Table of Contents
Introduction: How Reinforcement Learning Becomes the Engine of Smart AI
Every day, machines around us learn from their own mistakes and victories. They adapt, improve, and find solutions we never taught them. This is the world shaped by Reinforcement Learning, a technique that mirrors how humans master skills through trial and error. Think about learning to ride a bicycle. You wobble, fall, adjust your balance, and eventually cruise smoothly down the street. That exact pattern of learning by doing forms the heart of Reinforcement Learning.
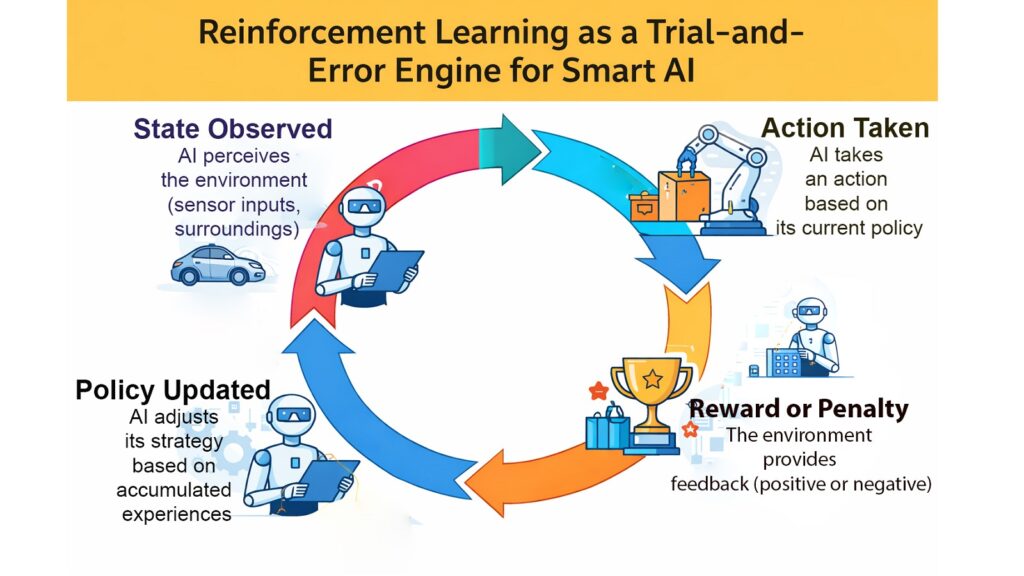
Reinforcement Learning stands apart from other artificial intelligence methods. It enables machines to make autonomous decisions by interacting with environments and receiving feedback. When an AI system takes an action, it observes the outcome and adjusts its strategy accordingly. Each success brings rewards, each failure brings lessons. Over thousands or millions of attempts, the system discovers patterns and strategies that maximize long-term success.
Systems like AlphaGo showed machines can learn to solve incredibly hard problems through trial and error. When DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated legendary Go player Lee Sedol in March 2016, over 200 million people worldwide watched the historic 4-1 victory in Seoul. This landmark moment demonstrated that Reinforcement Learning could tackle challenges once thought impossible for computers. Go, with its vast complexity and subtle strategy, had resisted automation for decades. Yet through continuous self-play and learning from experience, AlphaGo discovered winning strategies no human had conceived.
Tesla Autopilot provides another striking example of Reinforcement Learning in action. Tesla vehicles collect data from millions of miles driven daily, learning optimal driving behaviors from both human demonstrations and autonomous experiments. The fleet refines its understanding of lane keeping, obstacle avoidance, and traffic navigation through constant exposure to real-world scenarios. Warehouse robots at Amazon demonstrate similar adaptive intelligence, coordinating movements through complex facilities while learning efficient routes and avoiding collisions.
These six powerful applications reveal how Reinforcement Learning transforms modern AI from rigid, programmed systems into flexible, learning machines that improve with experience.
Reinforcement Learning Components Compared to Other AI Fields
| AI Component | Primary Focus & Application |
|---|---|
| Reinforcement Learning | Learns optimal decision-making through trial-and-error interaction with environments; excels at sequential decisions and long-term planning in robotics, games, and control systems |
| Machine Learning | Discovers patterns in data through statistical methods; includes supervised learning for classification and unsupervised learning for clustering across diverse applications |
| Natural Language Processing | Processes and generates human language; enables translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots, and text understanding through linguistic pattern recognition |
| Intelligent Robotics | Integrates perception, planning, and control for physical manipulation; combines sensors, actuators, and AI to perform tasks in manufacturing, surgery, and exploration |
| Computer Vision | Interprets visual information from images and video; powers facial recognition, medical imaging, autonomous navigation, and quality inspection systems |
| Expert Systems | Encodes domain expertise into rule-based reasoning systems; applies specialized knowledge for diagnosis, troubleshooting, and decision support in well-defined fields |
| Planning & Optimization | Finds efficient solutions to resource allocation and scheduling problems; uses algorithms like genetic methods and linear programming for logistics and operations |
| Knowledge Representation | Structures information for machine reasoning; employs ontologies, semantic networks, and knowledge graphs to enable intelligent information retrieval and inference |
1. How Reinforcement Learning Builds Adaptive Intelligence in Real Environments
Reinforcement Learning creates AI systems that continuously adapt to changing circumstances. Unlike pre-programmed robots that follow fixed instructions, systems powered by Reinforcement Learning observe their environment, assess results, and modify their behavior. This adaptability proves essential in unpredictable, dynamic settings where conditions shift moment by moment.
Consider autonomous delivery drones navigating urban landscapes. Wind patterns change, obstacles appear unexpectedly, and optimal routes vary by time of day. A Reinforcement Learning system learns from each flight. When strong winds push the drone off course, the system notes what corrections worked best. When a new building appears on a familiar route, the AI discovers alternative paths. Through thousands of flights, the drone develops robust strategies that handle diverse scenarios.
Industrial robots in manufacturing demonstrate similar adaptability. Production lines face equipment failures, material variations, and changing product specifications. Reinforcement Learning enables robots to adjust grip pressure when handling different materials, compensate for worn tools, and optimize assembly sequences as conditions evolve. The robot learns which actions produce quality outcomes and which lead to defects or delays.
Research from multiple institutions shows that Reinforcement Learning systems excel in environments with partial observability and uncertainty. When an autonomous vehicle encounters construction zones or unusual weather, it must make decisions with incomplete information. The system draws on learned experience to estimate likely outcomes and select safe, effective actions. This capacity for reasoning under uncertainty distinguishes Reinforcement Learning from simpler automation approaches.
Agricultural robots harvesting crops provide another compelling example. Ripeness varies across a field, weather affects picking conditions, and plant positioning differs for each harvest. Reinforcement Learning allows the robot to adjust its approach for each piece of fruit, learning optimal force, angle, and timing through repeated attempts. The system develops intuition about which techniques work best under specific conditions.
Reinforcement Learning Adaptation Mechanisms
| Adaptation Type | How It Works |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Environment Mapping | Continuously updates internal models as surroundings change; enables robots to recognize new obstacles and adjust paths in real-time navigation |
| Policy Refinement | Improves decision rules through experience; gradually learns which actions yield better outcomes in recurring situations |
| Transfer Learning | Applies knowledge gained in one context to similar new scenarios; allows skills learned in simulation to accelerate real-world adaptation |
| Exploration Strategies | Balances trying new approaches with exploiting proven methods; ensures systems discover better solutions while maintaining reliable performance |
| Multi-Scale Learning | Adapts at different time horizons from immediate reactions to long-term strategy; enables both quick responses and strategic planning |
| Contextual Adaptation | Recognizes different operating modes and adjusts behavior accordingly; switches strategies based on environmental conditions like weather or time |
2. Why Reinforcement Learning Enables Long-Term Decision-Making in AI Systems
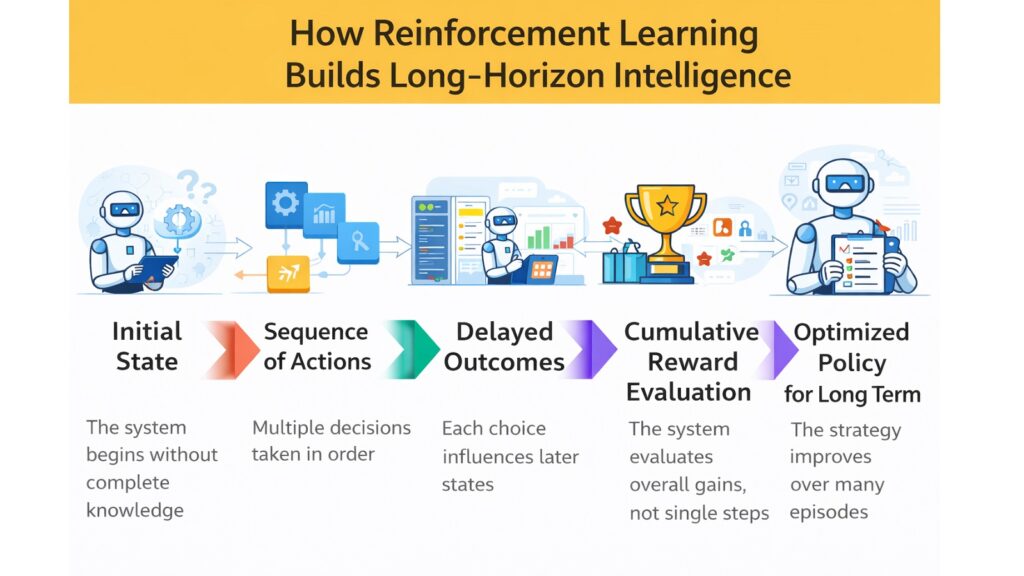
Reinforcement Learning excels at optimizing decisions across extended time horizons. While supervised learning predicts individual outcomes, Reinforcement Learning considers how current choices affect future possibilities. This temporal reasoning enables AI to make sacrifices now for greater benefits later, just as humans invest time learning skills that pay dividends over the years.
Data centers provide a perfect illustration of long-term optimization. DeepMind’s neural networks were trained on average future Power Usage Effectiveness, the ratio of total building energy to IT energy. The system learned that certain cooling adjustments increase energy use temporarily but reduce overall consumption. The machine learning approach achieved a 40 percent reduction in cooling energy, equating to a 15 percent reduction in overall PUE overhead. This required understanding how decisions cascade through complex thermodynamic systems over hours.
Predictive maintenance in industrial machinery demonstrates similar temporal reasoning. A Reinforcement Learning system might recommend running a component until optimal replacement time rather than following fixed schedules. The AI learns to balance immediate productivity against long-term equipment lifespan. It considers replacement costs, failure probabilities, and production schedules to minimize total lifecycle expenses. This holistic view contrasts with reactive approaches that only respond to breakdowns.
Financial trading systems use Reinforcement Learning to manage portfolios over quarters or years. The AI considers not just immediate returns but tax implications, market impact, and position building. It learns when to hold positions through short-term volatility for long-term appreciation. This patience and strategic thinking emerges from training the system to maximize cumulative rewards over thousands of trading days.
Supply chain optimization benefits enormously from long-horizon planning. Inventory decisions affect customer satisfaction weeks later, production scheduling impacts delivery times months ahead, and supplier relationships evolve over years. Reinforcement Learning systems learn to coordinate these interconnected decisions. They discover that slight overproduction now prevents stockouts during seasonal demand spikes, or that investing in supplier diversity creates resilience against future disruptions.
The cumulative reward framework allows systems to discover non-obvious strategies. Just as chess players sacrifice pieces for positional advantage, Reinforcement Learning finds moves that seem suboptimal in isolation but contribute to overall success. This distinguishes it from myopic optimization that only considers immediate outcomes.
Long-Term Planning Applications of Reinforcement Learning
| Application Domain | Planning Horizon & Optimization Goal |
|---|---|
| Data Center Energy Management | Hour-to-day scale cooling optimization; minimizes total energy consumption while maintaining equipment safety and performance specifications |
| Industrial Equipment Maintenance | Month-to-year scale lifecycle planning; balances immediate productivity against long-term replacement costs and failure risks |
| Supply Chain Coordination | Week-to-season scale inventory decisions; optimizes stock levels to meet future demand while minimizing holding costs and stockouts |
| Portfolio Management | Month-to-multi-year investment strategies; maximizes risk-adjusted returns while considering tax efficiency and position building |
| Grid Energy Storage | Hour-to-day scale charging decisions; optimizes battery use across variable electricity prices and renewable generation patterns |
| Agricultural Planning | Season-to-multi-year crop rotation; balances soil health, market prices, and long-term farm productivity |
3. How Reinforcement Learning Powers Autonomous Navigation and Control
Autonomous systems navigating the physical world rely heavily on Reinforcement Learning to master complex control tasks. Cars, robots, drones, and industrial equipment learn correct actions through repeated experience with their environments. The continuous feedback loop between action, observation, and adjustment enables these systems to develop sophisticated navigation capabilities.
Self-driving vehicles exemplify Reinforcement Learning in motion. Lane keeping requires constant micro-adjustments to steering based on visual input and vehicle dynamics. The system learns optimal correction magnitudes for different road conditions, speeds, and vehicle loads. Path planning involves selecting routes that balance travel time, safety, and fuel efficiency while adapting to traffic patterns. Tesla’s approach involves collecting data from millions of vehicles to refine autonomous driving capabilities continuously.
Speed control in autonomous vehicles presents another challenge where Reinforcement Learning shines. The system must maintain safe following distances, smoothly accelerate and decelerate for comfort, and respond to changing speed limits. Through millions of miles of experience, the AI learns how different throttle and brake inputs affect passenger comfort and safety. It discovers that gradual acceleration saves energy while abrupt braking startles passengers.
Warehouse autonomous guided vehicles coordinate complex movements through busy facilities. Pickers and AGVs need to synchronize and meet at certain item locations at matching times to execute pickups, while coordination among agents minimizes cramming at locations which causes delays. Research on Amazon’s Kiva system showed that Reinforcement Learning enables AGVs to select dynamic routes that avoid congestion and collisions while maintaining efficiency.
Obstacle negotiation requires split-second decisions based on sensor data. When an autonomous robot encounters an unexpected barrier, it must quickly assess size, distance, and movement. Reinforcement Learning trains the system to recognize which obstacles require stopping versus minor path adjustments. Industrial mobile robots in factories learn to navigate around human workers, equipment, and materials while maintaining productivity.
Drones demonstrate aerial control mastery through Reinforcement Learning. Maintaining stable flight in variable winds, executing precise landings on moving platforms, and avoiding obstacles at high speeds all emerge from trial-and-error learning. The drone experiments with control inputs, observes the results, and gradually refines its piloting skills. This learning process mirrors how human pilots develop intuition for aircraft handling.
Reinforcement Learning in Autonomous Navigation Systems
| Navigation Function | Reinforcement Learning Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Lane Keeping | Learns steering corrections from visual road markers and vehicle position; develops sensitivity to road curvature and surface conditions |
| Path Planning | Discovers optimal routes through repeated trials in similar scenarios; balances distance, safety, traffic, and energy consumption |
| Speed Regulation | Adjusts throttle and braking based on traffic flow and road conditions; learns smooth acceleration profiles for passenger comfort |
| Obstacle Avoidance | Recognizes threat levels and appropriate responses; distinguishes static barriers from moving agents requiring prediction |
| Coordination | Learns communication and yielding patterns when multiple autonomous systems share space; prevents congestion and conflicts |
| Precision Maneuvering | Masters fine control for tasks like parking and docking; develops sensitivity to clearances and surface interactions |
4. How Reinforcement Learning Helps Machines Learn Complex Skills from Scratch
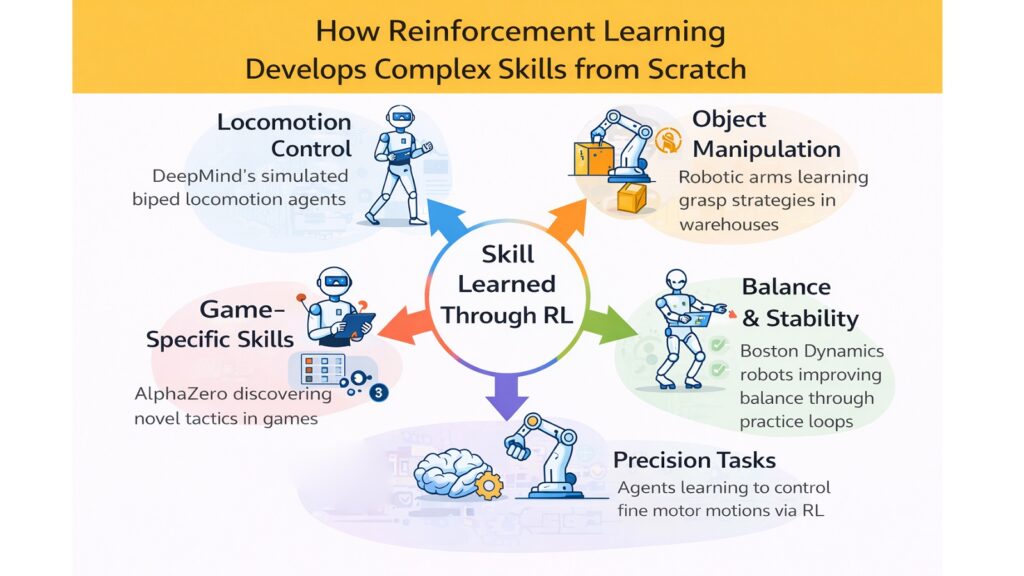
Reinforcement Learning enables AI systems to master intricate skills without explicit programming of every movement and decision. Through repeated trials and self-correction, machines discover techniques that humans never explicitly taught. This capability opens possibilities for automation in domains too complex for traditional programming approaches.
Robotic manipulation demonstrates this learning power vividly. Consider a robotic arm learning to catch a ball. The task involves estimating trajectory, positioning the gripper, timing closure, and absorbing impact. No programmer could specify every muscle equivalent command for each possible ball flight. Instead, Reinforcement Learning allows the robot to attempt thousands of catches, learning from successes and failures. Gradually, it develops catching strategies that work across different speeds, angles, and ball sizes.
AlphaGo Zero learned to play simply by playing games against itself, starting from completely random play, and defeated the previously published champion-defeating version of AlphaGo by 100 games to 0. This self-taught system received no human game demonstrations yet achieved superhuman performance. The AI discovered strategies through pure experimentation, accumulating thousands of years of human knowledge during just a few days of self-play.
Walking robots provide another compelling example. Boston Dynamics robots learned to maintain balance on irregular terrain, recover from pushes, and navigate obstacles through Reinforcement Learning experiments. The system tries different leg movements, observes which keep the robot upright, and refines its gait. This trial-and-error process produces natural-looking locomotion that adapts to slopes, stairs, and unstable surfaces. The robot essentially teaches itself to walk.
Object manipulation in unstructured environments showcases Reinforcement Learning’s versatility. A robot sorting packages must handle items of vastly different shapes, weights, and fragility. Through experimentation, it learns appropriate grip pressures for cardboard versus plastic, optimal lifting angles for awkward shapes, and stacking strategies that maintain stability. These skills emerge from experience rather than hard-coded rules.
DeepMind’s control suite demonstrates how Reinforcement Learning tackles diverse motor skills. Systems learned to manipulate objects with dexterous hands, balance poles, and coordinate complex limb movements. Each skill emerged from agents exploring action spaces and discovering which movement sequences achieved desired outcomes. The learning process resembles how children develop motor coordination through playful experimentation.
This self-learning capability proves particularly valuable for tasks in novel environments. When robots enter unfamiliar settings like disaster zones or other planets, they cannot rely on pre-programmed behaviors. Reinforcement Learning allows them to experiment safely in simulation, developing skills that transfer to real-world challenges. The machines become problem solvers rather than mere executors of fixed programs.
Complex Skills Mastered Through Reinforcement Learning
| Skill Domain | Learning Process |
|---|---|
| Object Catching | Learns trajectory prediction and timing through thousands of attempts; develops coordination between perception and gripper actuation |
| Bipedal Locomotion | Discovers gait patterns through falling and recovery; learns to maintain balance across varying terrain and disturbances |
| Dexterous Manipulation | Masters grip selection and force control for diverse objects; learns to adjust handling based on material properties |
| Board Game Strategy | Explores move sequences and evaluates outcomes; discovers non-obvious tactics through self-play and pattern recognition |
| Acrobatic Maneuvers | Learns complex motor sequences for flips and jumps; coordinates multiple joints for dynamic movements |
| Tool Use | Discovers effective tool handling through experimentation; learns to apply appropriate forces and angles for different tasks |
5. How Reinforcement Learning Optimizes Real-World Operations and Resource Use
Reinforcement Learning excels at finding efficient patterns in systems too complex for fixed rules. Logistics networks, supply chains, power grids, and building systems all involve countless interacting variables that defy simple optimization. These domains benefit enormously from AI that learns optimal strategies through experience with real-world complexity.
Supply chain management presents enormous optimization challenges. Thousands of products flow through networks of suppliers, warehouses, transportation routes, and retailers. Demand fluctuates unpredictably, delivery times vary, and disruptions occur frequently. Reinforcement Learning systems learn to coordinate these elements by observing which inventory decisions prevent stockouts, which routing choices minimize delays, and which supplier selections ensure reliability. The AI discovers patterns humans struggle to perceive in the overwhelming data.
Research shows that multi-agent Reinforcement Learning can solve large-scale chute mapping problems in robotic sortation centers with hundreds of agents. Amazon’s sortation facilities use Reinforcement Learning to optimize how packages route through conveyor systems. The AI learned which destination-to-location mappings maximize throughput while minimizing robot congestion. This type of coordination problem exceeds human planning capabilities due to combinatorial complexity.
Power grid optimization demonstrates Reinforcement Learning’s value in energy systems. Grids must balance generation and consumption instantaneously while managing renewable variability, peak demand charges, and equipment constraints. Reinforcement Learning systems learn when to charge batteries, which generators to dispatch, and how to route power for maximum efficiency. The AI discovers that sometimes running certain plants at higher output reduces overall costs through better load distribution.
HVAC optimization in commercial buildings provides measurable efficiency gains. DeepMind and Trane Technologies conducted live experiments in two commercial buildings, resulting in energy savings of approximately 9 percent and 13 percent respectively. The Reinforcement Learning system learned to precool spaces before peak heat, balance humidity and temperature tradeoffs, and sequence equipment for minimal energy consumption. These subtle strategies emerged from the AI observing thousands of days of building operations.
Logistics routing benefits from Reinforcement Learning that considers traffic patterns, delivery time windows, vehicle capacities, and fuel costs simultaneously. The system learns that sometimes longer routes save time by avoiding congestion, or that consolidating deliveries reduces trips despite carrying partial loads. These non-intuitive strategies become apparent through analyzing outcomes across millions of delivery scenarios.
Manufacturing scheduling represents another domain where Reinforcement Learning finds hidden efficiencies. Production involves coordinating machine availability, material flows, quality requirements, and due dates. The AI learns which job sequences minimize changeover times, which batch sizes optimize material usage, and when preventive maintenance least disrupts production. These operational improvements translate directly to cost savings and improved delivery performance.
Operational Optimization Through Reinforcement Learning
| Domain | Optimization Target & Measured Improvements |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Logistics | Minimizes transportation costs and delivery delays; studies show 15-30% reduction in route lengths and improved on-time delivery rates |
| Data Center Cooling | Reduces energy consumption while maintaining temperature specifications; demonstrated 30-40% cooling energy savings in Google facilities |
| Power Grid Management | Balances generation costs with renewable integration; achieves 10-20% improvement in dispatch efficiency and reduced curtailment |
| Building HVAC Control | Lowers heating and cooling energy while maintaining comfort; real deployments achieved 9-13% energy reduction in commercial buildings |
| Manufacturing Scheduling | Increases throughput and reduces changeover times; implementations report 20-35% improvement in production efficiency |
| Warehouse Operations | Optimizes robot routing and task allocation; research shows 15-25% reduction in order fulfillment time through learned coordination |
6. Why Reinforcement Learning Enables Human-Like Exploration and Creativity in AI
Reinforcement Learning encourages systems to explore beyond known solutions, leading to creative discoveries and novel strategies. This exploratory behavior mirrors human curiosity and innovation. The tension between exploitation and exploration drives systems to experiment while maintaining performance, producing unexpected breakthroughs.
Exploration versus exploitation represents a fundamental challenge in learning. Pure exploitation means always choosing the best-known action, which risks missing superior alternatives. Pure exploration means constantly trying new approaches, which sacrifices immediate performance. Reinforcement Learning balances these extremes by gradually shifting from exploration to exploitation as knowledge accumulates. Early in learning, the system tries diverse actions to discover what works. As patterns emerge, it focuses increasingly on proven strategies while occasionally experimenting with novelties.
AlphaGo played several inventive winning moves, including Move 37 which had a 1 in 10,000 chance of being used. This creative move upended centuries of Go wisdom, demonstrating that machines could discover strategies beyond human experience. Professional players initially thought the move was a mistake before recognizing its brilliance. The AI’s willingness to explore unconventional plays led to this groundbreaking discovery.
Game-playing AI systems frequently invent tactics human experts never considered. When DeepMind applied Reinforcement Learning to StarCraft II, the AI developed micro-management techniques and strategic timing that surprised professional players. The system experimented with unusual unit compositions and discovered effective combinations through trial and error. These inventions emerged because the AI explored the vast space of possible strategies without preconceptions about what should work.
Robotic manipulation research reveals similar creative problem-solving. When learning to grasp oddly-shaped objects, robots sometimes discover novel grip configurations that human operators would not attempt. A robotic arm might learn to balance an object on its palm rather than gripping directly, or use environmental features like table edges to assist manipulation. These creative solutions arise from the robot’s freedom to experiment with unconventional approaches.
Curiosity-driven learning extends Reinforcement Learning’s exploratory capabilities. Rather than only seeking task rewards, systems receive bonuses for encountering novel situations or unpredictable outcomes. This intrinsic motivation drives robots to explore their environments more thoroughly, discovering useful skills and knowledge. A curious robot might investigate objects not directly relevant to its current task, building general capabilities that prove valuable later.
Professional Go player Ke Jie commented that a pure self-learning AlphaGo is the strongest, noting humans seem redundant in front of its self-improvement. This observation highlights how Reinforcement Learning systems can transcend human-derived knowledge through relentless exploration and pattern discovery. The AI’s freedom from preconceptions allows it to question assumptions and test unconventional strategies.
The creative potential of Reinforcement Learning extends beyond games and robotics. Drug discovery applications use Reinforcement Learning to explore molecular design spaces, sometimes suggesting compounds chemists had not considered. The AI proposes structures based on learned relationships between molecular features and desired properties, occasionally producing surprising candidates that human intuition would overlook. This exploratory capability accelerates innovation in domains where exhaustive search proves impossible.
Exploration and Creativity Mechanisms in Reinforcement Learning
| Mechanism | How It Fosters Innovation |
|---|---|
| Epsilon-Greedy Exploration | Randomly selects exploratory actions with decreasing probability; ensures continuous exposure to alternative strategies |
| Upper Confidence Bounds | Balances trying less-tested actions with proven choices; gives preference to options with uncertain outcomes to reduce ambiguity |
| Curiosity-Driven Learning | Rewards agents for encountering novel states; motivates exploration of unfamiliar situations and skill development |
| Population-Based Training | Maintains diverse strategies across multiple agents; allows comparison and cross-pollination of different approaches |
| Counterfactual Reasoning | Evaluates what might have happened with different choices; enables learning from hypothetical scenarios |
| Hierarchical Exploration | Explores at multiple levels from low-level actions to high-level strategies; discovers both tactical techniques and strategic innovations |
Conclusion: Why Reinforcement Learning Will Shape the Future of Smarter AI
Reinforcement Learning has emerged as a foundational technology for creating truly autonomous and adaptable artificial intelligence. These six powerful capabilities demonstrate why the technique drives smart AI forward. From building adaptive intelligence in dynamic environments to enabling long-term decision-making, from powering autonomous navigation to helping machines learn complex skills from scratch, from optimizing real-world operations to enabling human-like exploration and creativity, Reinforcement Learning touches every dimension of intelligent systems.
The technique’s core strength lies in its alignment with how learning actually works. Trial and error, continuous adaptation, and learning from feedback represent natural intelligence principles that Reinforcement Learning embodies in algorithms. This foundation makes the approach remarkably versatile across domains from game playing to industrial control, from robotics to resource optimization.
Real-world deployments already demonstrate transformative impact. Google’s data centers save millions in energy costs through Reinforcement Learning optimization. Amazon’s warehouses coordinate thousands of robots using learned coordination strategies. Tesla vehicles accumulate driving experience that refines autonomous capabilities. These applications represent just the beginning of what becomes possible as the technology matures.
Looking forward, Reinforcement Learning will increasingly influence critical systems. Climate modeling may benefit from AI that learns optimal intervention strategies through simulation. Power grids will become smarter through systems that discover efficient renewable integration patterns. Manufacturing will see robots that continuously improve their skills through experience. Healthcare might employ AI assistants that learn personalized treatment strategies by observing patient outcomes.
The next generation of AI agents will combine Reinforcement Learning with other techniques to create systems with unprecedented capabilities. These agents will learn from experience while reasoning about knowledge, plan strategically while adapting tactically, and balance autonomy with human guidance. They will explore possibilities we have not imagined while respecting safety constraints and human values.
Reinforcement Learning represents more than an incremental improvement in AI technology. It provides a paradigm for creating machines that genuinely learn rather than merely execute pre-programmed instructions. As systems continue developing through this approach, they will handle increasingly complex challenges that currently require human expertise and judgment. The foundation for autonomous, adaptable, decision-making AI rests firmly on Reinforcement Learning principles that will only grow more powerful and pervasive in the coming years.
Future Applications and Impact of Reinforcement Learning
| Future Domain | Expected Impact |
|---|---|
| Climate Systems | Learns optimal carbon reduction strategies through environmental modeling; could discover efficient intervention timing and resource allocation |
| Smart Energy Grids | Coordinates renewable integration and storage systems; expected to reduce curtailment and improve grid stability through learned dispatch |
| Personalized Medicine | Develops individualized treatment protocols by learning from patient responses; promises better outcomes through adaptive care strategies |
| Advanced Robotics | Creates general-purpose robots that adapt to novel tasks; will enable machines to handle unpredictable real-world situations |
| Scientific Discovery | Accelerates research by exploring experimental design spaces; may propose novel hypotheses and experimental approaches |
| Urban Traffic Management | Optimizes signal timing and routing for entire city networks; could significantly reduce congestion and improve transportation efficiency |
Read More Tech Articles
- Computer Vision AI: 6 Essential Layers Behind Autonomy
- Quantum Computer Anatomy: 8 Powerful Components Inside
- Quantum Computing: 6 Powerful Concepts Driving Innovation
- 8 Powerful Smart Devices To Brighten Your Life
- 8 E-Readers: Epic Characters in a Library Adventure
- Smart TV Brands: 8 Epic Directors for Screen Magic
- Tablet Brands as Superheroes: 8 Amazing Tech Avengers
- 8 Amazing Fitness Tracker Brands as Story Characters
- Discover 8 Smart Speaker Brands As Motivational Speakers
- Reimagine 10 Best Smartphone Brands As Real Personalities