Table of Contents
Introduction: How Change Management Becomes the Pulse of Business Evolution
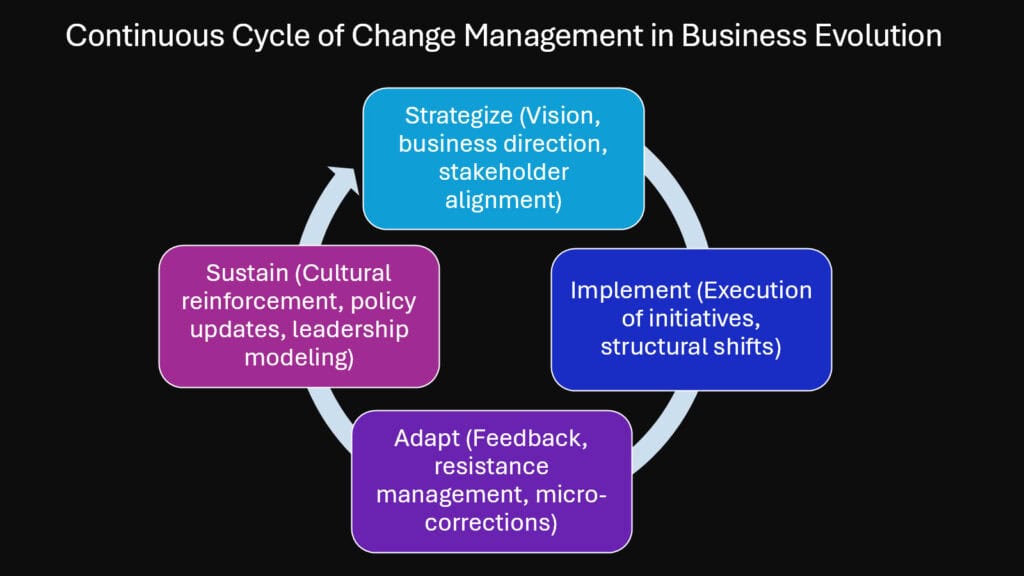
The rhythm of modern business has accelerated beyond recognition. Where once companies could afford to treat change as an occasional disruption, today’s marketplace demands constant adaptation. Recognition of change management’s strategic value has emerged as organizations acknowledge it as a strategic part of organizational endeavors. Change Management stands as the orchestrator of this complex symphony, transforming from a reactive HR function into the strategic nervous system that keeps businesses alive and thriving.
The evidence speaks clearly about the stakes involved. Up to 70% of change efforts fail due to poor communication and leadership misalignment, yet those organizations that master Change Management find themselves equipped with competitive advantages that extend far beyond simple survival. They discover agility where others find chaos, opportunity where others see threat, and growth where others experience decline.
Change Management operates as more than just process management. It functions as the bridge between where organizations are and where they need to be, creating pathways through uncertainty that allow businesses to maintain momentum while transforming their very foundation. This strategic approach recognizes that every department, every function, and every employee becomes part of a larger transformation ecosystem.
The six brilliant ways explored in this analysis reveal how Change Management elevates business performance through strategic alignment, workforce agility, organizational design, emotional trust, value creation, and digital transformation. Each approach demonstrates how proper change orchestration creates ripple effects that strengthen the entire organizational fabric. The modern economy rewards those who can adapt quickly while maintaining operational excellence, and Change Management provides the framework for achieving both simultaneously.
Understanding these mechanisms becomes crucial as businesses face unprecedented challenges from technological disruption, regulatory shifts, and evolving customer expectations. Organizations that view Change Management as optional find themselves struggling with resistance, inefficiency, and missed opportunities, while those that embrace it as essential infrastructure discover new levels of performance and resilience.
Table 1: Change Management Impact on HR Functions
| Human Resource Functions | Change Management Impact | Business Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Recruitment | Identifies future skill needs during transformation | Proactive talent acquisition aligned with strategic direction |
| Training | Develops change-specific capabilities and mindsets | Workforce prepared for new roles and responsibilities |
| Leadership | Builds change leadership competencies across levels | Leaders equipped to guide transformation initiatives |
| Employee Relations | Manages communication during uncertainty periods | Maintained trust and engagement throughout transitions |
| Employee Engagement | Creates involvement opportunities in change processes | Higher commitment to transformation outcomes |
| Orientation | Integrates change readiness into new hire experiences | New employees aligned with evolving organizational culture |
| Compensation | Aligns reward systems with new performance expectations | Incentives support desired behavioral changes |
| Organizational Development | Designs structures that support continuous adaptation | Organizations built for ongoing evolution |
| Onboarding | Incorporates change skills into integration programs | New team members ready for dynamic environments |
| Offboarding | Captures change insights from departing employees | Knowledge retention and continuous improvement |
1. Change Management Reinforces Competitive Advantage through Strategic Alignment
Porter’s Generic Strategies framework provides the foundation for understanding how Change Management creates sustainable competitive advantage. Organizations pursuing cost leadership, differentiation, or focus strategies must constantly adjust their internal capabilities to maintain market position. Change Management ensures these adjustments happen systematically rather than haphazardly.
When companies choose cost leadership, Change Management helps identify and eliminate inefficiencies while maintaining quality standards. It guides process optimization initiatives, technology implementations, and workforce restructuring in ways that reduce expenses without damaging core capabilities. The systematic approach prevents the common mistake of cutting costs in areas that actually support competitive advantage.
Differentiation strategies require even more sophisticated change orchestration. Companies must continuously innovate their products, services, or customer experiences while maintaining operational excellence. Change Management creates the internal flexibility needed for innovation by helping teams adopt new technologies, develop fresh skills, and embrace experimental approaches. It ensures that differentiation efforts align with overall strategic direction rather than creating organizational confusion.
Focus strategies depend on deep understanding of specific market segments or geographic regions. Change Management helps organizations maintain this focus while adapting to evolving customer needs within their chosen niche. It prevents scope creep that might dilute competitive advantage while ensuring the organization remains responsive to segment-specific changes.
The analytical perspective reveals that strategic alignment through Change Management creates multiplicative rather than additive effects. When internal capabilities align properly with chosen strategies, organizations experience performance improvements that exceed the sum of individual changes. This alignment also creates defensive advantages, making it harder for competitors to replicate successful approaches because they lack the internal change capabilities needed for implementation.
Research from leading consulting firms demonstrates that organizations with strong change capabilities maintain competitive advantages longer than those without such capabilities. They adapt faster to market shifts, implement strategic initiatives more effectively, and recover more quickly from setbacks. This resilience becomes particularly valuable during economic uncertainty or industry disruption.
Table 2: Porter’s Generic Strategies and Change Management Applications
| Strategy Type | Change Management Focus | Implementation Approach | Competitive Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Leadership | Process optimization and efficiency improvements | Systematic workflow analysis and automation | Sustainable cost advantages through operational excellence |
| Differentiation | Innovation capability and customer experience enhancement | Creative development processes and market responsiveness | Unique value propositions that competitors cannot easily copy |
| Cost Focus | Niche market efficiency and specialized operations | Targeted process improvements for specific segments | Dominant position in chosen market segments through superior economics |
| Differentiation Focus | Specialized expertise and customized solutions | Deep capability development for niche requirements | Premium positioning based on unmatched segment expertise |
2. Change Management Strengthens Workforce Agility and Talent Readiness
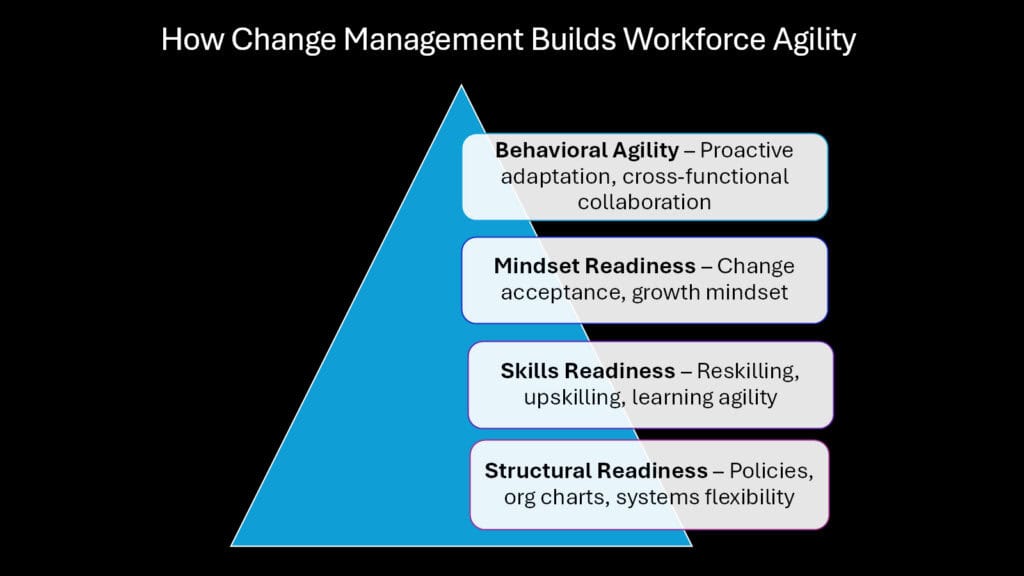
The velocity of skill obsolescence in today’s economy creates unprecedented challenges for workforce development. Traditional training approaches cannot keep pace with rapidly evolving job requirements, particularly in technology-driven industries. Change Management addresses this challenge by creating systematic approaches to talent readiness that anticipate rather than react to skill shifts.
Workforce agility emerges from psychological and structural factors working together. Change Management helps organizations develop growth mindsets among employees, making them more receptive to learning new skills and adapting to different roles. This psychological preparation proves just as important as technical training because it determines how quickly people embrace new challenges rather than resist them.
The structural elements involve creating career pathways that encourage versatility rather than narrow specialization. Change Management guides the design of job roles, performance metrics, and advancement opportunities to reward adaptability alongside expertise. This approach builds organizations where people actively seek new learning opportunities rather than avoiding them.
Analytics from recent studies indicate that organizations with strong change management practices report higher levels of employee adaptability and faster skill acquisition rates. These capabilities become particularly valuable during economic transitions when entire industries must rapidly evolve their workforce capabilities. Companies that cannot adapt their talent quickly find themselves unable to capitalize on new opportunities or respond to competitive threats.
The ripple effects extend beyond individual skill development to organizational learning capacity. Teams that regularly practice adapting to change develop collaborative problem-solving abilities that enhance overall performance. They become more creative in approaching challenges, more resilient when facing setbacks, and more innovative in developing solutions.
International examples demonstrate these principles across different economic contexts. Japanese companies have long emphasized workforce flexibility through rotation programs and cross-functional training. European organizations increasingly invest in reskilling initiatives that help workers transition between industries. American companies focus on agile workforce development that supports rapid scaling and pivoting of business models.
Table 3: Workforce Agility Components Through Change Management
| Agility Component | Development Method | Business Impact | Measurement Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Velocity | Continuous skill development programs | Faster adaptation to new technologies | Time to competency in new roles |
| Role Flexibility | Cross-functional experience and rotation | Ability to redeploy talent during transitions | Employee mobility across departments |
| Innovation Mindset | Creative problem-solving training | Generation of improvement ideas | Number of employee-driven innovations |
| Resilience Building | Change simulation and scenario planning | Maintained performance during disruption | Productivity levels during change periods |
| Collaboration Skills | Team-based change projects | Enhanced cross-functional cooperation | Project success rates in diverse teams |
3. Change Management Drives Innovation Through Organizational Design
The McKinsey 7-S Framework reveals how Change Management creates innovation-friendly environments by harmonizing structure, systems, style, staff, skills, strategy, and shared values. Innovation requires more than creative individuals; it demands organizational architectures that support experimentation, learning from failure, and rapid iteration of ideas.
Structural elements must balance stability with flexibility. Change Management helps organizations design reporting relationships, decision-making processes, and resource allocation mechanisms that support both operational excellence and innovative exploration. This balance prevents the common problem where innovation initiatives get starved of resources or killed by bureaucratic processes.
Systems integration becomes crucial for innovation success. Change Management ensures that performance measurement systems, communication technologies, and knowledge management platforms support rather than hinder creative work. Many organizations inadvertently discourage innovation through systems that punish failure or reward only short-term results.
Cultural alignment through shared values creates the foundation for sustained innovation. Change Management helps establish and reinforce values that encourage experimentation, celebrate learning, and reward calculated risk-taking. These cultural elements determine whether innovation initiatives receive genuine support or merely lip service from the organization.
The style component addresses leadership behaviors that either enable or constrain innovation. Change Management develops leadership capabilities that include comfort with ambiguity, willingness to challenge assumptions, and ability to provide resources for uncertain outcomes. Leaders who cannot adapt their style to support innovation become bottlenecks that limit organizational creative potential.
Staff and skills considerations involve recruiting and developing people with innovation capabilities while maintaining operational excellence. Change Management creates talent strategies that build diverse teams with complementary strengths, ensuring that innovative ideas can be both generated and implemented effectively.
Analysis of successful innovation programs reveals that organizations with integrated change management approaches achieve higher success rates and faster time-to-market for new products or services. They avoid the common pitfall of treating innovation as separate from operational excellence, instead creating synergies between stability and creativity.
Table 4: McKinsey 7-S Framework Application for Innovation Through Change Management
| Framework Element | Innovation Requirement | Change Management Intervention | Innovation Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy | Clear innovation direction aligned with business goals | Strategic planning that integrates innovation priorities | Focused resource allocation for high-impact opportunities |
| Structure | Flexible organizational forms that support experimentation | Design of innovation-friendly reporting relationships | Reduced bureaucratic barriers to creative work |
| Systems | Processes that enable rapid testing and learning | Performance systems that reward learning from failure | Faster iteration cycles and improved success rates |
| Shared Values | Culture that celebrates creativity and calculated risk-taking | Values alignment initiatives and culture change programs | Organizational commitment to innovation excellence |
| Style | Leadership approaches that enable rather than constrain innovation | Leadership development focused on innovation capabilities | Managers who effectively guide creative processes |
| Staff | Teams with diverse perspectives and complementary skills | Talent strategies that build innovation-capable workforces | Cross-functional collaboration that generates breakthrough ideas |
| Skills | Capabilities in both creative thinking and implementation | Training programs that develop innovation competencies | Employees who can both generate and execute innovative solutions |
4. Change Management Fosters Emotional Trust During Business Disruption
Business disruption triggers fundamental human responses that often work against organizational success. Fear of job loss, uncertainty about future roles, and concern about changing relationships create emotional turbulence that can derail even well-planned transformation initiatives. Change Management addresses these emotional dynamics by building trust through transparent communication, empathetic leadership, and consistent support systems.
The psychology of change reveals that people need to process emotional transitions before they can embrace new behaviors or approaches. Change Management creates structured opportunities for this processing through communication sessions, feedback mechanisms, and peer support networks. These interventions help employees move from resistance through exploration to commitment rather than getting stuck in negative emotional states.
Trust building requires consistent actions over time rather than one-time communications. Change Management establishes ongoing dialogue processes that keep people informed about progress, challenges, and adjustments to plans. This transparency reduces the anxiety that comes from uncertainty while building confidence in leadership’s ability to navigate complex transitions.
Emotional intelligence becomes a critical leadership capability during change periods. Change Management includes development programs that help managers recognize emotional responses, provide appropriate support, and maintain empathy while driving necessary changes. Leaders who cannot connect emotionally with their teams often find that technical excellence cannot overcome human resistance.
International research demonstrates significant variations in how different cultures process change emotionally. European organizations often emphasize consensus-building and extended consultation periods. Asian companies may focus on maintaining face and honor during transitions. American businesses typically prioritize speed and efficiency while providing individual support. Successful Change Management adapts emotional support strategies to cultural contexts.
The influence of emotional trust on business outcomes reaches well beyond mere employee satisfaction. Teams that trust their leaders during change implement new processes more quickly, generate more improvement suggestions, and maintain higher performance levels throughout transitions. They also recover more rapidly from setbacks and show greater resilience during subsequent changes.
Table 5: Emotional Trust Building Through Change Management
| Trust Component | Building Method | Emotional Impact | Business Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transparent Communication | Regular updates on progress and challenges | Reduced anxiety and uncertainty | Higher employee engagement during transitions |
| Empathetic Leadership | Training managers in emotional intelligence | Increased psychological safety | Better performance maintenance during change |
| Consistent Support | Ongoing coaching and assistance programs | Enhanced confidence in leadership | Faster adoption of new behaviors |
| Peer Networks | Change champion and support group systems | Collective resilience building | Improved teamwork and collaboration |
| Recognition Programs | Acknowledgment of adaptation efforts | Positive reinforcement of change behaviors | Sustained motivation throughout transformation |
5. Change Management Enhances Value Creation in the Customer Journey
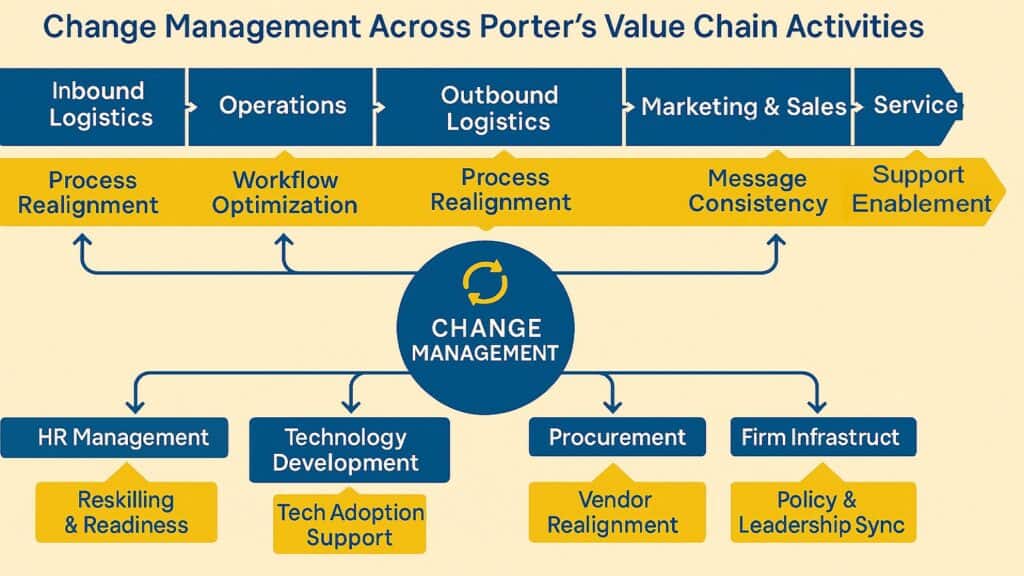
Porter’s Value Chain Analysis provides a systematic framework for understanding how Change Management improves both primary and support activities that impact customer experience. Every touchpoint along the customer journey presents opportunities for value enhancement when internal changes align properly with customer needs and expectations.
Primary activities including inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing, sales, and service all benefit from Change Management interventions. When organizations modify these activities, customer experience can either improve dramatically or deteriorate significantly depending on how well the changes are managed. Change Management ensures that customer-facing improvements happen smoothly while maintaining service quality.
Support activities such as firm infrastructure, human resource management, technology development, and procurement create the foundation for customer value creation. Changes in these areas often have delayed but significant impacts on customer experience. Change Management helps organizations anticipate and manage these ripple effects to prevent negative customer impacts while maximizing positive outcomes.
The analytical approach reveals that customer journey improvements require coordination across multiple value chain activities simultaneously. Change Management provides the orchestration needed to ensure that marketing promises align with operational capabilities, that technology changes support rather than complicate customer interactions, and that employee training prepares staff for new customer expectations.
Economic analysis from various markets demonstrates that organizations with strong change management capabilities achieve higher customer satisfaction scores and better retention rates during transformation periods. They avoid the common problem where internal changes create temporary service disruptions that damage customer relationships. Instead, they often use change initiatives as opportunities to strengthen customer connections.
Regional variations in customer expectations require different approaches to value chain changes. European customers often prioritize data privacy and environmental responsibility. Asian markets may emphasize relationship building and personalized service. American consumers generally prioritize convenience and efficiency. Change Management helps organizations adapt value chain modifications to meet these varying expectations.
The multiplicative effects of value chain improvements become apparent when changes in multiple activities reinforce each other. For example, technology upgrades that improve operations can also enhance customer service capabilities, creating compound benefits that exceed the sum of individual improvements.
Table 6: Value Chain Enhancement Through Change Management
| Value Chain Activity | Change Management Focus | Customer Impact | Value Creation Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inbound Logistics | Supplier relationship and process optimization | Improved product availability and quality | Enhanced customer satisfaction through reliable service |
| Operations | Production efficiency and quality improvements | Consistent product performance | Stronger brand reputation and customer loyalty |
| Outbound Logistics | Distribution network and delivery optimization | Faster and more reliable product delivery | Competitive advantage through superior logistics |
| Marketing and Sales | Customer communication and engagement enhancement | Better understanding of customer needs | Increased conversion rates and customer acquisition |
| Service | Support process improvement and capability building | Faster problem resolution and proactive assistance | Higher customer retention and positive word-of-mouth |
| Technology Development | Innovation systems and digital capability building | Advanced product features and service options | Market differentiation and premium positioning |
| Human Resource Management | Service-oriented culture and skill development | Improved customer interactions across all touchpoints | Consistent brand experience and customer advocacy |
| Procurement | Strategic sourcing and quality assurance | Cost-effective solutions with maintained quality | Competitive pricing while preserving customer value |
6. Change Management Accelerates Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption
Digital transformation represents one of the most complex change challenges facing organizations today. The digital transformation market is projected to reach $1,009.8 billion by 2025, yet technical implementations frequently fail to deliver promised benefits because organizations underestimate the human side of technology adoption. Change Management bridges this gap by addressing the cultural, behavioral, and organizational factors that determine technology success.
The technical deployment of digital systems represents only the beginning of the transformation. Change Management recognizes that technology adoption requires fundamental shifts in how people work, communicate, and make decisions. These behavioral changes often prove more challenging than the technical implementation itself, requiring sustained attention and support to achieve lasting results.
Cultural transformation becomes essential for digital success. Organizations must shift from traditional hierarchical decision-making to more collaborative, data-driven approaches. Change Management helps establish new norms around information sharing, experimentation, and continuous learning that support digital ways of working. Without these cultural shifts, even sophisticated technology implementations may fail to improve performance.
Workflow redesign requires careful orchestration to maintain productivity while implementing new systems. Change Management provides methodologies for sequencing changes, training users, and providing ongoing support that minimize disruption while maximizing adoption. This approach prevents the productivity dips that often accompany technology implementations.
AI integration in change management enables real-time sentiment analysis, adaptive communication strategies, and data-driven decision-making to improve adoption rates. This technological enhancement of Change Management itself demonstrates how digital tools can improve transformation processes when properly implemented.
International examples illustrate different approaches to digital transformation across economic contexts. Scandinavian countries emphasize employee participation and consensus-building during technology implementations. German organizations focus on engineering excellence and systematic rollout processes. Silicon Valley companies prioritize rapid iteration and learning from failure. Each approach requires different Change Management strategies to support cultural contexts.
The business impact extends beyond operational efficiency to strategic capabilities. Organizations that successfully manage digital transformation develop new abilities to serve customers, create products, and compete in digital markets. They also build change capabilities that prepare them for future technological disruptions.
Table 7: Digital Transformation Acceleration Through Change Management
| Transformation Element | Change Management Approach | Implementation Challenge | Business Capability Gained |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Platform | User-centered design and training programs | Resistance to new systems and processes | Enhanced operational efficiency and data-driven decision making |
| Data Analytics | Culture change toward evidence-based decisions | Shift from intuition-based to analytical approaches | Improved strategic insights and predictive capabilities |
| Automation Systems | Workforce transition and reskilling initiatives | Job displacement concerns and skill gaps | Reduced operational costs and improved accuracy |
| Customer Digital Experience | Cross-functional collaboration and design thinking | Integration across multiple customer touchpoints | Enhanced customer satisfaction and competitive differentiation |
| Cloud Infrastructure | Security awareness and new working practices | Data governance and access control challenges | Increased scalability and operational flexibility |
| Mobile Technologies | Remote work enablement and collaboration tools | Communication and coordination across distributed teams | Greater workforce agility and customer responsiveness |
Conclusion: Change Management Is the Leadership Blueprint for a Business-Ready Future

The evidence presented throughout this analysis converges on a single powerful conclusion: Change Management has evolved from a support function into the strategic backbone that determines organizational success in the modern economy. The six brilliant ways it elevates business performance create interconnected advantages that compound over time, building competitive moats that become increasingly difficult for rivals to cross.
Strategic alignment through Change Management enables organizations to maintain coherent direction while adapting to market shifts. This capability becomes particularly valuable during uncertain economic periods when companies must simultaneously cut costs, invest in growth, and maintain employee engagement. The systematic approach prevents the conflicting initiatives and resource waste that often characterize poorly managed transformation efforts.
Workforce agility represents perhaps the most sustainable competitive advantage in rapidly changing markets. Organizations that can quickly develop new capabilities, redeploy talent, and adapt to disruptive technologies will outperform those constrained by rigid skill sets and resistant cultures. Change Management provides the methodologies and mindsets needed to build this adaptability into organizational DNA.
The innovation outcomes achieved through proper organizational design create exponential rather than linear improvements. When structure, systems, and culture align to support creativity, organizations generate breakthrough solutions that redefine their industries. This innovation capability becomes self-reinforcing as success builds confidence and resources for further experimentation.
Emotional trust building through Change Management creates the psychological foundation for all other improvements. Without employee commitment and engagement, even the best strategies and technologies fail to deliver results. The investment in trust pays dividends across every aspect of organizational performance while building resilience for future challenges.
Value creation enhancement demonstrates how internal changes can dramatically improve customer outcomes when properly orchestrated. This customer focus ensures that transformation efforts create external value rather than just internal efficiency, building revenue growth alongside cost management.
Digital transformation acceleration positions organizations for future success in increasingly digital markets. Companies that master the human side of technology adoption gain advantages that extend far beyond current implementations, building capabilities for ongoing digital evolution.
The integration of these six approaches creates organizational systems that thrive on change rather than merely surviving it. These organizations view disruption as an opportunity, treat adaptation as a competitive advantage, and use transformation as a strategic weapon. They understand that Change Management is not about managing specific projects but about building organizational capabilities for continuous evolution.
Table 8: Change Management Impact on Business Functions
| Business Functions | Change Management Influence | Strategic Outcome | Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing | Customer-centric transformation and brand evolution | Enhanced market positioning and customer engagement | Stronger brand differentiation and market share growth |
| Sales | Process optimization and digital selling capabilities | Improved conversion rates and customer acquisition | Superior sales performance and revenue growth |
| Operations | Efficiency improvements and quality enhancement | Reduced costs and improved service delivery | Operational excellence and customer satisfaction |
| Finance | Financial process automation and strategic analysis | Better resource allocation and performance measurement | Enhanced profitability and financial resilience |
| Corporate Strategy | Strategic planning integration and execution excellence | Aligned organizational direction and faster strategy implementation | Sustained competitive positioning and market leadership |
| Information Technology | Digital transformation and technology adoption | Advanced technical capabilities and innovation enablement | Technology-driven competitive advantages and operational efficiency |
The future belongs to organizations that recognize Change Management as essential infrastructure rather than optional support. These companies invest in change capabilities during stable periods, preparing for inevitable disruptions rather than reacting to them. They understand that the ability to change effectively is itself the most important capability for long-term success.
As markets continue accelerating and disruption becomes constant, the organizations that master Change Management will write the success stories of tomorrow’s economy. They will transform challenges into opportunities, uncertainty into competitive advantage, and change itself into their most powerful strategic asset.




