Table of Contents
Introduction: AI Job Growth and the Bright Future Hidden Behind the Headlines
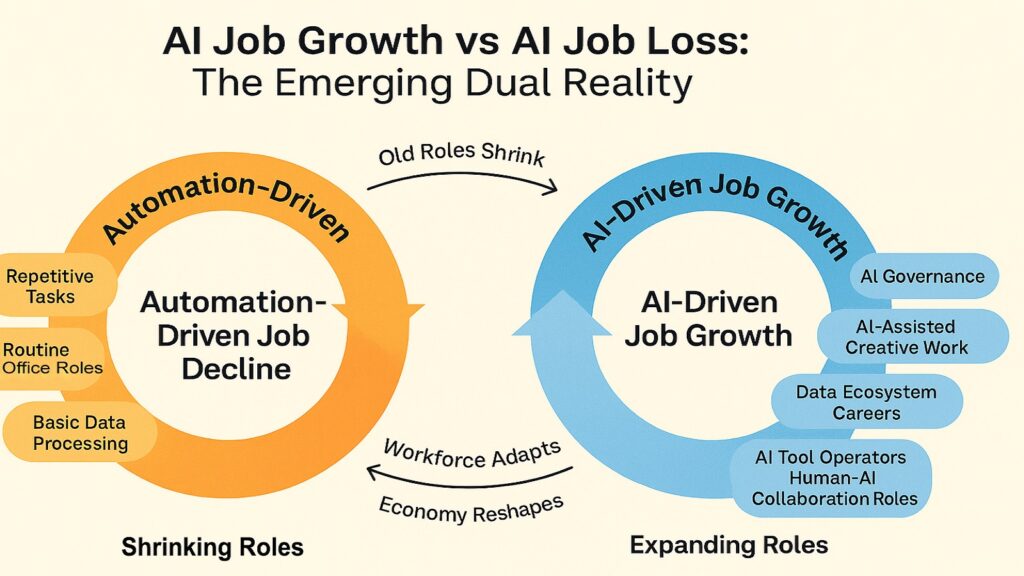
The headlines scream about layoffs. Every week brings another story about companies cutting positions because of artificial intelligence. We covered the topic of AI Job Losses in another article. Those job losses hurt real people in real ways. But while those stories dominate the news cycle, something else happens beneath the surface that deserves equal attention. The same force that disrupts old roles creates new ones at an even faster pace. This reality of AI Job Growth remains hidden behind the anxiety and fear that naturally come with change.
Consider the numbers. Industries most exposed to AI saw job availability increase by 38 percent between 2019 and 2024, according to analysis from PwC. Workers with AI skills now command wage premiums averaging 56 percent above similar roles without those skills. These are not just statistics. They represent actual opportunity expanding in real time across the economy. The disruption remains real, but the creation proves even more powerful.
The six trends explored here paint a picture of transformation rather than elimination. AI does not simply replace human effort. It amplifies what people can do when freed from repetitive tasks that machines handle better. The new roles emerging require creativity, judgment, and collaboration that only humans provide. Some jobs disappear, yes. But more appear in their place, often with better pay and more meaningful work. This phenomenon of AI Job Growth already reshapes how millions earn their living.
AI Job Growth: Current Market Indicators
| Market Signal | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Job posting growth in AI-exposed occupations | 38% increase from 2019 to 2024 across industries most affected by AI tools |
| Wage premium for workers with AI skills | 56% higher compensation compared to similar positions without AI capabilities |
| AI-related job postings increase | 25.2% year-over-year growth in dedicated AI positions through Q1 2025 |
| Productivity gains in AI-adopting sectors | Nearly 5 times higher labor productivity growth versus less-exposed industries |
| Revenue growth in AI-enabled companies | 27% per employee compared to 9% in companies with minimal AI adoption |
| Shift in degree requirements | 7 to 9 percentage point decrease in formal degree demands for AI-exposed roles |
1. AI Job Growth Through Human-AI Collaboration Trends
The factory floor tells the story best. A machine operator who once spent eight hours performing the same motion now monitors systems that handle repetitive tasks. She troubleshoots problems, suggests improvements, and trains new workers. Her hands stay clean. Her mind stays engaged. The machine does not replace her. It makes her more valuable. This pattern repeats across industries in countless variations, driving AI Job Growth through partnership rather than displacement.
PwC research shows that sectors leveraging AI tools see productivity growth approaching five times higher than those without. Workers equipped with these technologies complete tasks 66 percent faster, matching what would take 47 years of natural productivity improvements in the United States. The gains concentrate most heavily among less experienced workers, who improve output by 35 percent when given AI assistance. Senior employees maintain their performance while junior colleagues close the gap faster.
The new job titles reflect this collaboration. AI-assisted designers create twice as many concepts in the same time. Prompt engineers craft instructions that guide machine output. Data analysts who once spent weeks cleaning spreadsheets now focus on interpretation and strategy. Customer service representatives handle complex issues while chatbots resolve routine questions. Each role combines human judgment with machine speed and consistency.
This partnership creates value that neither humans nor machines generate alone. An architect sketches rough ideas that AI tools render into detailed plans within minutes. A financial analyst tests dozens of scenarios in the time previously required for three. A legal researcher finds relevant precedents across millions of pages in seconds, then applies expertise to build arguments. The human provides direction and evaluation. The machine provides scale and speed. Together, they accomplish what was impossible before, fueling AI Job Growth across professions.
AI Job Growth: Human-AI Collaboration Roles
| Collaboration Role | Function |
|---|---|
| AI Prompt Engineer | Designs and refines instructions that optimize AI system outputs for specific business needs |
| Machine Learning Operations Specialist | Maintains and monitors AI systems while ensuring they integrate smoothly with existing workflows |
| AI-Assisted Data Analyst | Leverages automated tools for data processing while focusing expertise on interpretation and strategy |
| Hybrid Customer Success Manager | Uses AI chatbots for routine inquiries while handling complex relationship-building and problem-solving |
| Augmented Research Analyst | Employs AI to scan vast information sources then applies human judgment to synthesize insights |
| AI Quality Assurance Reviewer | Evaluates machine outputs for accuracy and appropriateness using domain knowledge and context |
2. AI Job Growth in New Creative and Digital Hybrid Roles
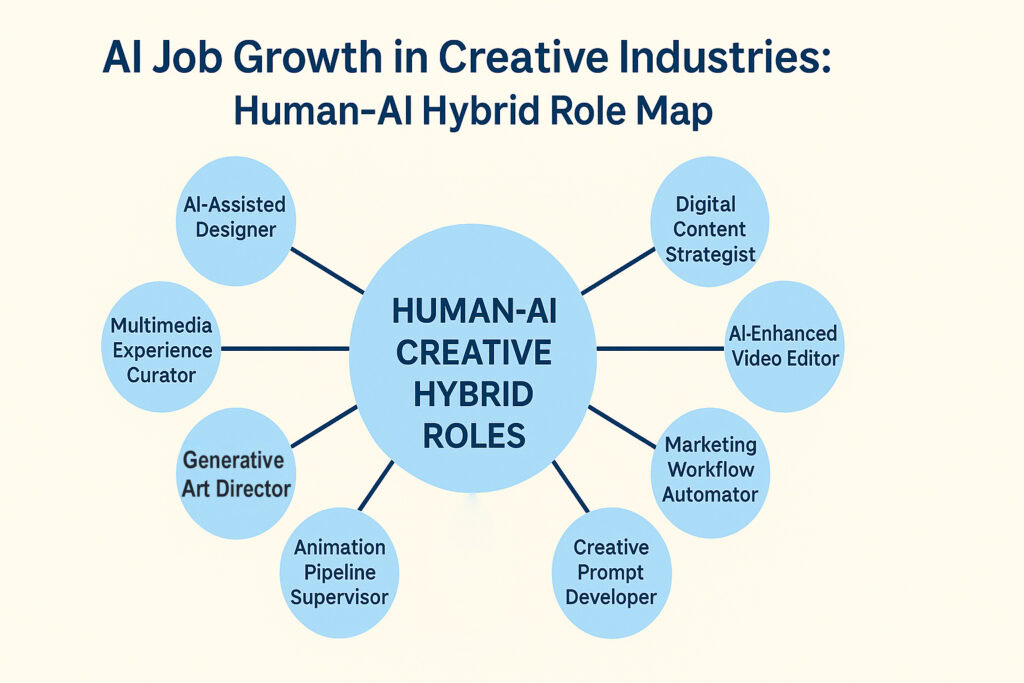
The designer sits at her desk surrounded by iterations. Twenty variations of the same logo spread across her screen. She created them in thirty minutes. Without AI assistance, producing this many options would have consumed two days. Now she spends that saved time refining the best concepts and discussing vision with clients. Her creativity expands rather than contracts. This multiplication of possibilities defines AI Job Growth in creative fields.
Job postings mentioning AI in design and creative sectors increased by over 120 percent during 2024, according to Autodesk research analyzing nearly three million listings. The fastest-growing positions include AI Content Creator, which surged 134.5 percent year over year. These roles blend human imagination with machine capability to produce work that neither could achieve independently. A video editor cuts footage while AI suggests transitions and color grades. A writer crafts narratives while algorithms check tone and optimize structure. A musician composes melodies while software generates harmonies and arrangements.
The creative process transforms under this hybrid approach. Marketing teams test dozens of campaign concepts instead of three. Animation studios produce complex sequences at a fraction of the previous cost. Photographers enhance images in seconds rather than hours. Media companies personalize content for different audiences simultaneously. Each innovation expands what small teams accomplish and creates demand for professionals who master both creative vision and technical tools.
These positions pay well and grow quickly. Design skills now rank as the most in-demand capability in AI-specific job listings, surpassing traditional technical competencies like coding. Companies seek people who understand aesthetics, storytelling, and human psychology while wielding powerful digital tools. The combination remains rare enough to command premium compensation. As AI handles more technical execution, human creativity becomes a scarce and valuable resource, driving AI Job Growth in these hybrid roles.
AI Job Growth: Creative and Digital Hybrid Positions
| Hybrid Creative Role | Core Contribution |
|---|---|
| AI-Enhanced Content Strategist | Develops creative concepts and brand narratives while using AI tools to test messaging effectiveness |
| Generative AI Visual Designer | Combines artistic vision with AI image generation to produce original creative assets rapidly |
| Synthetic Media Producer | Creates and edits video content using AI-powered tools for animation, voice synthesis, and effects |
| Interactive Experience Designer | Builds engaging digital experiences by merging human-centered design principles with AI capabilities |
| AI-Assisted Copywriter | Crafts compelling marketing copy and content while leveraging AI for ideation and optimization |
| Multimedia Automation Specialist | Develops workflows that integrate AI tools into creative production pipelines efficiently |
3. AI Job Growth Fueled by the Rise of AI Governance and Ethics Careers
The boardroom fills with questions. Should we deploy this algorithm? Does it treat all customers fairly? What happens if it makes a mistake? Who bears responsibility? These questions did not exist a decade ago. Now they drive entire careers dedicated to ensuring AI systems work safely and ethically. This expansion of governance roles represents one of the fastest sources of AI Job Growth.
More than 100,000 professionals with expertise in AI ethics and governance are now requested annually in job postings, according to research analyzing over four million listings from 2018 to 2023. The demand grew rapidly in both absolute terms and as a proportion of all AI-related positions. Responsible AI mentions in job descriptions increased from practically zero in 2019 to nearly one percent of all AI postings by 2025. The EU AI Act and similar regulations worldwide create an urgent need for compliance specialists who understand both technology and law.
The work itself spans multiple domains. AI Ethics Officers evaluate systems for fairness and bias. AI Governance Managers design policies that guide development and deployment. Algorithmic Auditors test models for discriminatory outcomes. Regulatory Compliance Specialists ensure systems meet evolving legal standards. Data Privacy Analysts protect sensitive information used in training. Risk Assessment Coordinators identify potential harms before they occur. Each position requires unique combinations of technical knowledge, ethical reasoning, and stakeholder communication.
Companies recognize these roles as essential rather than optional. As AI touches more decisions about lending, hiring, healthcare, and law enforcement, the consequences of poorly designed systems grow severe. Organizations that deploy AI without governance face lawsuits, regulatory fines, and reputation damage. Those who invest in ethical frameworks gain a competitive advantage and public trust. The AI governance market grew from 227 million dollars in 2024 to a projected 2.78 billion by 2033, representing a 32 percent annual growth rate. This expansion creates sustained AI Job Growth for professionals who bridge technology and responsibility.
AI Job Growth: Governance and Ethics Positions
| Governance Role | Primary Responsibility |
|---|---|
| AI Ethics Officer | Establishes and enforces ethical guidelines ensuring AI systems align with organizational values |
| Algorithmic Fairness Auditor | Tests AI models for discriminatory outcomes and bias across demographic groups |
| AI Regulatory Compliance Manager | Ensures AI deployments meet legal requirements under frameworks like the EU AI Act |
| Responsible AI Program Director | Designs and implements organization-wide strategies for ethical AI development |
| AI Risk Assessment Specialist | Identifies potential harms from AI systems before deployment and develops mitigation plans |
| AI Transparency Coordinator | Creates documentation and communication strategies explaining AI decisions to stakeholders |
4. AI Job Growth Driven by the Expansion of Data and Synthetic Data Work
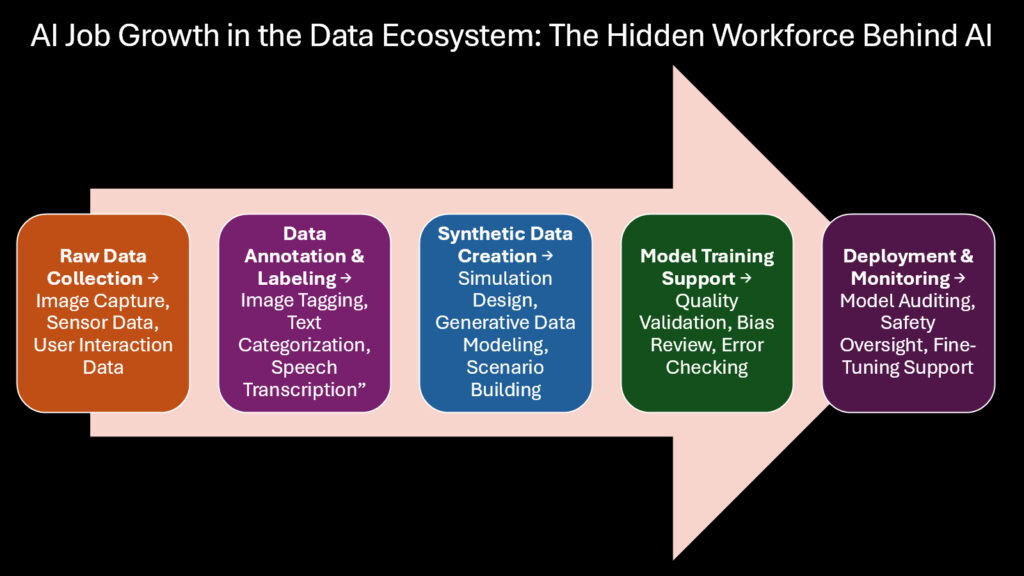
The algorithm learns from examples. Show it a thousand labeled images and it recognizes patterns. Feed it a million customer transactions and it predicts behavior. Every AI breakthrough depends on clean, organized data that humans prepare. This fundamental requirement creates a massive demand for workers who label, annotate, and curate the information that trains intelligent systems. The data labeling market reached 2.2 billion dollars in 2024 and is projected to expand at 27.4 percent annually through 2031, fueling substantial AI Job Growth.
The work takes many forms. Data annotators draw boxes around objects in images to teach computer vision systems. Transcriptionists convert speech to text for language models. Labelers categorize customer service tickets to train chatbots. Quality reviewers verify that annotations meet standards. Each task requires human judgment to identify what matters in messy real-world information. Companies like Scale AI employ thousands performing these essential functions that remain invisible to most technology users.
Synthetic data adds another dimension. Rather than collecting and labeling real information, engineers now create artificial datasets that mimic reality. This approach solves problems around privacy, scarcity, and cost. Healthcare researchers generate synthetic patient records to train diagnostic AI without exposing private medical information. Autonomous vehicle companies simulate millions of miles of driving scenarios that would take decades to capture naturally. Financial institutions create synthetic transaction data for testing fraud detection without risking actual customer information.
The synthetic data generation market exploded alongside AI adoption. It addresses data scarcity in specialized domains where examples remain limited. A hospital might have hundreds of rare disease cases instead of the thousands needed to train reliable AI. Synthetic generation bridges that gap. It also speeds development by producing labeled examples automatically rather than through manual annotation. Jobs in this field require understanding both statistical modeling and domain expertise. The combination drives AI Job Growth among data scientists, simulation engineers, and specialized annotators who validate synthetic outputs.
AI Job Growth: Data and Synthetic Data Roles
| Data Role | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Data Annotation Specialist | Labels text, images, video, and audio to create training datasets for machine learning models |
| Computer Vision Annotator | Identifies and marks objects in visual data enabling AI to recognize patterns and features |
| Synthetic Data Engineer | Designs algorithms that generate artificial datasets mimicking real-world information patterns |
| Data Quality Analyst | Reviews labeled datasets for consistency and accuracy ensuring model training effectiveness |
| Domain-Specific Labeling Expert | Applies specialized knowledge in fields like medicine or law to annotate complex professional data |
| Data Pipeline Coordinator | Manages workflows connecting data collection, annotation, validation, and model training processes |
5. AI Job Growth Emerging from the Global Upskilling and Reskilling Wave
The warehouse manager faced a choice. His team needed new skills to work with automated inventory systems. Traditional training would take months and cost thousands per worker. Instead, he enrolled them in an AI-powered learning platform that personalized instruction based on each person’s background. Within six weeks, his team operated the new systems confidently. The program cost a fraction of conventional training and delivered better results. This democratization of skill development drives AI Job Growth by making career transitions faster and more accessible.
Nearly 92 percent of technology roles now require evolution to incorporate AI capabilities, according to the AI-Enabled ICT Workforce Consortium. Skills demanded by employers in AI-exposed occupations change 25 percent faster than in other fields. Workers face urgent pressure to adapt, but AI itself provides the solution. Intelligent tutoring systems assess individual knowledge gaps and customize learning paths. Virtual practice environments let people develop expertise without expensive equipment or supervision. Automated feedback loops accelerate improvement by identifying mistakes immediately.
Major companies invest billions in these programs. PwC committed three billion dollars to upskilling initiatives accessible to all employees. Amazon allocated over 1.2 billion dollars to prepare its workforce for automation and robotics. Google announced more than 130 million dollars in funding for AI training globally. SAP pledged to upskill two million people worldwide by 2025. These investments reflect recognition that workforce capability determines competitive advantage. Organizations that develop talent internally capture more value than those scrambling to hire scarce specialists.
Accessibility matters most. Previously, learning advanced skills required university degrees, expensive bootcamps, or years of apprenticeship. AI-powered platforms deliver quality instruction for hundreds of dollars instead of tens of thousands. Workers in rural areas have access to the same training as those in major cities. People with full-time jobs learn at night and on weekends. Formal degree requirements dropped 7 to 9 percentage points for AI-exposed positions between 2019 and 2024, as employers prioritized demonstrated capability over credentials. This shift opens pathways for millions who lacked traditional qualifications, expanding AI Job Growth across demographics and geographies.
AI Job Growth: Upskilling and Reskilling Programs
| Training Initiative | Impact |
|---|---|
| AI-Powered Learning Platforms | Deliver personalized instruction that adapts to individual skill levels and learning speeds |
| Corporate Upskilling Programs | Companies invest billions training existing workforce rather than replacing workers with automation |
| Online Certification Programs | Provide affordable credentials focused on practical AI skills without requiring formal degrees |
| Micro-Degree Programs | Offer targeted training in specific AI applications completed in weeks rather than years |
| Skills-Based Hiring Initiatives | Employers reduce degree requirements by 7-9 points emphasizing demonstrated AI capabilities instead |
| Public-Private Training Partnerships | Government and industry collaborate on programs that make AI education accessible nationwide |
6. AI Job Growth Through Small Business Innovation and Productivity Gains
The bakery owner works alone. She bakes, manages inventory, handles social media, answers emails, and keeps books. Before AI tools, she struggled to find time for anything beyond survival. Now she uses automated scheduling for social posts, AI-generated images for marketing, chatbots for common customer questions, and smart inventory prediction. She still works hard but accomplishes what previously required three people. Her revenue doubled in eighteen months. She plans to hire two assistants next quarter. This multiplication of small business capability drives AI Job Growth from the bottom up.
Small and medium enterprises comprise 43.5 percent of the United States GDP and employ more than half the workforce. Their productivity traditionally lags larger competitors by about 40 percent due to limited resources and expertise. AI tools narrow that gap dramatically. McKinsey estimates that AI adoption could add up to 3.4 percentage points to annual productivity growth, which would increase federal tax revenue by more than six billion dollars annually. Small businesses gain the most because they operate furthest from the efficiency frontier.
The AI and automation tools become more accessible every month. Marketing automation that once cost thousands now runs for tens of dollars. AI writing assistants help non-native speakers communicate professionally. Image generators let businesses without designers create compelling visuals. Customer relationship management systems powered by AI guide sales conversations and predict which prospects will convert. Financial tools forecast cash flow and identify cost savings. Even complex analyses like market research and competitive intelligence have become affordable through AI-powered platforms.
As small businesses grow faster, they create more jobs. A freelance consultant who previously handled three clients simultaneously now manages eight using AI tools for research, proposal writing, and project management. She needs an administrative assistant. A small manufacturer doubles output using predictive maintenance and automated quality control. He adds a second shift. A retail store optimizes inventory with AI forecasting and expands to a second location. They hire four more employees. Each efficiency gain creates capacity for expansion. The productivity improvements do not eliminate work. They enable growth that generates new positions, sustaining AI Job Growth throughout the economy.
AI Job Growth: Small Business Innovation With AI Applications
| Business Functions | AI-Enabled Improvement |
|---|---|
| Marketing and Customer Acquisition | AI tools automate social media scheduling, generate marketing content, and optimize ad targeting |
| Customer Service Operations | Chatbots handle routine inquiries allowing small teams to focus on complex relationship-building |
| Financial Management and Planning | AI-powered accounting automates invoicing, expense tracking, and cash flow forecasting |
| Inventory and Supply Chain | Predictive algorithms optimize stock levels reducing waste and preventing shortages |
| Sales Process Optimization | AI systems qualify leads, personalize outreach, and predict conversion likelihood |
| Product Development | Automated market research and customer feedback analysis guide innovation decisions |
Conclusion: AI Job Growth and the Expanding Possibilities of Tomorrow’s Economy
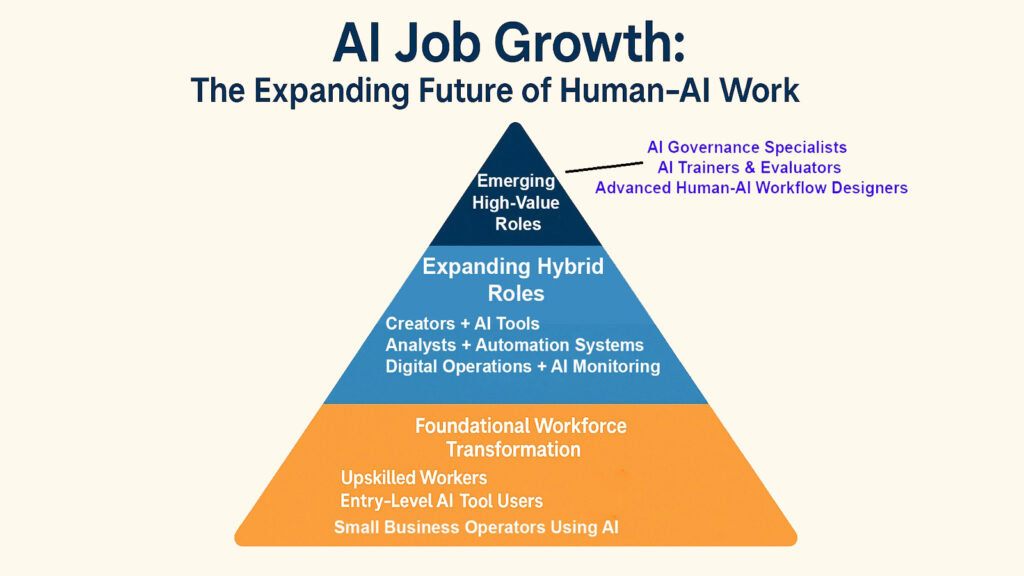
The six trends converge on a single truth. AI does not simply eliminate roles and leave workers stranded. It transforms how value gets created and shifts labor toward activities that require human judgment, creativity, and social connection. The transitions hurt individuals and communities caught unprepared. But the overall trajectory points toward AI Job Growth that creates more opportunity than it destroys, often with better compensation and more engaging work than what disappeared.
The evidence accumulates across multiple dimensions. Workers with AI skills command wage premiums averaging 56 percent above similar positions without those capabilities. Job availability in AI-exposed occupations increased 38 percent even while automation advanced. AI-related positions grew 25 percent year over year through early 2025. Industries adopting AI tools see productivity gains approaching five times higher than those without. Revenue per employee increased 27 percent in companies leveraging AI compared to 9 percent for those that do not. Each data point reinforces the same pattern of expansion rather than contraction.
The new roles reflect different priorities. Where industrial automation replaced physical labor, AI augments cognitive work. Where previous technologies centralized expertise, AI tools democratize capability. Where earlier transformations benefited those with advanced degrees, AI-powered learning makes skill development accessible to millions without traditional credentials. The shift favors adaptability over tenure, creativity over repetition, and collaboration over isolation. Those who embrace these changes thrive. Those who resist struggle.
The Global economy needs more human judgment as AI handles more routine execution. This fundamental dynamic sustains AI Job Growth even as specific positions disappear. The path forward requires investment in people. Companies must train existing workers rather than simply hiring new ones. Governments need to expand access to education and support transitions. Individuals should embrace lifelong learning as a necessity rather than an option. AI, automation, and technology can enable these changes.
However, the social structures supporting them remain inadequate. Closing that gap determines whether AI Job Growth reaches its full potential or leaves too many behind. The opportunity exists. The choice remains whether we build systems that let everyone participate in the AI transformation or accept an economy that works well only for some. That decision shapes not just employment but the kind of society we become. A sustained AI job growth would need concrete social reform where everyone gets access to AI tools.
AI Job Growth: Long-Term Economic Indicators
| Economic Measure | Projected Impact |
|---|---|
| Labor productivity growth potential | AI adoption could add 2.9-3.4 percentage points to annual productivity gains |
| Global economic value addition | Generative AI features may contribute up to 4.4 trillion dollars annually to world economy |
| Net job creation by 2030 | World Economic Forum projects 78 million new positions after accounting for displacement |
| GDP growth from AI by 2030 | Local economies may experience up to 26 percent increase in GDP through AI integration |
| AI specialist job multiplier | For every AI specialist role in 2012, seven similar positions exist today |
| Skills premium continuation | Workers with AI capabilities maintain 50-56 percent wage advantage over those without |




