstrates this principle through a comprehensive training program that teaches all employees to think from the customer’s perspective. Flight attendants, baggage handlers, maintenance crews, and administrative staff are trained in customer service principles and company values. This consistency creates a unified customer experience that differentiates Southwest from competitors who treat customer service as a departmental responsibility rather than an organizational capability.
Training in customer-centric thinking transforms how employees approach their daily responsibilities. Finance teams trained in customer impact consider how billing processes affect customer satisfaction. Human resources teams understand how employee engagement directly influences customer experiences. Information technology teams design systems that enhance rather than complicate customer interactions. This holistic approach ensures that customer needs remain central to all business decisions.
The customer journey mapping becomes more effective when employees from different functions understand how their work connects to customer experiences. Upskilling programs that include customer journey analysis help employees identify touchpoints where they can positively influence customer perceptions. This understanding leads to proactive improvements rather than reactive problem-solving after customer complaints arise.
Cross-functional training in customer psychology and behavioral economics enables employees to anticipate customer needs and preferences. When team members understand how customers make decisions, they can design processes and communications that align with customer mental models. This alignment reduces friction in customer interactions and increases satisfaction across all touchpoints.
| Function | Customer-Centric Focus | Customer Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Operations | Quality impact on customer experience | Consistent product delivery |
| Finance | Customer-friendly billing processes | Reduced customer frustration |
| Human Resources | Employee engagement effects on service | Improved customer interactions |
| Information Technology | User experience design principles | Seamless digital experiences |
| Supply Chain | Customer delivery expectations | Reliable product availability |
5. Training Drives Innovation Through the Learning Organization Model
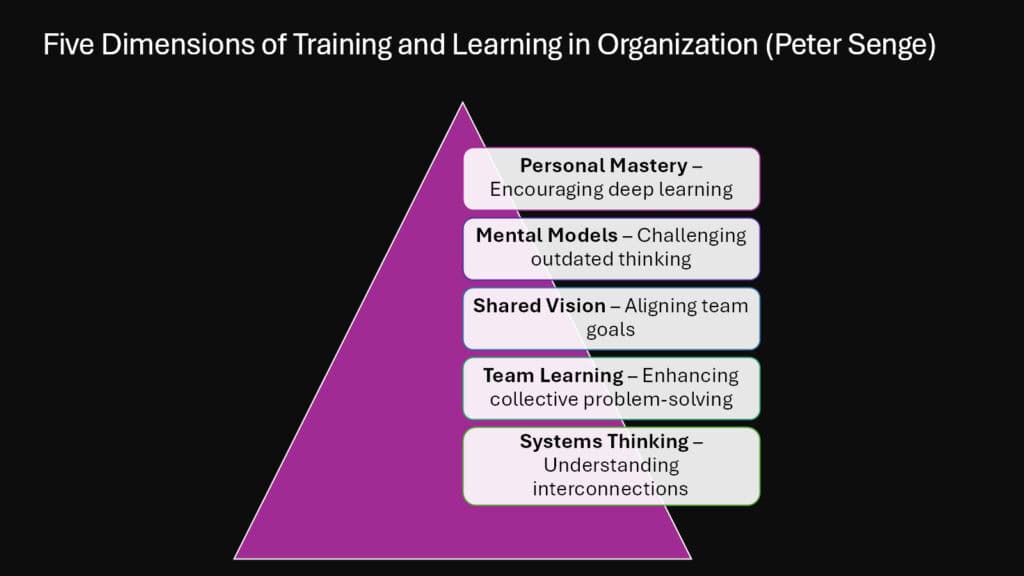
Peter Senge’s Learning Organization Model reveals how companies that embed continuous learning into their culture nurture experimentation, adaptability, and innovative thinking. Training becomes the foundation for organizational learning that enables companies to stay ahead in competitive markets through systematic knowledge creation and application.
Google exemplifies this approach through its famous “20 percent time” policy and comprehensive learning programs. The company encourages employees to spend time on experimental projects while it trains them in innovation methodologies, design thinking, and collaborative problem-solving. This combination of freedom and structured learning capability has produced breakthrough innovations from Gmail to Google Maps that have transformed entire industries.
Learning organizations use training to develop five key disciplines that Senge identifies as essential for innovation. Personal mastery training helps employees clarify their vision and focus their energy on continuous improvement. Mental models training challenges assumptions and encourages diverse perspectives. Training for a shared vision harmonizes personal aspirations with the goals of the organization. Collaborative learning and skill enhancement foster teamwork capabilities essential for addressing complex challenges. Coaching in systems thinking enables employees to comprehend the impact of their actions on the larger organization.
Training in innovation methodologies creates systematic approaches to creative problem-solving. Design thinking workshops teach employees to empathize with customers, define problems clearly, generate multiple solutions, and test ideas rapidly. Lean startup methodologies provide frameworks for experimentation and learning from failure. These structured approaches to innovation increase the likelihood of breakthrough discoveries while reducing the cost of failed experiments.
The learning organization model emphasizes double-loop learning, where organizations question underlying assumptions rather than simply improving existing processes. Training programs that encourage this deeper level of reflection help organizations identify new opportunities and challenge industry conventions. This capability becomes particularly valuable during periods of technological disruption when traditional approaches may become obsolete.
| Learning Discipline | Components | Innovation Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Mastery | Goal setting, self-awareness development | Individual creativity enhancement |
| Mental Models | Assumption challenging, perspective taking | Breakthrough thinking |
| Shared Vision | Collaborative planning, alignment workshops | Unified innovation direction |
| Team Learning | Group problem-solving, dialogue techniques | Collective intelligence |
| Systems Thinking | Complexity analysis, relationship mapping | Holistic innovation approaches |
6. Training Optimizes Workforce Productivity and Resource Efficiency
Workforce productivity depends on more than individual effort—it requires systematic approaches to skill development, process optimization, and resource allocation. Training investments that minimize rework, reduce downtime, and eliminate skill mismatches create operational flow that maximizes the value of talent and time across the organization.
Manufacturing companies like Siemens demonstrate this principle through comprehensive coaching programs that combine technical skills with lean manufacturing principles. Their apprenticeship programs develop highly skilled workers who understand both their specific roles and how their work contributes to overall efficiency. This coaching approach reduces defects, minimizes waste, and creates flexible workforces that can adapt to changing production requirements.
Training optimizes productivity by eliminating the hidden costs of inadequate skills. When employees lack proper training, they make errors that require correction, work inefficiently, and may damage equipment or relationships. These hidden costs often exceed the direct expenses of upskilling programs. Comprehensive training investments prevent these inefficiencies while building capabilities that compound over time.
Resource efficiency emerges when training enables employees to use tools, technology, and processes more effectively. Software upskilling that helps employees leverage advanced features increases output without additional technology investments. Safety training that prevents accidents reduces insurance costs and maintains productivity. Leadership mentoring that improves delegation and communication reduces management overhead while increasing team effectiveness.
The multiplier effect of training becomes apparent when skilled employees can train others, creating cascading improvements throughout the organization. Train-the-trainer programs develop internal capacity for continuous skill development, reducing dependence on external providers while ensuring that the upskilling and coaching remain aligned with organizational needs and culture.
Modern training approaches leverage technology to scale learning while maintaining personalization. Adaptive learning systems adjust content difficulty based on individual progress. Virtual reality methods provide safe environments for practicing dangerous or expensive procedures. Microlearning delivers just-in-time training that fits into busy schedules while maintaining retention.
| Productivity Area | Training Investment | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Skills | Equipment operation, software proficiency | Reduced learning curves |
| Process Optimization | Lean methods, workflow analysis | Elimination of waste |
| Safety Protocols | Risk management, emergency procedures | Prevention of costly incidents |
| Time Management | Prioritization, planning techniques | Increased output per hour |
| Quality Control | Error prevention, continuous improvement | Reduced rework and defects |
Conclusion: Training as the Growth Engine Behind Market Leaders
The evidence overwhelmingly supports a fundamental truth: companies that lead their industries consistently invest in training not reactively, but proactively, as a foundational engine for growth, agility, and excellence. This strategic approach to human development creates sustainable competitive advantages that compound over time, distinguishing market leaders from organizations that treat training as discretionary spending.
Training transforms individual capabilities into collective organizational intelligence, enabling companies to respond faster to market changes, deliver superior customer value, and maintain competitive positioning even during periods of disruption. The six pathways explored in this analysis—strategic capability building, organizational agility enhancement, core competency development, customer-centric thinking, innovation through learning, and productivity optimization—work synergistically to create market leadership that competitors struggle to replicate.
The most successful organizations understand that training investments generate returns that extend far beyond immediate skill development. These returns manifest in reduced employee turnover, increased customer satisfaction, improved innovation capacity, and enhanced operational efficiency. When combined, these benefits create a virtuous cycle where training investments enable better business performance, which provides resources for additional training investments.
Looking forward, the importance of training will only increase as technological advancement accelerates and market conditions become more volatile. Organizations that build robust training capabilities now will be better positioned to navigate future challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. The question for business leaders is not whether to invest in training, but how to design training systems that maximize strategic value while building the adaptive capacity needed for long-term success.
Market leadership ultimately depends on organizational capabilities that can not be purchased or quickly replicated. Training represents the most reliable path to building these capabilities, creating the human capital that drives innovation, efficiency, and customer value. Companies that recognize this truth and act upon it will continue to define their industries while others struggle to keep pace.
| Market Leadership Factor | Training Contribution | Sustainable Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Innovation Capacity | Continuous learning, experimentation skills | Ongoing breakthrough potential |
| Operational Excellence | Process optimization, quality management | Sustained cost leadership |
| Customer Loyalty | Service excellence, relationship building | Competitive differentiation |
| Organizational Agility | Adaptability, change management | Market responsiveness |
| Talent Retention | Career development, engagement | Institutional knowledge preservation |
| Strategic Execution | Leadership development, alignment | Consistent performance delivery |




