Table of Contents
Introduction: Exit Management as the Hidden Driver of Workplace Morale
Most organizations treat employee departures like necessary evils, rushing through paperwork while counting down to the final handshake. This shortsighted approach misses a profound opportunity. Exit Management represents far more than administrative closure—it serves as a strategic Human Resources function with enormous implications for organizational health and employee morale.
When executed thoughtfully, Exit Management transforms what could be a deflating experience into a morale-boosting demonstration of company values. The process extends beyond simple farewells to shape trust, reinforce cultural foundations, and signal to remaining employees how the organization truly values its people. Research from the Society for Human Resource Management indicates that organizations with structured exit processes experience higher retention rates and improved employee engagement scores.
The ripple effects of effective Exit Management touch every corner of organizational life. Employees observe how their colleagues are treated during departure, forming lasting impressions about their own future security and the company’s integrity. A well-managed exit process creates positive closure while maintaining relationships that often prove valuable for future collaboration, referrals, and reputation management.
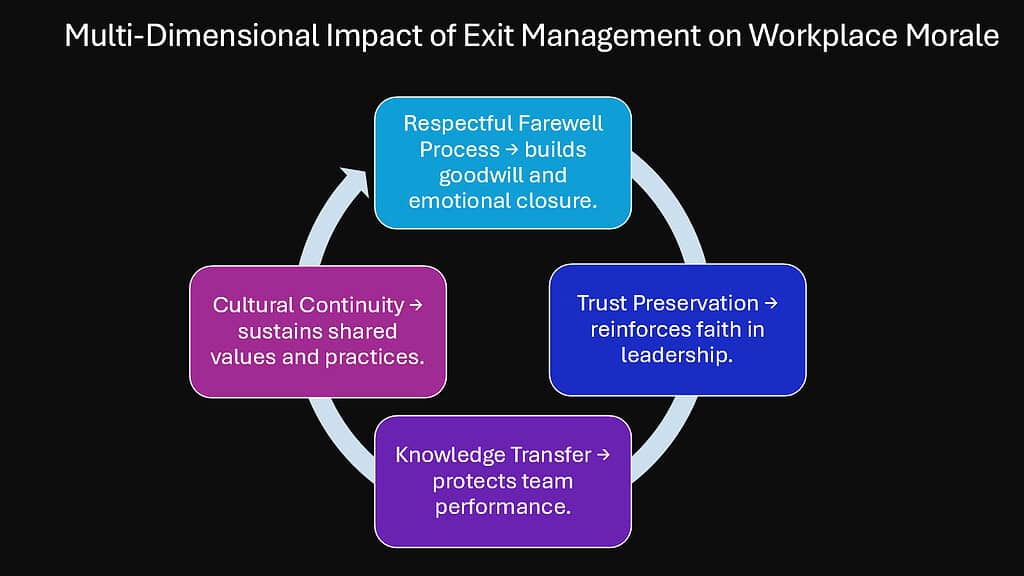
This strategic approach to Exit Management influences internal morale through six critical pathways: honoring psychological contracts, demonstrating organizational values publicly, addressing hygiene factors that prevent morale deterioration, maintaining transparent communication channels, providing stability during transitions, and converting departing employees into retention advocates. Each pathway represents a missed opportunity when Exit Management lacks strategic focus.
The following analysis explores how these six mechanisms transform routine departures into powerful tools for sustaining and enhancing workplace morale, ultimately contributing to organizational resilience and competitive advantage.
Table 1: Exit Management Impact on Core HR Functions
| HR Function | Exit Management Impact | Morale Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Recruitment | Alumni networks provide referrals and employer branding | Positive reputation attracts quality candidates |
| Training | Knowledge transfer prevents skill gaps | Continuity maintains team confidence |
| Leadership | Succession planning demonstrates forward thinking | Stability reassures remaining staff |
| Employee Relations | Respectful exits model conflict resolution | Trust in fair treatment increases |
| Employee Engagement | Departure feedback identifies improvement areas | Responsiveness shows organizational commitment |
| Organizational Development | Exit patterns reveal structural issues | Proactive changes boost morale |
| Change Management | Structured transitions minimize disruption | Predictability reduces anxiety |
| Compensation and Benefits | Exit interviews validate competitive positioning | Fairness perceptions strengthen |
| Onboarding | Exit analysis of early departures improves onboarding processes | Comprehensive onboarding creates positive morale which lasts even during departure |
| Offboarding | Exit management is the foundation of effective offboarding processes | Departing employees’ final experience shapes their willingness to maintain positive relationships |
1. Exit Management and The Psychological Contract
The psychological contract represents unwritten expectations between employees and organizations, extending far beyond formal job descriptions and employment agreements. According to Psychological Contract Theory, developed by organizational psychologist Denise Rousseau, these implicit agreements significantly influence employee behavior, commitment, and satisfaction. Exit Management provides a crucial test of how organizations honor these unspoken commitments when relationships conclude.
When companies handle departures with dignity and respect, they signal to remaining employees that psychological contracts will be honored throughout the employment lifecycle. This demonstration builds trust among current staff, who observe firsthand how the organization treats people during vulnerable transitions. Conversely, poorly managed exits breach psychological contracts not just with departing employees, but with everyone who witnesses the process.
The psychological contract encompasses expectations about career development, work-life balance, job security, and mutual respect. During exits, organizations have opportunities to demonstrate commitment to these areas through comprehensive handover support, flexible departure timing, positive references, and genuine appreciation for contributions made. These actions reinforce that the psychological contract remains valid even when employment ends.
Research from the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development shows that organizations maintaining strong psychological contracts experience lower turnover rates and higher employee engagement. The exit process serves as a visible demonstration of whether these contracts represent genuine commitments or mere rhetoric. Employees mentally evaluate their own psychological contracts based on how colleagues are treated during departures.
Effective Exit Management transforms potential contract breaches into contract fulfillment opportunities. When organizations invest time in proper knowledge transfer, provide career transition support, and maintain professional relationships post-departure, they demonstrate authentic commitment to employee wellbeing beyond immediate business needs.
Table 2: Psychological Contract Elements in Exit Management
| Contract Element | Exit Management Demonstration | Morale Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Mutual Respect | Professional departure conversations | Dignity preserved for all employees |
| Career Support | References and networking assistance | Investment in long-term success recognized |
| Knowledge Value | Comprehensive handover processes | Expertise acknowledged and preserved |
| Relationship Continuity | Alumni networks and ongoing contact | Relationships transcend employment status |
| Fair Treatment | Consistent exit procedures | Predictable, equitable treatment expected |
| Growth Recognition | Achievement celebrations | Contributions valued and remembered |
2. Exit Management as a Public Display of Organizational Values
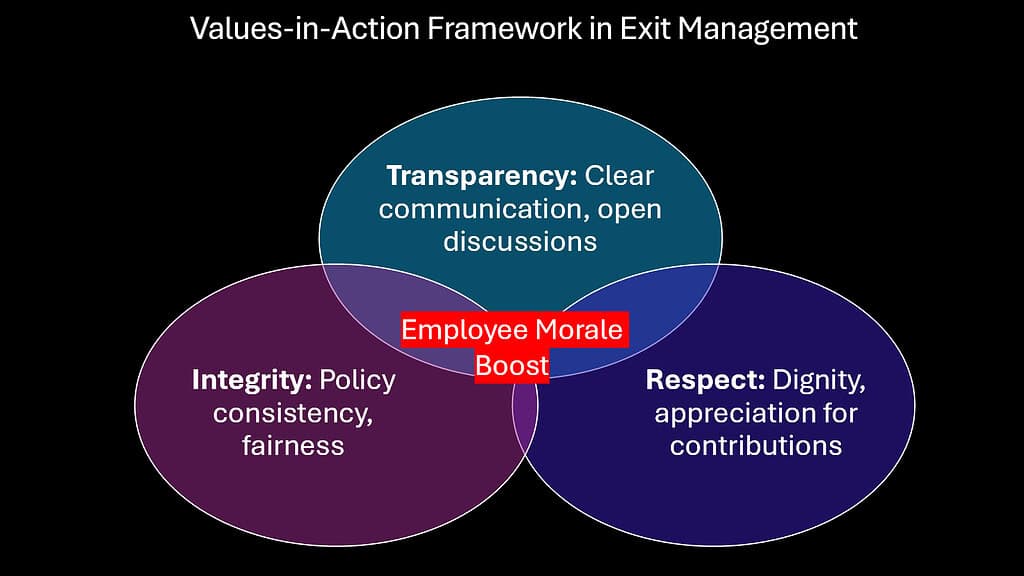
Organizational values often remain abstract concepts until tested by real situations that reveal authentic company character. Exit Management provides one of the most visible opportunities for organizations to demonstrate whether stated values translate into consistent behavior. Every departure becomes a public performance watched closely by remaining employees, customers, and industry observers.
When organizations handle exits with transparency, respect, and genuine care, they reinforce cultural foundations that extend far beyond individual departures. These demonstrations create powerful precedents that shape employee expectations and behaviors throughout their tenure. On the other hand, poorly or inconsistently managed exits can erode declared values and foster skepticism regarding the integrity of the organization.
The public nature of Exit Management amplifies its impact on internal morale. Employees witness how colleagues are treated during departures, forming lasting impressions about company culture and their own potential experiences. Positive exit experiences become stories that circulate throughout the organization, reinforcing cultural narratives about how people are valued and treated.
Organizations with strong Exit Management practices often find that departing employees become advocates rather than critics. This transformation occurs when exit processes align with stated values around respect, growth, and relationship building. The advocacy effect extends beyond individual departures to create sustained positive reputation that attracts talent and strengthens employee retention.
The demonstration effect proves particularly powerful in knowledge-based industries where reputation and relationships drive business success. Companies known for handling exits professionally often find former employees referring top talent, providing business opportunities, and defending the organization’s reputation in professional networks.
Table 3: Value Demonstration Through Exit Practices
| Organizational Value | Exit Management Practice | Morale Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| Respect for People | Dignified farewell processes | Individual worth recognized |
| Transparency | Open communication about departures | Trust in organizational honesty |
| Growth Mindset | Career development support | Investment in human potential |
| Relationship Building | Alumni network maintenance | Long-term partnership approach |
| Excellence Standards | Thorough knowledge transfer | Quality maintained through transitions |
| Integrity | Consistent exit procedures | Reliable organizational behavior |
3. Exit Management Through the Lens of Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory
Frederick Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory differentiates between hygiene factors that avert job dissatisfaction and motivators that foster job satisfaction. Exit Management primarily operates within the hygiene factor domain, addressing elements that, when handled poorly, create significant morale problems throughout the organization. Understanding this distinction helps explain why effective Exit Management serves as a foundation for sustained workplace morale.
Hygiene factors include company policies, supervision quality, working relationships, and job security perceptions. Exit Management directly influences each of these areas through the messages sent about organizational stability, leadership competence, and policy consistency. When exits are managed professionally, they reinforce hygiene factors that prevent morale deterioration among remaining staff.
Poor Exit Management creates hygiene factor deficiencies that poison workplace atmosphere. Abrupt departures without explanation generate anxiety about job security. Inconsistent exit procedures suggest policy weaknesses. Hostile or disrespectful treatment of departing employees damages trust in supervision quality. These deficiencies create lasting morale problems that extend far beyond individual departures.
Research conducted by Harvard Business School demonstrates that organizations addressing hygiene factors through structured processes experience more stable employee satisfaction levels. Exit Management serves as a critical hygiene factor maintenance mechanism, ensuring that departures do not destabilize the workplace environment for remaining employees.
The theory suggests that while Exit Management may not directly motivate employees, it prevents demotivation that occurs when departures are handled poorly. This prevention function proves crucial for maintaining baseline morale levels that enable other motivational initiatives to succeed.
Table 4: Herzberg’s Factors Applied to Exit Management
| Hygiene Factor | Exit Management Application | Morale Protection Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Company Policy | Consistent exit procedures | Predictable treatment expectations |
| Supervision | Professional departure handling | Leadership competence demonstrated |
| Working Relationships | Respectful colleague transitions | Interpersonal trust maintained |
| Job Security | Transparent communication about changes | Anxiety reduced through clarity |
| Working Conditions | Smooth knowledge transfer | Operational continuity preserved |
| Salary and Benefits | Fair final compensation handling | Equitable treatment confirmed |
4. Exit Management as a Morale-Protecting Communication Channel
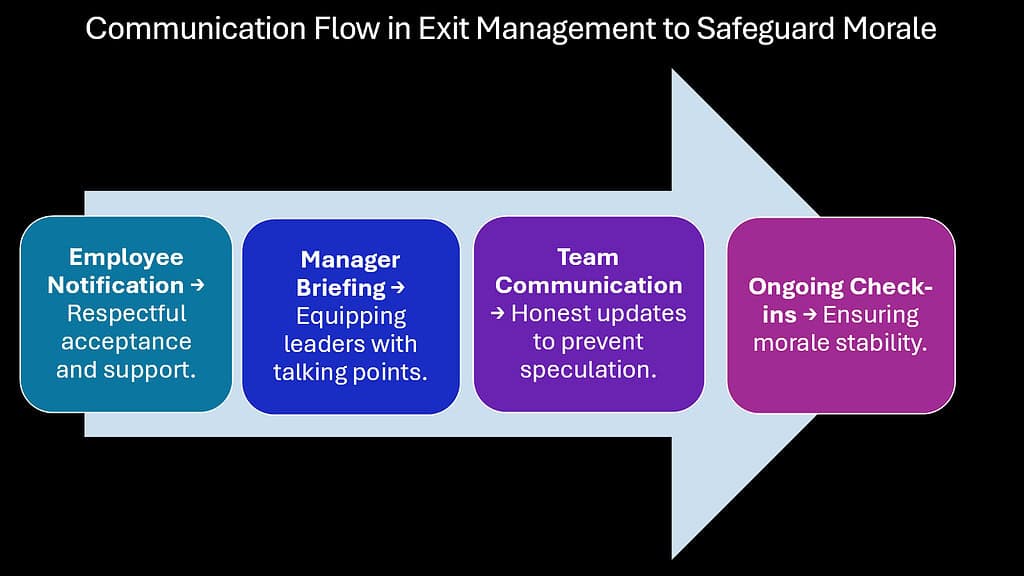
Communication failures during employee departures create fertile ground for speculation, rumors, and anxiety among remaining staff. Effective Exit Management establishes clear communication channels that protect team morale by providing accurate information while respecting privacy boundaries. This communication strategy prevents the rumor mills that often emerge during periods of organizational change.
The absence of structured communication around departures creates information vacuums that employees fill with speculation. These informal narratives often prove more damaging than factual explanations, as they tend toward worst-case scenarios and conspiracy theories. Proactive communication through Exit Management channels prevents these destructive narratives from taking root.
Organizations successful in maintaining morale during departures typically establish clear protocols for what information gets shared, when announcements occur, and how questions are addressed. This structure provides psychological safety for remaining employees while maintaining appropriate confidentiality for departing colleagues.
The communication function extends beyond simple announcements to include ongoing dialogue about organizational changes, succession plans, and team adjustments. When employees receive regular updates through established channels, they feel informed and included rather than anxious and excluded from important organizational developments.
Cross-cultural research from organizations operating in diverse markets shows that communication preferences during exits vary significantly across different cultural contexts. However, the fundamental principle of providing clear, timely information consistently strengthens morale regardless of cultural setting.
Table 5: Exit Management Communication Channels and Morale Protection
| Communication Channel | Information Shared | Morale Protection Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Team Announcements | Departure timing and transition plans | Reduces uncertainty and speculation |
| One-on-One Conversations | Individual impact and support available | Addresses personal concerns directly |
| Organizational Updates | Broader context and strategic implications | Maintains big picture perspective |
| FAQ Documentation | Common questions and standard responses | Provides consistent information access |
| Follow-up Sessions | Progress updates and adjustment support | Demonstrates ongoing care and attention |
| Alumni Communications | Continued relationship and success stories | Reinforces positive departure narrative |
5. Exit Management and Lewin’s Change Management Model
Kurt Lewin’s three-stage Change Management Model—Unfreeze, Change, and Refreeze—provides valuable framework for understanding how structured Exit Management stabilizes organizational morale during personnel transitions. Employee departures represent significant changes that require careful management to prevent morale disruption and maintain operational effectiveness.
The Unfreeze phase entails equipping the organization for change by tackling resistance and fostering readiness for transition. In Exit Management context, this means acknowledging departure impact, communicating transition plans, and addressing concerns that naturally arise when team dynamics shift. Organizations that skip this preparation phase often experience prolonged morale difficulties as employees struggle to process the change.
During the Change stage, actual transition occurs through knowledge transfer, responsibility redistribution, and relationship adjustments. Effective Exit Management structures this phase to minimize disruption while ensuring continuity. The key lies in managing both practical elements like task handovers and emotional elements like team adjustment to new dynamics.
The Refreeze stage establishes new stability by reinforcing adjusted team structures, celebrating successful transitions, and integrating lessons learned. Organizations that complete this stage effectively emerge stronger from departures, with improved processes and enhanced confidence in their ability to handle future changes.
Research from organizational development specialists indicates that structured approaches to personnel transitions, following Lewin’s model, result in faster team adjustment periods and maintained productivity levels. The model provides roadmap for preventing the morale dips that often accompany organizational changes.
Table 6: Lewin’s Model Applied to Exit Management
| Change Stage | Exit Management Activities | Morale Stabilization Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Unfreeze | Departure announcement and impact assessment | Psychological preparation reduces shock |
| Unfreeze | Concern addressing and support offering | Resistance minimized through communication |
| Change | Knowledge transfer and task redistribution | Continuity maintained during transition |
| Change | Team dynamic adjustment and support | New working relationships established |
| Refreeze | Process documentation and lesson integration | Organizational learning captured |
| Refreeze | Success celebration and forward focus | Positive narrative reinforced |
6. Exit Management as a Retention and Advocacy Tool
The final interaction between organizations and departing employees creates lasting impressions that influence both employee retention and external reputation management. When Exit Management transforms departing employees into advocates rather than critics, it generates powerful retention effects among current staff while enhancing employer brand reputation in external markets.
Employees observe how colleagues are treated during departures, using these observations to predict their own potential experiences. Positive exit experiences signal that the organization values people beyond their immediate utility, creating psychological safety that encourages longer tenure among current staff. This retention effect proves particularly valuable in competitive talent markets where employees have multiple options.
The advocacy transformation occurs when departing employees feel respected, supported, and valued throughout their exit process. These positive experiences motivate former employees to recommend the organization to their networks, provide references for recruitment efforts, and defend the company reputation in professional settings. The advocacy effect extends organizational reach far beyond current employee boundaries.
Strategic Exit Management recognizes that today’s departing employee may become tomorrow’s client, partner, or even returning employee. Maintaining positive relationships through professional exit processes creates valuable network connections that often generate business opportunities and strategic partnerships. This long-term perspective transforms exits from costs into investments.
Organizations implementing systematic approaches to Exit Management as retention tool often discover that improved exit processes correlate with reduced overall turnover rates. The demonstration effect proves powerful in showing current employees that their eventual departures, should they occur, will be handled with dignity and professionalism.
Table 7: Exit Management Retention and Advocacy Outcomes
| Exit Management Element | Retention Impact | Advocacy Result |
|---|---|---|
| Professional Farewell Process | Current employees feel valued | Positive employer brand reputation |
| Career Transition Support | Investment in people demonstrated | Network referrals and recommendations |
| Alumni Network Inclusion | Long-term relationship value shown | Ongoing business connections maintained |
| Reference and Recommendation Provision | Future career support guaranteed | Reciprocal professional support |
| Celebration of Contributions | Achievement recognition culture reinforced | Success stories shared externally |
| Flexible Departure Timing | Individual needs respected | Considerate treatment reputation established |
Conclusion: Exit Management as a Long-Term Investment in People and Culture

The strategic importance of Exit Management extends far beyond administrative necessity to encompass fundamental questions about organizational character, cultural integrity, and long-term competitive advantage. Organizations recognizing Exit Management as a critical Human Resources function position themselves to harvest significant returns through enhanced morale, strengthened retention, and improved reputation.
The six pathways explored demonstrate how thoughtful Exit Management creates compound benefits that accumulate over time. Honoring psychological contracts builds trust that encourages deeper employee engagement. The public display of values strengthens the cultural foundations that draw in and keep exceptional talent. Attention to hygiene factors prevents morale deterioration that undermines organizational effectiveness. Strategic communication protects team cohesion during transitions. Structured change management stabilizes morale during periods of adjustment. Transformation of departing employees into advocates extends organizational influence beyond current workforce boundaries.
These benefits prove particularly valuable in knowledge-based economies where talent represents the primary source of competitive advantage. Organizations that invest in Exit Management systems often discover that these investments generate returns far exceeding their costs through reduced recruitment expenses, decreased training requirements, and enhanced productivity from more engaged workforces.
The economic implications extend beyond individual organizations to encompass entire industry ecosystems. When companies within specific sectors adopt professional Exit Management practices, they collectively raise standards that benefit all participants through improved talent mobility, enhanced knowledge sharing, and strengthened professional networks.
Future organizational success increasingly depends on ability to manage human capital transitions effectively while maintaining cultural consistency and operational excellence. Exit Management provides the framework for achieving these goals while transforming necessary departures into opportunities for organizational strengthening and cultural reinforcement.
The question facing organizational leaders is not whether to invest in Exit Management systems, but how quickly they can implement approaches that transform departures from potential morale threats into powerful tools for organizational development and competitive advantage.
Table 8: Long-Term Exit Management Investment Returns
| Investment Area | Immediate Benefit Of Exit Management | Long-Term Organizational Return |
|---|---|---|
| Process Development | Standardized departure procedures | Consistent positive experiences and reputation |
| Communication Systems | Reduced departure-related anxiety | Enhanced trust and organizational transparency |
| Knowledge Management | Preserved institutional memory | Accelerated new hire productivity and continuity |
| Relationship Maintenance | Alumni network development | Expanded business opportunities and referrals |
| Cultural Reinforcement | Values demonstration | Strengthened employer brand and talent attraction |
| Succession Planning | Smooth leadership transitions | Organizational resilience and adaptive capacity |




